
Malware Removal 101: Techniques and Tools
In the digital era, the threat of malware is ever-present, evolving continuously to exploit new vulnerabilities in our systems. As individuals and organizations alike grapple with the potential risks associated with malware attacks, understanding the nuances of malware and mastering the art of its removal have become indispensable skills. In this section, we will delve deep into the background of malware and underscore the importance of malware removal.
Understanding Malware
In this section, we will dissect the complex world of malware, exploring its various types, understanding how it spreads, and assessing its potential impact on systems. Let’s embark on this enlightening journey step by step.
What is Malware?
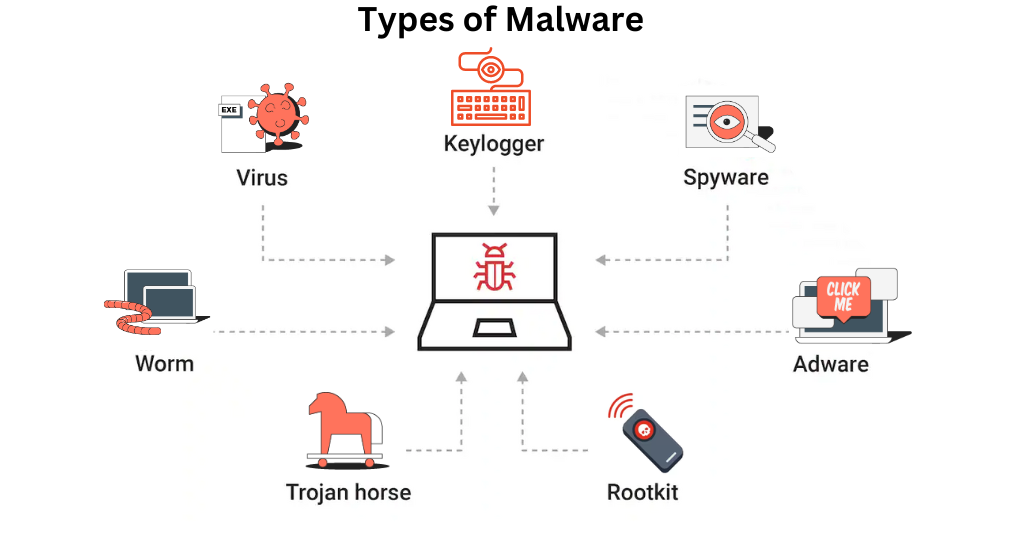
Malware is a general term used to describe a variety of malicious software, including viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, spyware, and more. These malicious programs are designed to infiltrate, damage, or disrupt systems, often without the user’s knowledge.
Types of Malware
To safeguard against malware effectively, it’s essential to understand the different types that exist. Here, we categorize and detail the most common types of malware that have been plaguing the digital space:
| Malware Type | Primary Function | Transmission Method | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Virus | File Corruption | Infected Files | Moderate to High |
| 2. Worm | Self-Replication | Network Vulnerabilities | High |
| 3. Trojan | Unauthorized Access | Disguised as Legitimate Software | High |
| 4. Ransomware | Data Encryption | Phishing Emails, Exploit Kits | Very High |
| 5. Spyware | Data Collection | Bundled with Software | Moderate |
| 6. Adware | Ad Delivery | Bundled with Software | Low to Moderate |
| 7. Rootkit | Unauthorized Access | Exploit Kits, Phishing Emails | Very High |
How Malware Spreads
Infection Vectors
Malware can infiltrate systems through various channels, including:
- Email Attachments: Malware often comes as attachments in spam emails. Once opened, it can install itself on the system.
- Malicious Websites: Visiting compromised websites can result in malware being downloaded onto your system.
- Software Downloads: Downloading software from untrusted sources can bring along malware.
- Removable Drives: Malware can spread through infected USB drives and other removable media.
- Exploit Kits: These are tools used by attackers to exploit known vulnerabilities in systems to deliver malware.
The Impact of Malware on Systems
- Data Breach
Malware can lead to data breaches, where sensitive information is accessed and possibly sold or used for fraudulent activities. - Financial Loss
Organizations can suffer substantial financial losses due to malware attacks, including the costs of mitigation and potential fines. - Reputation Damage
A malware attack can severely damage an organization’s reputation, resulting in loss of customers or partners. - System Downtime
Malware can cause system outages, disrupting operations and resulting in downtime, which can be costly for businesses.
Preventive Measures
As the saying goes, “prevention is better than cure.” In the context of malware, this adage holds immense significance. Implementing preventive measures is the first line of defense against the ever-present threat of malware. In this section, we will explore step-by-step the most effective practices to keep malware at bay.
Safe Browsing Habits
1. Keep Software and Browsers Updated – Regularly update your operating system, browsers, and software applications. Software updates often include security patches that fix vulnerabilities.
2. Use a Secure Browser – Opt for browsers known for their robust security features. Popular choices include Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Microsoft Edge.
3. Be Cautious with Email Attachments and Links – Avoid opening email attachments or clicking on links from unknown or suspicious sources. Even seemingly harmless emails can harbor malware.
4. Employ Email Filtering – Enable email filtering to automatically identify and quarantine potentially malicious emails. Many email providers offer this feature.
5. Educate Yourself and Others – Stay informed about common phishing and scam tactics. Educate family members, friends, and colleagues to recognize and avoid potential threats.
Regular Software Updates
6. Enable Automatic Updates – Set up automatic updates for your operating system and software whenever possible. This ensures that you receive critical security patches promptly.
7. Remove Unnecessary Software – Uninstall software applications and browser extensions that you no longer use. Each installed program is a potential entry point for malware.
8. Use a Standard User Account – Avoid using an administrator account for daily activities. A standard user account limits the changes malware can make to your system.
Utilizing Antivirus Software
9. Install Reputable Antivirus Software – Choose a well-known and trusted antivirus program. Popular options include Norton, McAfee, and Bitdefender.
10. Regular Scanning – Schedule regular antivirus scans to check for malware on your system. Ensure that real-time protection is enabled.
11. Be Wary of Free Antivirus Software – Exercise caution when considering free antivirus software. Some may come bundled with adware or may not provide adequate protection.
By diligently following these preventive measures, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce their vulnerability to malware attacks. The proactive approach to cybersecurity is a formidable defense against the ever-evolving landscape of digital threats.
Identifying Malware Infections
Recognizing the presence of malware on your system is a crucial step in mitigating its impact. In this section, we will provide a step-by-step guide on how to identify malware infections, including common symptoms to watch out for and the tools available for effective detection.
Common Symptoms of Malware Infections
Identifying malware infections hinges on recognizing common symptoms in computer systems. These symptoms encompass issues such as a significant system slowdown, which can indicate resource-heavy malware. Persistent pop-up messages promoting questionable products or services may signal adware or harmful malware. Frequent system crashes or freezes often result from malware destabilization. Unexplained spikes in data usage may indicate covert data transmission by malware. Suspicious changes to browser settings are associated with malicious extensions or toolbars. Unexpected file modifications or deletions are signs of malware activity. Finally, antivirus software alerts about detected malware necessitate immediate action. Recognizing these symptoms enables swift responses to mitigate malware’s impact on computer systems.
Tools for Malware Detection
Utilizing effective tools for detecting malware is essential in fortifying system security. Trusted antivirus and anti-malware software conduct routine scans, identifying and removing various malware types. Online scanners, offered by many antivirus providers, offer hassle-free malware detection and removal. Specific malware removal tools like Malwarebytes, AdwCleaner, and ComboFix target and eliminate specific threats. Additionally, firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) monitor network traffic for anomalies, proactively blocking potential malware threats. Employing these tools collectively enhances cybersecurity, ensuring swift malware detection and removal, strengthening system defense.
How to Use Malware Detection Tools
Effectively using malware detection tools involves a strategic approach to maintain robust system security. Configure scheduled scans for ongoing protection, initiate manual scans regularly, and follow software instructions to address detected malware. Keep antivirus and anti-malware software updated to stay resilient against evolving threats, enhancing overall cybersecurity.
Malware Removal Techniques
Once malware has infiltrated a system, it’s imperative to promptly and effectively remove it to prevent further damage and protect sensitive data. In this section, we will explore step-by-step malware removal techniques, including both manual and automated methods, to help users regain control of their compromised systems.
Step 1: Isolate the Infected System
Isolate the infected system for containment. Begin by disconnecting it from the internet to halt communication with malware command and control servers. Additionally, disable shared resources like file and printer sharing to prevent malware spread to other networked devices. These actions minimize the risk of further infection, facilitating effective removal.
Step 2: Identify and Isolate Malware
The focus is on identifying and isolating malware effectively. Firstly, employ reputable antivirus and anti-malware software for comprehensive system scans, automatically detecting and removing known malware. If automated scans prove insufficient, proceed to manually inspect the system for any suspicious files, processes, or registry entries. For guidance, consult online resources or consider seeking professional assistance. Finally, quarantine and remove any identified malicious files to eliminate the malware from the system, ensuring a secure environment.
Step 3: Restore System to a Clean State
The focus is on restoring the system to a clean state. This can be achieved through two approaches. First, utilize the system restore feature if available, reverting the system to a state before the malware infection occurred. Alternatively, in more severe cases where malware has deeply entrenched itself, consider a complete operating system reinstallation. Ensure data backups are available to safeguard essential files throughout this process. These actions aim to return the system to a secure and functional state after malware removal.
Step 4: Strengthen Security Measures
In the effort to fortify your system’s security, two essential steps are paramount. Firstly, promptly apply all available operating system and software updates, including security patches, to seal potential vulnerabilities that malware could exploit. Secondly, ensure the highest level of protection by upgrading or replacing your antivirus and anti-malware software with the latest versions. These actions collectively bolster your defenses against malware and evolving threats.
Step 5: Educate and Train Users
In the final step of malware mitigation, user education plays a vital role. Start by raising user awareness about safe internet practices, teaching them to identify phishing attempts, and emphasizing the importance of avoiding suspicious downloads and email attachments. These proactive measures empower users to protect themselves and their systems, reducing the risk of future malware infections.
By following these meticulous malware removal techniques, individuals and organizations can effectively address malware infections and enhance their overall cybersecurity posture.
Post-Removal Actions
After successfully removing malware from a system, it’s essential to take post-removal actions to ensure the system’s integrity and prevent future infections. This section will provide a step-by-step guide on what to do following malware removal, covering security checks, system optimization, and ongoing protection measures.
Step 1: Verify Complete Malware Removal
Begin by running a thorough system scan using trusted antivirus and anti-malware software to confirm that no traces of malware remain. Additionally, check for any system alterations the malware may have made in settings, files, or the registry, and restore them to their original state if needed. This verification process assures that the system is clean and secure.
Step 2: Update and Patch
Firstly, keep the operating system current by installing the latest security patches and updates, which seal potential vulnerabilities that malware could exploit. Secondly, update all software applications to their latest versions, as outdated software can serve as an entry point for malware. It’s advisable to enable automatic updates whenever feasible for ongoing protection.
Step 3: Strengthen Security
Thoroughly review and configure firewall settings to bolster protection against both incoming and outgoing threats. Second, if available, set up and activate an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) to vigilantly monitor network traffic for any signs of suspicious activities. These measures work together to fortify your system’s defense against potential threats, ensuring a secure digital environment.
Step 4: Backup Important Data
Incorporating data backup as part of your post-malware removal strategy is essential. Consistently back up crucial data to an external and secure location. This proactive step ensures that your data remains protected in the event of future malware attacks or system failures, providing a safety net for your valuable information.
Step 5: Educate Users
Consistently instruct users on safe internet practices, underscoring the significance of vigilance against phishing attempts and the avoidance of suspicious downloads. This ongoing training empowers users to be proactive in protecting their systems, reducing the risk of future malware encounters.
Step 6: Implement Ongoing Protection Measures
In the realm of ongoing protection measures, prioritize real-time safeguarding through up-to-date antivirus and anti-malware software. This ensures a constant defense against emerging threats. Additionally, bolster security by implementing robust email filtering, which automatically identifies and isolates malicious emails. This proactive measure minimizes the risk of malware infiltrating systems via email attachments or links, enhancing overall cybersecurity.
Conclusion
In the ongoing battle against malware, understanding its types and effective removal techniques is crucial. Malware, including viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, and spyware, constantly threatens our digital world.
It spreads through email, malicious websites, downloads, removable drives, and exploit kits, leading to data breaches, financial losses, reputation damage, and system downtime.
Preventive measures like safe browsing, regular updates, and user education are vital. Post-removal actions, including verification, updates, and data backup, ensure system integrity.
In this fight against malware, knowledge and proactive measures are key to a secure digital environment.


Leave a Reply