
How to Implement AI in Healthcare
In the realm of modern medicine, few innovations hold as much transformative potential as Artificial Intelligence (AI). As we stand on the brink of a new era in healthcare, AI is not just a buzzword; it’s a revolutionary force poised to reshape every facet of patient care, diagnostics, treatment, and even administrative tasks.
What is AI in Healthcare?
At its core, AI in healthcare refers to the use of complex algorithms and software to emulate human cognition in the analysis of intricate medical data. It’s about machines being able to tackle tasks that traditionally required human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation. In the medical field, this translates to tasks like diagnosing diseases, suggesting treatments, predicting patient outcomes, and even automating administrative tasks.
Why is AI Important in Healthcare?
The importance of AI in healthcare can be summarized in three key points:
- Efficiency: With the ever-growing amount of patient data, it’s becoming increasingly challenging for healthcare professionals to process and interpret all the information. AI can quickly analyze vast datasets, making predictions and suggestions at speeds unimaginable for a human.
- Accuracy: Machines, unlike humans, are not prone to fatigue or cognitive biases. This means that, given the right data and training, AI can make highly accurate predictions and diagnoses, reducing the margin of error.
- Personalization: AI can help tailor medical treatments to individual patient needs, leading to what’s often referred to as ‘personalized medicine’. By analyzing a patient’s genetic makeup, AI can suggest treatments that are most likely to work for that specific patient.
The Current Landscape of AI in Healthcare
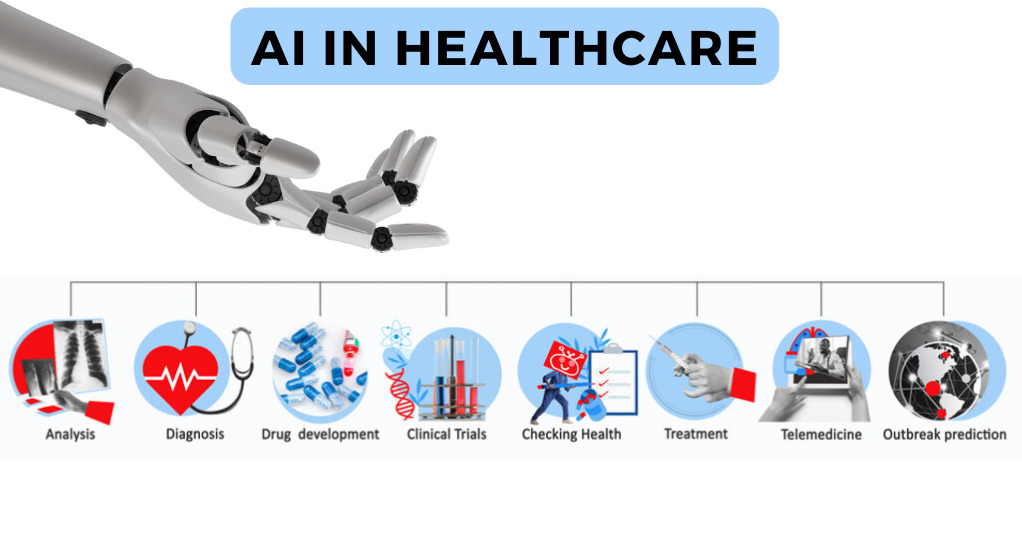
Today, AI’s footprint in healthcare is evident in various applications:
- Diagnostics: Tools that can read and interpret medical images for signs of diseases such as cancer, more quickly and accurately than human counterparts.
- Treatment Design: Algorithms that analyze data to recommend treatment plans or predict patient outcomes.
- Drug Discovery and Manufacturing: AI can help in the rapid discovery and production of new drugs by analyzing complex biochemical interactions.
- Managing Medical Records: Drawing and analyzing data from vast amounts of patient medical records to improve services.
- Predictive Analysis: Using patient data and machine learning to predict disease outbreaks, patient admissions, and other important predictions.
| Application | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Diagnostics | Interpret medical images | Detect tumors in X-rays |
| Treatment Design | Recommend treatment plans | Suggest radiation therapy for cancer patients |
| Drug Discovery | Rapid discovery of new drugs | Find new compounds for rare diseases |
| Medical Records | Analyze and manage patient data | Predict patient’s future health needs |
| Predictive Analysis | Predict future health events | Forecast disease outbreaks |
As we delve deeper into the specifics of how AI is implemented in various healthcare sectors, it’s crucial to understand that the technology is still in its nascent stages. While there have been significant advancements and success stories, there are also challenges and ethical considerations that need addressing.
The Evolution of AI in Healthcare
The journey of AI in healthcare is a testament to the rapid advancements in technology and its integration into the medical field. To appreciate the current state and potential of AI, it’s essential to understand its historical context and evolution.
The 1960s and 1970s marked the inception of AI’s role in healthcare. The first problem-solving program, known as Dendral, was designed for applications in organic chemistry. While not directly related to medicine, Dendral paved the way for MYCIN, one of the earliest systems to use artificial intelligence in medicine. MYCIN was designed to identify bacteria causing severe infections and recommend antibiotics. However, despite its innovative approach, MYCIN and similar systems like INTERNIST-1 and CASNET did not see widespread use in routine medical practices.
Digital Health Records and Genomic Sequencing

The 1980s and 1990s witnessed significant technological advancements, including the proliferation of microcomputers and enhanced network connectivity. This era recognized the need for AI systems in healthcare to accommodate imperfect data and leverage the expertise of physicians. The growth of genomic sequencing databases and the widespread implementation of electronic health record systems further propelled AI’s integration into healthcare. These digital records provided a treasure trove of data, ripe for AI analysis and interpretation.
AI’s Modern Role and Potential
Today, AI’s capabilities in healthcare extend far beyond basic data analysis. With improvements in natural language processing and computer vision, machines can now replicate human perceptual processes. Robot-assisted surgeries have become more precise, and tree-based machine learning models have introduced flexibility in establishing health predictors.
Moreover, institutions like The Mayo Clinic, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, and the British National Health Service have developed AI algorithms tailored for their specific needs. Large technology companies, including IBM and Google, have also ventured into healthcare AI, further emphasizing its growing importance.
AI in Diagnostics
Diagnostics is a cornerstone of medical practice, ensuring accurate disease identification and subsequent treatment. With the integration of AI, the diagnostic process is undergoing a transformative change, enhancing both its speed and accuracy.
Radiology: Enhancing Image Interpretation
Radiology, the medical specialty focusing on imaging to diagnose and treat diseases, has been one of the primary beneficiaries of AI. Traditional imaging techniques, such as X-rays, MRI, and CT scans, generate vast amounts of data that radiologists must interpret. AI, with its advanced image recognition capabilities, can assist in:
- Detecting abnormalities: AI algorithms can identify tumors, fractures, or other anomalies in medical images with high precision.
- Predictive analytics: Beyond mere detection, AI can predict the progression of diseases like cancer, helping doctors plan treatments more effectively.
- Reducing human error: By providing a second opinion, AI can help radiologists avoid oversight or misinterpretation.
Pathology: Digital Analysis and Disease Detection
Pathology, the study of disease causes and effects, has also seen significant advancements with AI integration. Digital pathology, which involves scanning traditional glass slides to create digital images, can be analyzed using AI for:
- Cellular analysis: AI can identify and count cells, detect cellular structures, and even classify cell types in blood samples.
- Disease classification: Algorithms can differentiate between benign and malignant tumors, classify types of cancer, and even grade the severity of diseases.
- Predictive modeling: AI can predict disease progression based on cellular and molecular data, aiding in treatment planning.
AI’s Role in Early Detection
One of the most promising aspects of AI in diagnostics is its potential for early disease detection. By analyzing subtle patterns and changes in medical data that might be overlooked by human eyes, AI can identify diseases at their nascent stages. Early detection often translates to better patient outcomes, as treatments can be initiated sooner.
Challenges in AI Diagnostics
While the potential of AI in diagnostics is vast, it’s essential to recognize the challenges:
- Data quality: AI’s accuracy is only as good as the data it’s trained on. Inconsistent or low-quality data can lead to incorrect diagnoses.
- Over-reliance: While AI can assist healthcare professionals, it’s crucial that it doesn’t replace human judgment. Doctors and radiologists bring years of experience and intuition that machines cannot replicate.
- Ethical concerns: Patient data privacy and the potential misuse of AI tools are significant concerns that need addressing.
AI in Treatment Protocols
The integration of AI into treatment protocols is reshaping the way healthcare professionals approach patient care. By leveraging the power of data-driven insights, AI offers a more personalized and efficient treatment pathway for patients.
Personalized Medicine: Tailoring Treatments to Individual Genetic Profiles
The concept of personalized medicine revolves around tailoring medical treatments to individual patient needs. AI plays a pivotal role in this by:
- Genomic Analysis: By analyzing a patient’s genetic makeup, AI can identify potential genetic mutations or susceptibilities to certain diseases. This information can guide healthcare professionals in selecting treatments that are more likely to be effective for the specific patient.
- Treatment Recommendations: AI algorithms can sift through vast medical databases to recommend treatments that have shown the best outcomes for patients with similar genetic profiles and medical histories.
Robot-Assisted Surgeries: Precision and Efficiency

Robot-assisted surgeries, where surgeons use robotic systems to aid in surgical procedures, have gained significant traction in recent years. AI enhances these systems by:
- Enhanced Precision: AI algorithms can analyze surgical data in real-time, guiding surgeons with pinpoint accuracy and reducing the risk of human error.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: With AI’s guidance, surgeons can perform procedures with smaller incisions, leading to quicker recovery times and reduced hospital stays.
- Post-operative Monitoring: Post-surgery, AI can monitor patients for any signs of complications, ensuring timely interventions if needed.
Predictive Analysis in Treatment
Predictive analysis, powered by AI, can forecast patient responses to treatments. This is particularly valuable in:
- Treatment Optimization: By predicting how a patient will respond to a particular treatment, healthcare professionals can adjust dosages or switch to alternative treatments if necessary.
- Risk Assessment: AI can predict potential risks or complications associated with treatments, allowing for preemptive measures.
Challenges in AI Treatment Protocols
While AI offers numerous advantages in treatment protocols, there are challenges to consider:
- Interpreting AI Recommendations: Healthcare professionals must be trained to interpret and act on AI recommendations, ensuring they align with the patient’s best interests.
- Ethical Dilemmas: Decisions about a patient’s treatment should always prioritize the patient’s well-being. Relying solely on AI might lead to situations where the most cost-effective treatment is chosen over the most effective one.
- Technical Limitations: AI is only as good as the data it’s trained on. Inaccurate or biased data can lead to suboptimal treatment recommendations.
Monitoring and Patient Care
The realm of patient monitoring and care has always been a critical component of healthcare. With the advent of AI, there’s a paradigm shift in how patients are monitored and cared for, both within medical facilities and in their homes.
Wearable Devices: Continuous Health Monitoring
The rise of wearable technology, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, has opened a new frontier for health monitoring. These devices, when integrated with AI, can:
- Real-time Data Analysis: Continuously monitor vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels, providing instant feedback to users.
- Anomaly Detection: AI can detect irregular patterns or anomalies in the data, alerting users and healthcare professionals to potential health issues.
- Lifestyle Recommendations: Based on the data collected, AI can suggest lifestyle changes, such as increased physical activity or dietary adjustments, to improve overall health.
Telemedicine: Remote Patient Care and AI-enhanced Consultations

Telemedicine, the practice of caring for patients remotely, has seen a surge, especially in the wake of global health crises. AI enhances telemedicine by:
- Virtual Health Assistants: AI-driven chatbots or virtual assistants can answer patient queries, schedule appointments, and even provide basic medical advice.
- Remote Monitoring: For patients with chronic conditions, AI can analyze data from wearable devices and provide feedback, reducing the need for frequent in-person visits.
- Diagnostic Support: AI can assist doctors during virtual consultations by analyzing patient data in real-time and suggesting potential diagnoses or treatments.
Predictive Care and Hospital Admissions
Hospitals and healthcare facilities can leverage AI to predict patient admissions, optimizing bed management and resource allocation. By analyzing factors like local disease outbreaks, weather patterns, and historical admission data, AI can forecast patient inflow, helping hospitals prepare in advance.
Challenges in AI Monitoring and Patient Care
Despite the advantages, there are challenges to consider:
- Data Privacy: With continuous monitoring, there’s a vast amount of personal health data being generated. Ensuring this data remains private and secure is paramount.
- Over-reliance on Technology: While AI can provide valuable insights, it’s essential for patients and healthcare professionals not to become overly reliant on it, overlooking human intuition and expertise.
- Accessibility: Ensuring that AI-driven monitoring and care solutions are accessible to all, regardless of socio-economic status, is crucial to avoid healthcare disparities.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
As with any transformative technology, the integration of AI into healthcare brings forth a myriad of challenges and ethical considerations. While the potential benefits are vast, it’s crucial to address these concerns to ensure the responsible and effective use of AI in medical practices.
Data Privacy Concerns
- Patient Confidentiality: With AI systems analyzing vast amounts of patient data, there’s a heightened risk of breaches, potentially compromising patient confidentiality.
- Data Misuse: There’s a potential for misuse of patient data, either for unauthorized research or commercial purposes, which can infringe on patient rights.
Representation Biases in AI Algorithms
- Training Data Biases: If AI algorithms are trained on data that lacks diversity, they might perform poorly for underrepresented groups. This can lead to misdiagnoses or ineffective treatment recommendations.
- Ethical Implications: Biased algorithms can exacerbate existing healthcare disparities, leading to unequal care quality for different demographic groups.
The Balance Between Automation and Human Touch
- Over-reliance on AI: There’s a risk that healthcare professionals might overly rely on AI recommendations, sidelining their expertise and intuition.
- Loss of Human Interaction: In areas like telemedicine, while AI can enhance efficiency, it’s essential to ensure that patients still receive the human interaction and empathy that’s integral to healthcare.
Transparency and Accountability
- Black Box Dilemma: Many advanced AI algorithms, especially deep learning models, are often seen as “black boxes,” where their decision-making processes are not transparent. This can pose challenges in understanding and justifying medical decisions made by AI.
- Accountability: In cases of misdiagnoses or treatment errors stemming from AI recommendations, determining accountability can be complex. Is it the algorithm, the data, the healthcare professional, or the institution at fault?
Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
- Standardization: As AI systems become more prevalent in healthcare, there’s a need for standardized guidelines and best practices to ensure their safe and effective use.
- Continuous Monitoring: AI models, once deployed, need continuous monitoring and updating to reflect the latest medical knowledge and data.
The Future of AI in Healthcare
As we look ahead, the horizon of AI in healthcare is brimming with possibilities. The advancements we’ve witnessed so far are just the tip of the iceberg, with the future promising even more groundbreaking innovations and applications.
Predictive Modeling for Disease Outbreaks
- Epidemic Forecasting: AI can analyze vast datasets, from travel patterns to climate data, to predict potential disease outbreaks, enabling timely interventions and resource allocation.
- Personal Health Forecasts: Beyond large-scale outbreaks, AI can also predict individual health risks based on genetic, behavioral, and environmental factors.
Enhancing Drug Interactions and Discovery
- Rapid Drug Development: Traditional drug discovery processes are time-consuming and expensive. AI can accelerate this by analyzing complex biochemical interactions, leading to faster and more cost-effective drug development.
- Personalized Drug Interactions: AI can predict how individuals might react to specific drugs based on their genetic makeup, ensuring safer and more effective medication use.
The Role of AI in Global Health Crises
- Resource Allocation: In situations like global pandemics, AI can assist in optimizing the allocation of medical resources, from ventilators to hospital beds.
- Real-time Data Analysis: AI can provide real-time insights into disease spread, mortality rates, and recovery patterns, aiding in timely decision-making during health crises.
Integrating AI with Other Technologies
- AI and IoT: The integration of AI with the Internet of Things (IoT) can lead to smarter medical devices, from wearable health monitors to intelligent hospital equipment.
- Augmented Reality (AR) in Surgery: Combining AI with AR can provide surgeons with enhanced visuals during procedures, overlaying critical data onto the surgical field.
Conclusion
The future of AI in healthcare paints a picture of a world where medical practices are more efficient, personalized, and proactive. As we stand on the cusp of this new era, it’s crucial to approach it with a balanced perspective, embracing the innovations while addressing the challenges. The road ahead is filled with potential, and with collaboration, research, and ethical considerations, AI is set to redefine the very fabric of healthcare.


Leave a Reply