
How to Protect Your Online Activities with a VPN
In today’s digital age, our lives are more intertwined with the internet than ever before. From social interactions to financial transactions, and from entertainment to work, the online world has become an integral part of our daily existence. However, with this increased connectivity comes a heightened risk to our personal and private information. Every click, every search, and every download can potentially expose us to a myriad of online threats.
| Online Activity | Potential Risk |
|---|---|
| Online Shopping | Credit card fraud, identity theft |
| Social Media Browsing | Personal data leakage, cyberbullying |
| Online Banking | Financial fraud, account hacking |
| Streaming Services | Geo-restrictions, bandwidth throttling |
| Web Browsing | Tracking, targeted ads, malware |
Enter the Virtual Private Network, commonly known as a VPN. A VPN is not just a tool; it’s a shield that stands between you and potential online threats. It ensures that your online activities remain private, secure, and free from unwanted prying eyes. By creating a secure tunnel between your device and the internet, a VPN masks your IP address, encrypts your data, and provides you with the anonymity you need in the vast expanse of the digital realm.
But what exactly is a VPN? How does it work? And why is it becoming increasingly essential for internet users around the world? This article aims to answer these questions and guide you on a journey to understand the importance of VPNs in ensuring online privacy.
Understanding VPNs
A Virtual Private Network, or VPN, is a technology that creates a secure and encrypted connection over a less secure network, such as the internet. Think of it as a protective tunnel that your online data travels through, keeping it safe from potential threats and prying eyes.
How Does a VPN Work?
At its core, a VPN works by rerouting your internet connection through its own private servers rather than your internet service provider (ISP). This process is known as tunneling. When you access a website or an online service, it sees the connection coming from the VPN server’s IP address and not your own, effectively masking your online identity.
Figure 1: A simple diagram illustrating the VPN tunneling process.
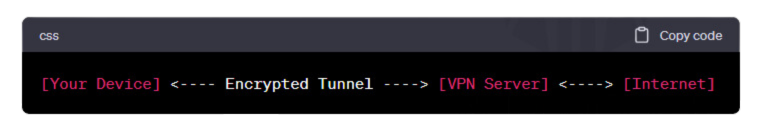
Key Components of a VPN:
- Tunneling Protocols: These are the methods by which your data is transferred securely from your device to the VPN server. Common protocols include OpenVPN, L2TP/IPsec, and PPTP.
- Encryption: This ensures that the data within the VPN tunnel is unreadable to anyone who might intercept it. Techniques such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) with 256-bit keys are often used, offering a high level of security.
- Server Network: Reputable VPN providers have a vast network of servers located worldwide. This allows users to connect to a server in a location of their choice, which can be particularly useful for bypassing geo-restrictions.
Benefits of Using a VPN:
- Privacy: Your real IP address is hidden, ensuring your online activities remain anonymous.
- Security: Your data is encrypted, protecting it from hackers and cybercriminals.
- Freedom: Bypass internet censorship and access content that might be restricted in your region.
- Reduced Online Tracking: Prevent websites and online advertisers from tracking your browsing habits and personal information.
In essence, a VPN acts as a middleman between you and the internet. While this might seem like it would slow down your connection, modern VPNs are designed to offer fast and seamless online experiences, ensuring that you can browse, stream, and download without any noticeable difference in speed.
Why You Need a VPN
The internet, while a vast reservoir of information and connectivity, is also rife with potential pitfalls. Every day, millions of users unknowingly expose themselves to threats that can have significant consequences. Here’s why a VPN is no longer just an option, but a necessity:
- Protecting Personal Data: In an era where data breaches are commonplace, a VPN provides an added layer of security. Whether you’re shopping online, accessing your bank account, or simply browsing, a VPN ensures that your credentials, financial details, and other personal information are encrypted and out of reach from cybercriminals.
- Bypassing Internet Censorship: Many countries impose restrictions on what their citizens can access online. A VPN allows users to bypass these restrictions by making it appear as though they are accessing the internet from a different location. This is especially useful for journalists, researchers, and everyday citizens in countries with stringent internet censorship laws.
- Ensuring Anonymity: Every time you visit a website, you leave behind digital footprints that can be tracked. Advertisers, websites, and even governments can monitor your online behavior. A VPN masks your IP address, ensuring that your online activities remain private and anonymous.
- Accessing Geo-Restricted Content: Ever tried to watch a show or access content only to find it’s not available in your region? VPNs can help. By connecting to a server in a different country, you can access content as if you were physically present there.
- Preventing Bandwidth Throttling: ISPs sometimes throttle, or intentionally slow down, your internet connection based on your online activities. This is especially common for users who stream videos, play online games, or engage in other bandwidth-intensive tasks. A VPN hides your online activities from your ISP, ensuring consistent internet speeds.
Types of VPNs
While the primary function of all VPNs is to provide a secure and private connection, there are different types tailored to specific needs:
- Remote Access VPNs: Ideal for individual users, these VPNs allow users to connect to a remote server to access a private network. They are commonly used by employees working remotely to access company resources.
- Site-to-Site VPNs: Used primarily by businesses, these VPNs connect entire networks to each other. For instance, a business might use a site-to-site VPN to connect its office network with its data center network.
- Extranet-Based Site-to-Site VPNs: These are used when companies want to share a particular part of their network with another organization, without giving them access to their entire network.
Each type of VPN serves a unique purpose and is designed to cater to specific needs. Whether you’re an individual looking to protect your online activities or a business aiming to secure your network, there’s a VPN out there for you.
Setting Up a VPN
Setting up a VPN might seem like a daunting task, especially for those who aren’t tech-savvy. However, with the right guidance and a step-by-step approach, it can be a straightforward process. Here’s how you can set up a VPN:
- Choosing the Right VPN Service:
The initial step in setting up a VPN is selecting an appropriate service. Your choice should align with your specific requirements, be it personal browsing, business-related tasks, or specialized activities like streaming. It’s crucial to verify that the VPN provider has servers in the desired locations, especially if you aim to bypass geo-restrictions. Another vital consideration is the provider’s privacy policy; a strict no-logs policy ensures that your online activities remain confidential. - Installation and Configuration:
After settling on a VPN provider, you’ll need to download the necessary software from their official website or the relevant app store. Once downloaded, run the installer and follow the on-screen prompts. After installation, launch the VPN application and sign in using the credentials you either created or were provided during the sign-up process. From there, you can choose a server location and establish a connection, securing your online activities. - Optimizing Performance:
To get the most out of your VPN, certain adjustments might be necessary. Most VPNs offer a variety of tunneling protocols. While OpenVPN is often hailed for its security, other protocols like L2TP or IKEv2 might offer faster speeds in specific scenarios. If you notice a lag in your connection, consider switching to a different server, as some might be congested during peak times. Lastly, for uninterrupted protection, ensure your VPN has a kill switch feature. This function automatically disconnects your device from the internet if your VPN connection unexpectedly drops.
Security Mechanisms of VPNs
VPNs are synonymous with online security, and for a good reason. Here’s a deeper look into the security mechanisms that make VPNs so robust:
- Encryption:
Encryption stands as the cornerstone of VPN security. It involves converting data into a code to prevent unauthorized access. In the context of VPNs, encryption scrambles your data, rendering it unreadable to anyone who might intercept it. Even if a hacker manages to capture the data, without the decryption key, it remains indecipherable. Modern VPNs often employ advanced encryption standards, such as AES with 256-bit keys, to ensure maximum security. - Authentication:
Beyond encryption, authentication plays a pivotal role in VPN security. It’s the process of verifying the identity of a user or server before establishing a connection. VPNs employ authentication to ensure that both the user and the server are genuine, preventing potential man-in-the-middle attacks where malicious entities might try to impersonate a legitimate server or user. - IP Masking:
IP masking is another essential feature of VPNs. Every device connected to the internet has a unique IP address, which can reveal information about your location and online activities. VPNs mask your real IP address, making it appear as though your connection originates from the VPN server’s location. This not only ensures online anonymity but also allows users to bypass geo-restrictions and access content from different regions. - Double VPN:
For those seeking an added layer of security, some VPNs offer a double VPN feature. This involves routing your traffic through two separate VPN servers, effectively encrypting your data twice. While this might slightly reduce connection speeds, it provides an enhanced level of privacy, especially beneficial for users in regions with stringent online surveillance.
VPNs in Mobile Environments
In an age where smartphones have become extensions of ourselves, ensuring their security is paramount. Mobile VPNs cater to this need, offering protection and privacy on-the-go.
- The Rise of Mobile VPNs:
The proliferation of smartphones has driven the demand for mobile VPNs. With over 3 billion smartphone users globally, these tools have become indispensable. Mobile VPNs are designed to protect users while they are on the move. Public Wi-Fi networks, commonly found in cafes, airports, and hotels, pose considerable security risks. Mobile VPNs counteract these risks by encrypting your data, ensuring it remains secure even on untrusted networks. Additionally, the shift towards remote work has made secure mobile connections a necessity, allowing employees to access company resources from various locations. - Benefits for Remote Workers and Frequent Travelers:
Mobile VPNs offer several advantages, particularly for remote workers and frequent travelers. They ensure consistent access to company resources, regardless of location, providing a secure link to corporate networks. Travelers can use mobile VPNs to bypass internet censorship, accessing content that might be restricted or censored in certain countries. Moreover, these VPNs secure financial transactions, whether it’s booking accommodations, renting vehicles, or making online purchases, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected. - Choosing the Right Mobile VPN:
Selecting the appropriate mobile VPN is crucial. Ensure that the VPN service offers a dedicated app compatible with your mobile operating system, whether it’s Android, iOS, or another platform. Opt for VPNs with no-log policies to guarantee that your mobile online activities are not stored. Furthermore, consider the impact on your device’s battery life, as some VPN apps can be more energy-intensive than others. Finally, prioritize user-friendly interfaces designed for mobile devices, enabling straightforward server switching and configuration adjustments. - Setting Up a Mobile VPN:
Configuring a mobile VPN is a relatively straightforward process. Begin by visiting your mobile app store and searching for the chosen VPN service’s app. Once you’ve located it, download and install the app on your device. Then, open the app and follow the provided on-screen instructions. Afterward, log in using your credentials and adjust the settings as needed. This may involve selecting a server location, choosing an encryption protocol, or enabling features such as a kill switch. With these steps completed, your mobile online activities are securely protected.
Potential Pitfalls and Misconceptions
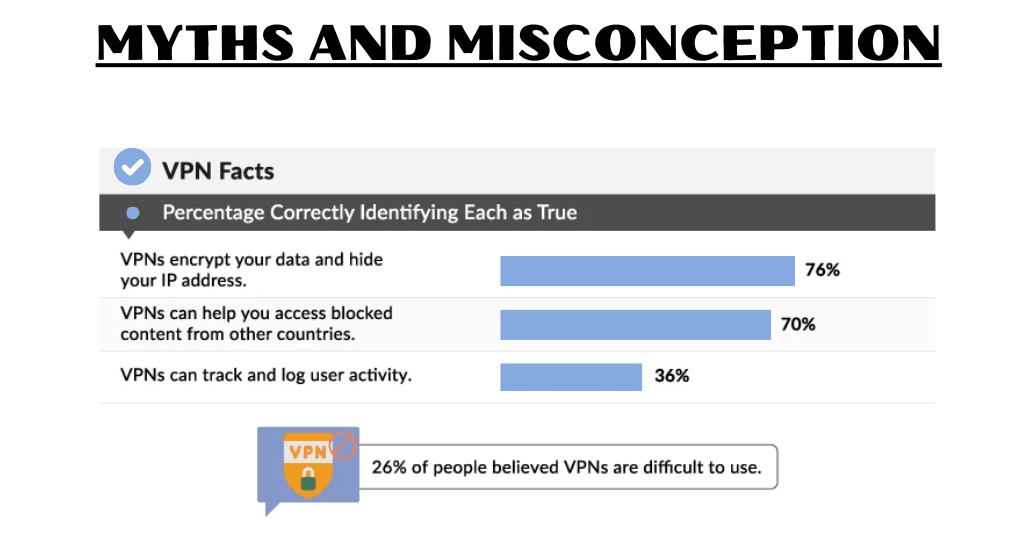
While VPNs offer a plethora of benefits, it’s essential to be aware of potential pitfalls and common misconceptions:
- VPNs Provide Complete Anonymity: While VPNs mask your IP address and encrypt your data, they don’t make you entirely anonymous. For complete anonymity, one might consider tools like Tor in conjunction with a VPN.
- All VPNs are Equal: Not all VPNs offer the same level of security, speed, or privacy. It’s essential to research and choose a reputable service.
- Free VPNs are Just as Good: Free VPNs might be tempting, but they often come with limitations. Some might log your activities, offer fewer server options, or even sell your data to advertisers.
- VPNs are Only for Tech-Savvy Individuals: Modern VPNs are designed with user-friendliness in mind. With intuitive interfaces and easy-to-follow setup processes, they cater to both tech-savvy users and beginners.
Conclusion
In today’s digital era, the vast opportunities offered by the internet come hand-in-hand with challenges and threats to our personal and financial information. VPNs have emerged as essential tools, providing a robust shield against these cyber threats. By encrypting data and masking IP addresses, they ensure our online interactions remain private, secure, and free from unwanted intrusions. As we navigate this interconnected world, making informed decisions about our online privacy tools, like choosing the right VPN, becomes paramount.
As we conclude this guide, it’s clear that in an age of increasing digital vulnerabilities, taking proactive measures for online privacy is not just beneficial—it’s crucial. With the right knowledge and tools, we can confidently traverse the digital realm, ensuring our online identities remain protected. Here’s to a safer and more informed digital future for all.


Leave a Reply