How IoT Revolutionizes Urban Living in Smart Cities
In today’s fast-paced world, technology is a game-changer, especially in how we live in our cities. At the heart of this transformation is the Internet of Things (IoT), a network of connected devices that communicate with each other. Imagine street lights that adjust brightness based on the time of day, or traffic lights that change their timing to ease congestion. This is the role of IoT in creating smart cities.
Smart cities use IoT to make life easier, safer, and more efficient for everyone. From the way we travel to how we manage resources like water and electricity, IoT is at the forefront of it all. In this article, we’ll explore how IoT is turning our urban spaces into smart cities. We’ll see how it’s changing everything from the air we breathe to the way we get around. Let’s dive into this exciting journey and discover how IoT is shaping the future of our cities.
Understanding the Basics of IoT in Smart Cities
In our journey to understand smart cities, it’s crucial to start at the foundation: the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT is like a big team where each player is a smart device, from sensors on roads to cameras on buildings. These devices talk to each other and share information. This communication is what makes a city ‘smart’.
The Ingredients of a Smart City
- Smart Sensors: These are the eyes and ears of a smart city. They collect data like temperature, traffic flow, and energy use.
- Connectivity: This is the network that lets devices talk to each other. It’s like the internet, but for city devices.
- Data Processing: Here’s where the magic happens. The data collected by sensors is turned into useful information. Think of it as a brain interpreting what the eyes and ears sense.
How These Elements Work Together
Imagine a street with smart sensors. These sensors detect how busy the road is and send this information over the network. The city’s system then processes this data and might decide to change traffic light timings to reduce congestion. This is IoT in action, making life smoother and cities smarter.
Table of Comparison: Traditional Cities vs Smart Cities
| Feature | Traditional Cities | Smart Cities |
|---|---|---|
| Traffic Control | Manual and Fixed Timings | Adaptive and Automated |
| Energy Management | General Usage Patterns | Customized, Efficient Use |
| Safety | Reactive Measures | Proactive Surveillance |
This table helps us see the differences between how traditional cities and smart cities operate, thanks to IoT.

Smart cities are not just a futuristic concept; they are already becoming a reality in many parts of the world. As we continue to embrace IoT, our urban spaces will become more efficient, safer, and more responsive to our needs.
How IoT is Enhancing Urban Infrastructure
IoT is like a superhero for our cities, making urban infrastructure smarter and more efficient. By using IoT, cities can handle challenges like traffic jams, power shortages, and even public safety issues much better. It’s like giving our city the power to think and react on its own.
Transforming Traffic and Transportation
- Smart Traffic Lights: These lights change their timings based on real-time traffic data. It’s like they can see where the traffic is and adjust to keep things moving smoothly.
- Connected Public Transport: Buses and trains that use IoT can report their locations and adjust routes to avoid delays. It’s as if they can find the quickest path by themselves.
Upgrading Energy and Utilities
- Smart Energy Grids: These grids manage electricity flow to where it’s needed most, reducing waste and saving energy.
- Water Management: IoT sensors can detect leaks and monitor water usage, ensuring there’s enough water for everyone without wasting it.
Key Benefits of IoT in Urban Infrastructure
- Less traffic congestion
- Better public transport
- Lower energy consumption
- Efficient water use
- Improved public safety
IoT is turning our urban areas into intelligent spaces that respond to our needs and challenges. It’s not just about technology; it’s about making our daily lives easier and our cities more livable. As we move forward, IoT will continue to play a big role in shaping the future of urban living.
The Role of IoT in Public Safety and Security
In the world of smart cities, keeping people safe and secure is a top priority. IoT steps in here like a watchful guardian. It uses technology to make sure that people are safe, whether they’re walking home at night or during emergencies. It’s like having an extra set of eyes always looking out for dangers.

Enhancing Surveillance and Emergency Response
- Smart Cameras and Sensors: These devices are placed around the city. They can spot unusual activities and alert the authorities. It’s like having a vigilant neighbor who’s always on the lookout.
- Emergency Services Integration: In an emergency, IoT can help by making sure that help arrives quickly. It can guide emergency vehicles through the fastest route, avoiding any delays.
IoT in Crime Prevention and Control
- Data-Driven Policing: Police can use data from IoT devices to understand where and when crimes might happen. It’s like having a crystal ball that helps predict and prevent crime.
- Community Safety Apps: IoT enables apps that let people report incidents or get alerts about their neighborhood. It’s like having a community watch group right in your pocket.
How IoT Enhances Public Safety
- Faster emergency responses
- Better crime detection and prevention
- Real-time public safety alerts
- Safer streets and neighborhoods
- Quick assistance in accidents or natural disasters
IoT is transforming public safety by making it more proactive and responsive. It’s not just about technology; it’s about creating a safer environment for everyone in the city. With IoT, cities are not just smart; they’re secure too.
Revolutionizing Environmental Management with IoT
IoT is playing a big role in making our cities not just smarter, but also greener and more sustainable. It’s like having a green thumb for the whole city, helping to take care of the environment in new and innovative ways. By monitoring air quality, managing waste, and saving energy, IoT is making our cities better places to live.
Monitoring and Improving Air Quality
- Air Quality Sensors: These sensors check the air for pollution and give us data to help keep the air clean. It’s like having a weather forecast but for air quality.
- Smart Trees and Gardens: IoT isn’t just about gadgets. In some cities, ‘smart trees’ with sensors are used to monitor air quality and provide green spaces.
Smart Waste Management and Recycling
- IoT-Enabled Trash Bins: These bins can tell when they’re full and need to be emptied. It’s like the bin is saying, “Hey, I’m full, come and empty me!”
- Efficient Recycling Systems: IoT helps to sort and manage recycling, making sure waste is handled in the best way possible.
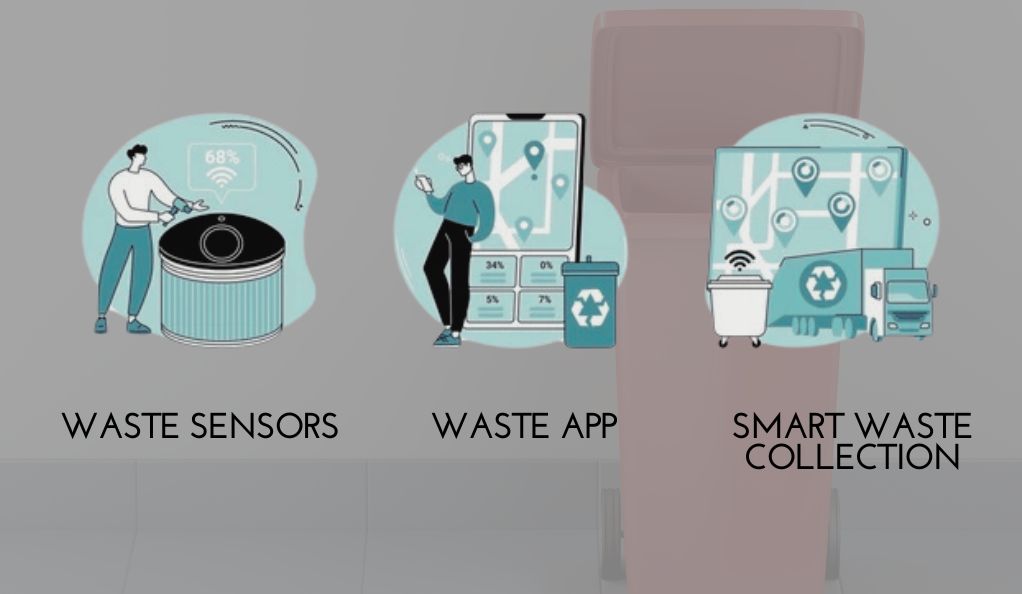

Benefits of IoT in Environmental Management
- Cleaner air to breathe
- Less waste in streets and landfills
- Better recycling methods
- Greener, more pleasant urban spaces
- Reduced environmental footprint of cities
With IoT, we’re not just building smarter cities; we’re building healthier, more sustainable environments. It’s a step towards not just living in our cities but also caring for them.
Reimagining Public Amenities through IoT Innovation
IoT is transforming the way we use and enjoy public amenities, making them more convenient, accessible, and efficient. It’s like giving a high-tech upgrade to everything in the city – from parks to libraries. This change is making everyday life easier and more enjoyable for residents and visitors alike.
Enhancing Healthcare and Educational Facilities
- Smart Healthcare Systems: Hospitals and clinics use IoT for better patient care. This includes things like wearable health monitors and smart beds. It’s like having a nurse who’s always watching over patients.
- IoT in Education: Schools are using IoT to make learning more interactive. From smart boards to connected classrooms, it’s like giving students and teachers the best tools for education.

Improving Connectivity and Public Spaces
- Wi-Fi Hotspots: Many cities are installing public Wi-Fi networks. It’s like having the internet everywhere you go, for free.
- Smart Parks and Public Areas: Parks with IoT features like lighting and information boards make visits safer and more informative. It’s like the park is talking to you, telling you its story.
The Impact of IoT on Public Amenities
- Better access to healthcare and education
- Free and widespread internet connectivity
- Safer and more interactive public spaces
- Real-time information access in public areas
- Enhanced experience in recreational and cultural sites
IoT is not just about adding technology to public amenities; it’s about rethinking how we can make these spaces work better for everyone. With IoT, public amenities are no longer just places we use; they become experiences that we enjoy.
Navigating the Complexities of IoT Integration in Urban Landscapes
Integrating IoT into urban landscapes is like solving a complex puzzle. It involves balancing technological innovation with practical challenges. While the benefits are vast, cities face hurdles in implementing IoT systems, from ensuring privacy and security to managing financial and technological resources.
Addressing Privacy and Security Concerns
- Protecting Data: With IoT devices collecting tons of data, keeping this information safe is crucial. It’s like having a digital lock on every piece of data.
- Ensuring Network Security: Cities need to protect their IoT networks from cyber threats. It’s like building a digital fortress around the city’s technology.
Overcoming Technological and Financial Hurdles
- Technological Challenges: Cities need the right technology and expertise to make IoT work. It’s like assembling the right tools and team for a big project.
- Financial Planning: Implementing IoT can be costly. Cities have to find ways to fund these projects, like a family saving up for a big home improvement.
Key Steps for Successful IoT Integration
- Establishing strong data protection measures
- Building robust cybersecurity systems
- Investing in the right technology and expertise
- Developing effective funding strategies
Navigating these complexities is essential for the successful integration of IoT in urban landscapes. It’s a journey that requires careful planning, strong security measures, and smart financial management. By overcoming these challenges, cities can unlock the full potential of IoT to transform urban living.
Charting the Future: IoT’s Progressive March in Urban Development
As we look ahead, the role of IoT in shaping our cities is not just a trend, it’s a journey towards a smarter future. This journey is like planting seeds today for a forest of tomorrow, where each IoT device adds to a larger vision of advanced, efficient, and responsive urban living. This progressive march of IoT in urban development is set to redefine how we interact with our city spaces.
Anticipating Technological Advances in IoT
- Emerging IoT Technologies: The future will bring more advanced IoT devices. Imagine drones delivering packages or sensors that detect pollution at a hyper-local level. It’s like our cities getting smarter by the day.
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence: IoT will increasingly work with AI to make better decisions. It’s like giving the city a brain that learns and improves over time.
Envisioning the Impact on Urban Living
- Transformed Cityscapes: Cities will become more efficient and sustainable, like having a living organism that adapts and evolves.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Residents will experience greater convenience, safety, and well-being. It’s like living in a city that truly understands and responds to your needs.
Future Prospects of IoT in Cities
- Smart transportation systems with autonomous vehicles
- Advanced energy grids that adapt to real-time demand
- Buildings that regulate their own climate and energy use
- Public services that are more responsive and personalized
Conclusion
As we’ve seen, IoT is more than just technology; it’s a new way of making our cities smarter, safer, and more sustainable. From managing traffic to saving energy, IoT is changing how we live in urban areas. It’s like having a friendly neighbor who’s always there to help. These changes are just the beginning. As IoT grows, our cities will become even more connected, responsive, and efficient.
Looking forward, the potential of IoT in urban development is huge. It promises a future where cities are not just places to live but dynamic spaces that enhance our lives in countless ways. Imagine a city that not only understands your needs but also adapts to meet them. That’s the promise of IoT – a brighter, smarter future for everyone.


Leave a Reply