
How to Manage Inventory in an E-commerce Business
In today’s digital age, where online shopping has become a staple for consumers worldwide, the backbone of every successful e-commerce business lies in its inventory management. Inventory management, often overlooked, is the silent hero that ensures businesses run smoothly, customers remain satisfied, and profits soar.
Why is Inventory Management Crucial in E-commerce?
Inventory management is the art and science of efficiently maintaining, tracking, and selling stock or inventory. In the realm of e-commerce, it plays a pivotal role for several reasons:
- Customer Satisfaction: Imagine a scenario where a customer places an order, only to be informed later that the product is out of stock. Such situations can tarnish a brand’s reputation and lead to lost sales. Effective inventory management ensures that products are always available, leading to prompt deliveries and satisfied customers.
- Cash Flow Management: Unsold inventory is essentially tied-up capital. By managing inventory effectively, businesses can ensure that they don’t overstock or understock, optimizing cash flow.
- Operational Efficiency: Efficient inventory management can streamline operations, reduce storage costs, and minimize losses due to expired or unsold goods.
The Digital Transformation of Inventory Management
With the rise of e-commerce platforms and digital tools, inventory management has undergone a significant transformation. Gone are the days of manual stock-taking and spreadsheet tracking. Today, advanced software solutions offer real-time tracking, predictive analytics, and automated restocking, making the process more accurate and efficient.
| Traditional vs. Digital Inventory Management |
|---|
| Traditional |
| Manual stock-taking |
| Spreadsheet-based tracking |
| Reactive restocking |
| Limited data analysis |
Understanding Different Inventory Management Techniques
In the vast world of e-commerce, one size does not fit all. Different businesses have varied needs, and as such, there are multiple inventory management techniques to cater to these requirements. Let’s delve into some of the most popular methods and understand their benefits and potential risks.
Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory Management: Benefits and Risks
What is JIT?
The Just-in-Time inventory management technique revolves around ordering inventory only when it’s needed for sales, reducing the costs associated with holding stock. Originating from Japan, this method has gained popularity due to its efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
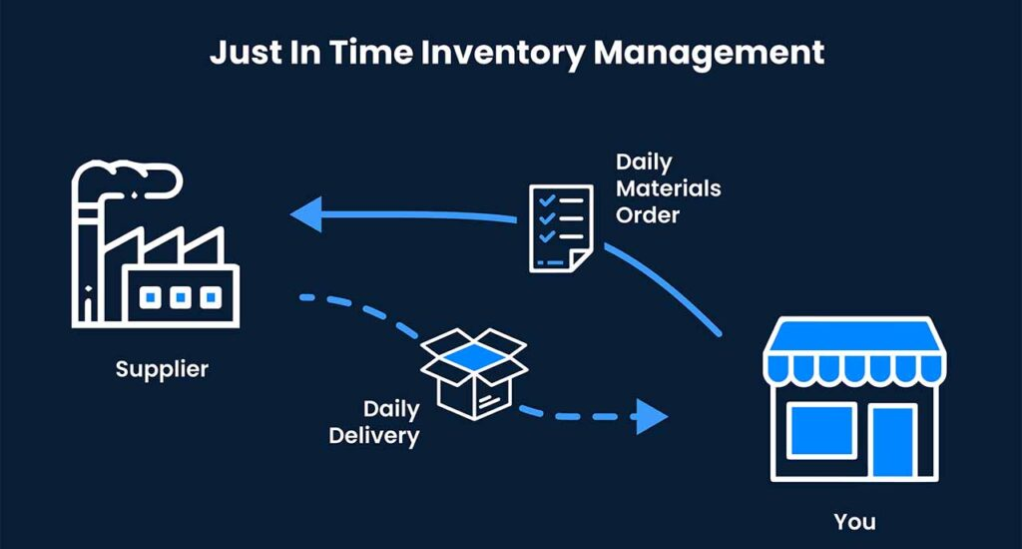
Benefits:
- Reduced Holding Costs: By not storing excess inventory, businesses can save on storage, insurance, and other related costs.
- Improved Cash Flow: Money isn’t tied up in unsold stock, making funds available for other business needs.
- Less Wastage: With fewer goods stored, there’s a reduced risk of products becoming obsolete or going to waste.
Risks:
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Relying heavily on suppliers means that any disruption can lead to stockouts.
- Potential for Rushed Orders: With the need for quick restocking, there might be instances of paying more for expedited shipping.
First In, First Out (FIFO) Inventory Management: Ensuring Product Freshness
What is FIFO?
FIFO is a method where the oldest inventory items are sold first. This is especially crucial for perishable goods or products with an expiration date.
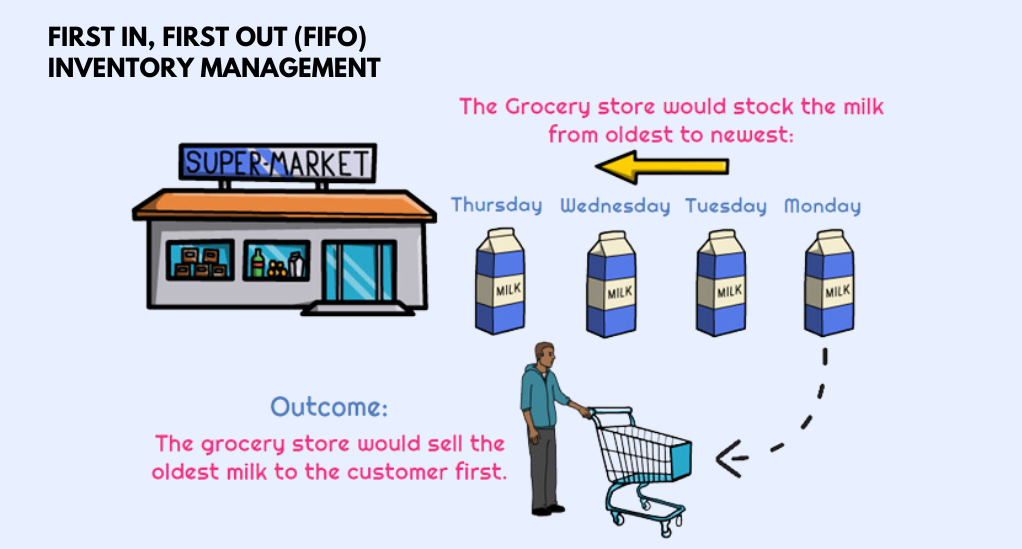
Benefits:
- Minimized Wastage: Products are sold in the order they’re received, ensuring that nothing expires or goes bad.
- Consistent Product Quality: Customers receive products that are fresh and in good condition.
Risks:
- Higher Costs for Fluctuating Prices: If the cost of goods rises, businesses might face higher expenses as they’re selling older, cheaper stock while buying new stock at higher prices.
Dropshipping: The “Anti-Inventory” Solution
What is Dropshipping?
Dropshipping is a retail fulfillment method where a store doesn’t keep the products it sells in stock. Instead, when a store sells a product, it purchases the item from a third party and has it shipped directly to the customer.
Benefits:
- Low Startup Costs: No need for a large capital to start, as there’s no inventory to purchase.
- Flexible Product Offering: Businesses can offer a wider variety of products without the need for large warehouses.
Risks:
- Lower Profit Margins: As businesses act as middlemen, the profit margins can be slimmer.
- Less Control Over Inventory and Shipping: Relying on third-party suppliers can lead to potential stockouts or shipping delays.
The Role of Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
Navigating the intricacies of e-commerce inventory management can be a daunting task, especially for businesses scaling rapidly. This is where Third-Party Logistics, commonly known as 3PL, comes into play.
What is 3PL?
Third-Party Logistics providers are external companies that handle various logistics-related operations for businesses. This can range from warehousing and inventory management to order fulfillment and transportation.
Benefits:
- Scalability: As your business grows, 3PL providers can easily adapt to increased order volumes, ensuring seamless operations.
- Expertise: Leveraging the expertise of 3PLs means benefiting from their experience, technology, and infrastructure.
- Cost-Effective: Outsourcing logistics can often be more cost-effective than building and managing in-house operations, especially for businesses that are still scaling.
Risks:
- Less Direct Control: Entrusting a third party with logistics means relinquishing direct control over certain aspects of the business.
- Potential for Miscommunication: Relying on an external entity can sometimes lead to communication gaps, affecting order fulfillment or customer service.
Predictive Analytics: Forecasting Future Demand
In the age of data-driven decision-making, predictive analytics has emerged as a game-changer for e-commerce inventory management.
What is Predictive Analytics?
Predictive analytics involves using historical data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning techniques to identify future outcomes. In the context of inventory management, it helps businesses forecast future product demand.
Benefits:
- Accurate Forecasting: By analyzing past sales data, businesses can make informed predictions about future sales trends.
- Optimized Stock Levels: Predictive analytics helps in maintaining the right amount of stock, preventing overstocking or stockouts.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: With products always in stock and timely deliveries, customer satisfaction levels see a significant boost.
Risks:
- Data Accuracy: The effectiveness of predictive analytics hinges on the accuracy of the data fed into the system.
- Over-reliance: Solely depending on predictive analytics without considering external factors (like market trends or global events) can lead to skewed results.
The Importance of Scanning Systems
In the fast-paced world of e-commerce, accuracy is paramount. Scanning systems play a pivotal role in ensuring that inventory is tracked meticulously, reducing the margin for human error.
What are Scanning Systems?
Scanning systems, often integrated with barcodes or QR codes, allow businesses to quickly and accurately track products throughout the supply chain. From the moment items enter the warehouse to the point they’re shipped out, every movement is recorded.
Benefits:
- Speed and Efficiency: Manual inventory checks can be time-consuming. Scanning systems expedite the process, allowing for real-time updates.
- Reduced Errors: Human error is inevitable. Scanning systems minimize mistakes, ensuring accurate inventory counts.
- Enhanced Data Collection: Beyond just tracking inventory, scanning systems can provide insights into sales trends, product performance, and more.
Risks:
- Technical Glitches: Like all technology, scanning systems are not immune to malfunctions or glitches, which can disrupt operations.
- Initial Setup Costs: Implementing a robust scanning system requires an initial investment in technology and training.
Setting Par Levels for Optimal Stock
Ensuring that you have just the right amount of stock is a delicate balancing act. This is where par levels come into the picture.
What are Par Levels?
A par level is the minimum amount of stock that a business should have on hand at all times. Once inventory drops below this level, it’s a signal to reorder.
Benefits:
- Consistent Stock Levels: Par levels ensure that popular products are always in stock, preventing potential lost sales.
- Streamlined Reordering: With clear par levels set, businesses can automate the reordering process, ensuring timely restocks.
- Improved Cash Flow: By maintaining optimal stock levels, businesses can avoid tying up capital in excess inventory.
Risks:
- Changing Market Dynamics: Par levels need regular reviews. What worked a few months ago might not be optimal today due to changing market demands or trends.
- Over-reliance: Solely depending on par levels without considering other factors (like upcoming marketing campaigns or seasonal demands) can lead to stockouts or overstocking.
The Power of Inventory Management Software
In the digital age, relying solely on manual processes for inventory management can be a recipe for disaster. Enter inventory management software – the digital solution to streamline and optimize inventory processes.
What is Inventory Management Software?
It’s a digital tool that helps businesses track products across the supply chain, from procurement to sales. These software solutions offer features like real-time tracking, automated reordering, and detailed analytics.
Benefits:
- Real-time Updates: With cloud-based solutions, businesses can monitor inventory levels in real-time, making informed decisions on the go.
- Automated Processes: From reordering stock to generating sales reports, automation reduces manual workload and enhances accuracy.
- Data-Driven Insights: Modern software solutions provide detailed analytics, helping businesses identify trends, forecast demand, and optimize stock levels.
Risks:
- Integration Challenges: For businesses with existing systems, integrating new software can pose challenges.
- Training and Adaptation: Implementing new software requires training staff, which can take time and resources.
Regular Audits and Quality Control
While digital tools and software provide a high degree of accuracy in inventory management, the importance of human oversight cannot be understated. Regular audits and quality control checks are essential to ensure that the digital data matches the physical stock and that products meet the desired quality standards.
What are Regular Audits?
Audits involve physically counting inventory items and comparing them against the recorded numbers in the inventory management system. This process helps identify discrepancies, theft, damage, or other issues that might not be immediately evident through digital tracking alone.
Benefits:
- Accuracy Assurance: Regular audits ensure that the digital data aligns with the actual stock, ensuring accurate inventory levels.
- Loss Prevention: By identifying discrepancies early, businesses can take measures to prevent theft or address other issues leading to inventory loss.
- Operational Efficiency: Accurate inventory data ensures smooth operations, from order fulfillment to restocking.
Risks:
- Time-Consuming: Physical audits, especially in large warehouses, can be time-intensive.
- Human Error: Manual counting can introduce errors, especially if not done meticulously.
Quality Control in E-commerce
Quality control is the process of ensuring that the products sold meet the desired quality standards. In e-commerce, where customers cannot physically inspect products before purchase, maintaining high-quality standards is paramount.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Delivering high-quality products consistently ensures customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Reduced Returns: Quality products mean fewer returns, saving costs and enhancing brand reputation.
- Competitive Edge: In a saturated e-commerce market, offering top-notch quality can set a business apart from its competitors.
Risks:
- Increased Costs: Implementing rigorous quality control measures can increase operational costs.
- Potential Delays: Extensive quality checks can sometimes delay product shipments, especially if issues are identified.
Organizing the Warehouse Layout for Efficiency
The physical layout of a warehouse plays a crucial role in the efficiency of inventory management. An optimized layout ensures that products are easily accessible, reduces the time taken for order fulfillment, and enhances overall operational efficiency.
Why is Warehouse Layout Important?
The design and organization of a warehouse directly impact the speed and accuracy of order processing. A well-organized warehouse ensures that the most frequently sold items are easily accessible, reduces unnecessary movement, and minimizes the chances of errors.
Benefits:
- Faster Order Fulfillment: An optimized layout ensures that products are quickly located and processed for shipping.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Efficient design reduces the time employees spend picking and processing orders, leading to cost savings.
- Enhanced Safety: A clutter-free, organized warehouse reduces the risk of accidents and ensures a safer working environment.
Key Strategies for Warehouse Optimization:
- Zone Picking: Group similar items or items that are frequently sold together in the same area. This reduces travel time for pickers.
- Vertical Storage: Utilize vertical space by installing taller storage units. This maximizes storage capacity without increasing the warehouse footprint.
- Wide Aisles: Ensure aisles are wide enough for easy movement, especially if using machinery like forklifts.
- Clear Signage: Clearly label all areas, shelves, and bins to reduce search time and minimize errors.
- Regular Re-evaluation: As sales trends change, the warehouse layout should be periodically reassessed and adjusted accordingly.
Risks:
- Over-optimization: Trying to make the warehouse too efficient can sometimes lead to confusion, especially if changes are made too frequently.
- Costs: Significant changes to warehouse layout, like installing new shelving or moving large sections, can be costly.
Conclusion
E-commerce inventory management is a multifaceted endeavor, encompassing everything from selecting the right management techniques to ensuring the physical layout of the warehouse is optimized for efficiency. As the e-commerce landscape continues to evolve, businesses must stay adaptable, leveraging both technological solutions and tried-and-true strategies to ensure inventory management success. By doing so, they not only ensure smooth operations but also enhance customer satisfaction, setting the stage for sustained growth and success in the competitive online marketplace.


Leave a Reply