How to Set Up a VPN on Various Devices
In today’s digital age, where data breaches and privacy concerns are rampant, securing your online activities has never been more crucial. One of the most effective tools to enhance your online security and privacy is a Virtual Private Network, commonly known as a VPN. But what exactly is a VPN, and how does it bolster your online safety? Let’s dive in.
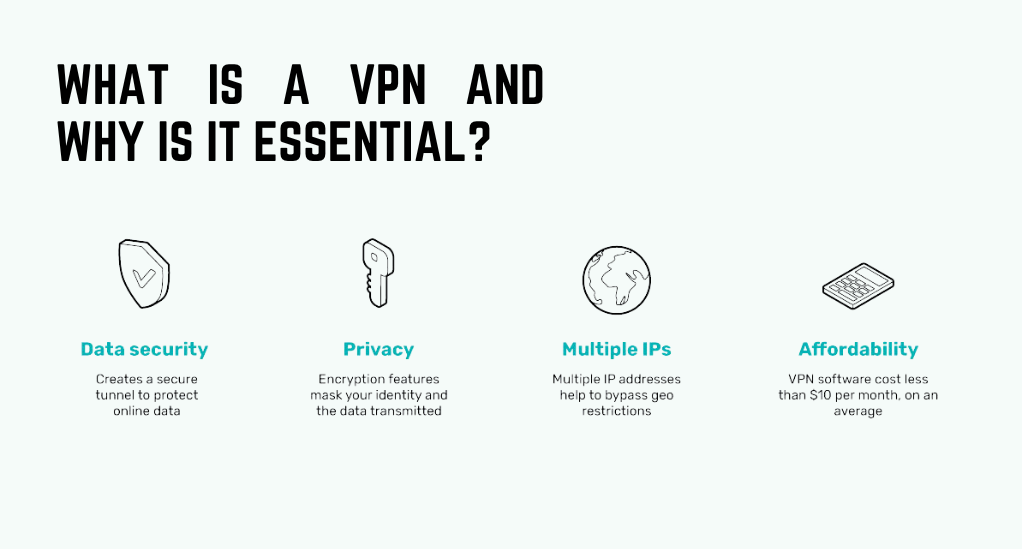
What is a VPN and why is it essential?
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a technology that creates a secure and encrypted connection over a less secure network, such as the internet. Think of it as a secure tunnel between your device and the internet. This tunnel ensures that all data passing through it remains confidential, making it difficult for hackers, advertisers, or even your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to monitor or intercept your online activities.
| VPN Components | Function |
|---|---|
| Encryption | Scrambles data to make it unreadable without the correct decryption key. |
| Server Location | VPN servers located worldwide allow users to appear as if they’re browsing from a different location. |
| IP Masking | Hides your real IP address, making your online actions virtually untraceable. |
The essence of a VPN is not just about masking your IP or changing your server location. It’s about ensuring that your personal data, like your browsing history, login credentials, or online transactions, remains private. In an era where personal data is a valuable commodity, a VPN acts as your personal guard, ensuring your information remains in safe hands.
The underlying technology behind VPNs
At its core, a VPN relies on encryption protocols to secure data transmission. When you connect to a VPN server, your device communicates using these protocols, ensuring that the data packets sent and received are encrypted and secure. Common protocols include OpenVPN, L2TP/IPsec, and PPTP, each offering varying levels of security and speed.
Another crucial aspect is the VPN server network. Reputable VPN providers have servers across the globe, allowing users to connect from virtually anywhere. This global network not only provides users with the ability to bypass geo-restrictions but also ensures a faster and more reliable connection.
The Primary Uses of a VPN
As we’ve established the foundational understanding of what a VPN is, it’s equally essential to comprehend why one might need it. VPNs have a multitude of applications, ranging from personal to professional. Let’s explore some of the primary uses of a VPN.
Bypassing Geographic Restrictions
Have you ever tried to watch a video or access content online, only to be met with the message, “This content is not available in your region?” This is a result of geo-restrictions, where certain content is limited to specific geographic locations. VPNs can be a game-changer in such scenarios.
By connecting to a VPN server located in a region where the content is accessible, you can effectively “trick” the website into thinking you’re browsing from that location. This allows you to access region-restricted content, be it movies, TV shows, news, or even specific websites, from anywhere in the world.
Ensuring Privacy on Public Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi networks, like those in coffee shops, airports, or hotels, are notoriously insecure. While they offer the convenience of connectivity on the go, they are also breeding grounds for cybercriminals. These networks are often unencrypted, making it easy for hackers to intercept data being transmitted over the network.
When you connect to a VPN while on public Wi-Fi, your data is encrypted, making it nearly impossible for cybercriminals to decipher. This ensures that your personal information, such as passwords, credit card details, and emails, remains safe from prying eyes.
Hiding Your Online Identity and Activities
In an age of targeted advertising and data brokers, maintaining online anonymity has become increasingly challenging. Every click, search, and website visit is often tracked, analyzed, and sold to the highest bidder.
A VPN provides a cloak of invisibility online. By masking your real IP address and routing your traffic through a secure server, your online actions become virtually untraceable. This not only prevents websites and advertisers from building a detailed profile about you but also ensures that your online habits remain private.
How Does a VPN Function?
Having understood the importance and primary uses of a VPN, it’s crucial to delve deeper into its workings. A VPN might seem like a complex tool, but its core functionality is based on simple principles of encryption and routing.
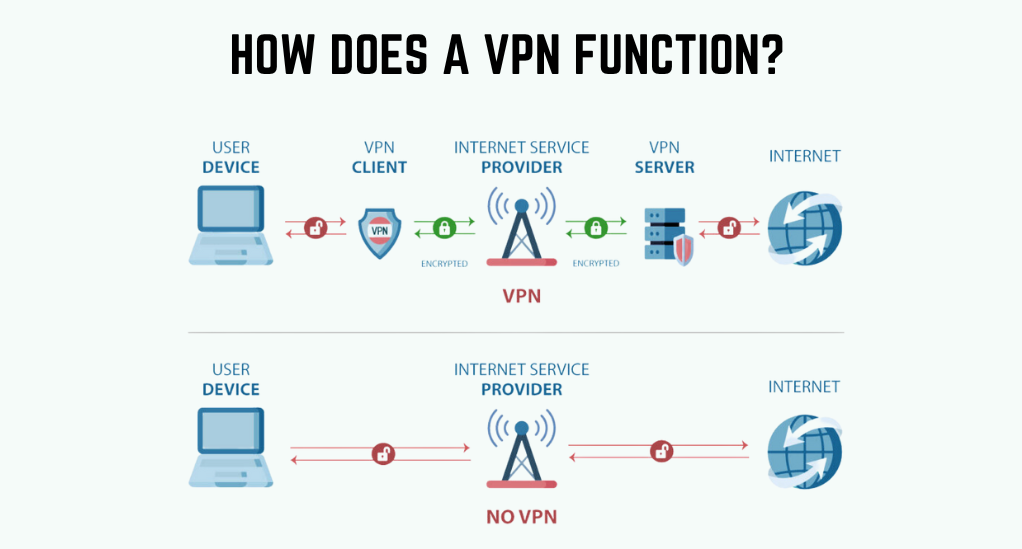
The Process of Encryption and Routing
When you connect to a VPN, your device establishes a secure connection to a VPN server. This connection is encrypted, meaning that all the data you send and receive is scrambled, rendering it unreadable to anyone who might intercept it.
- Initiation: Once you decide to use a VPN, the software on your device (often called a VPN client) initiates a connection request to the VPN server.
- Handshake: The VPN client and server then perform what’s known as a “handshake.” This process involves verifying each other’s identity and agreeing on encryption protocols and keys to use during the session.
- Encryption: Post-handshake, any data sent from your device is encrypted using the agreed-upon encryption key. This encrypted data is then sent through a secure “tunnel” to the VPN server.
- Decryption and Routing: Upon reaching the VPN server, the encrypted data is decrypted. The server then routes this data to the intended online destination, be it a website, online service, or another server.
- Response: When the online destination sends data back, the VPN server encrypts it and sends it through the secure tunnel back to your device. Your VPN client then decrypts the data, allowing you to see and interact with it.
How VPNs Disguise Your Online Presence
One of the standout features of a VPN is its ability to mask your IP address. But how does it achieve this?
When you connect to a VPN server, it assigns you a new IP address, typically based on its location. To the online world, it appears as though you’re browsing from the location of the VPN server, not your actual location. This IP masking not only allows you to bypass geo-restrictions but also adds an additional layer of anonymity to your online activities.
Setting Up a VPN on Windows
Windows, being one of the most widely used operating systems globally, offers both native and third-party solutions for VPN connectivity. Whether you’re using a VPN service’s application or opting for a manual setup, the process is relatively straightforward.
Using a VPN Service’s Application
Most reputable VPN providers offer dedicated applications for Windows, simplifying the setup process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Choose a VPN Service: Research and select a VPN service that best fits your needs. Consider factors like server locations, speed, security protocols, and user reviews.
- Download and Install: Visit the VPN service’s official website and download the Windows application. Follow the installation prompts to set up the software on your system.
- Login and Connect: Launch the VPN application and sign in using your credentials. Once logged in, select a server location and click on the ‘Connect’ button.
- Verify Connection: Ensure that your connection is secure. Most VPN applications will display a connected status, and you can also check your IP address online to confirm it’s changed.
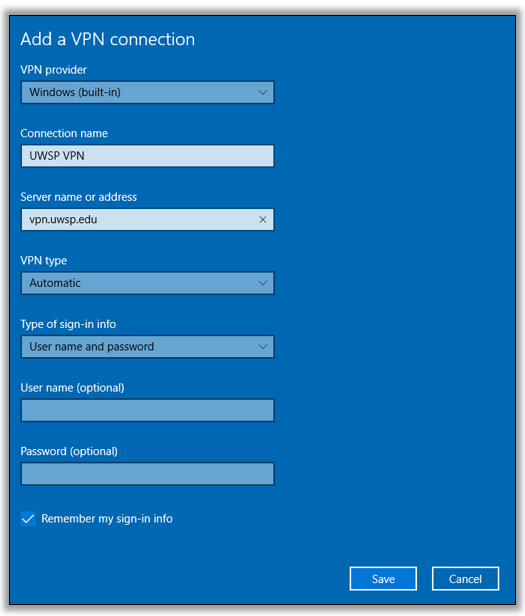
Manual Configuration and Connection
For those who prefer a hands-on approach or are using a VPN service without a dedicated application, Windows offers native VPN support:
- Open Settings: Click on the Windows icon, select ‘Settings’, then choose ‘Network & Internet’.
- VPN Settings: Navigate to the ‘VPN’ section and click on ‘Add a VPN connection’.
- Enter Details: Fill in the required fields:
- VPN Provider: Choose ‘Windows (built-in)’.
- Connection Name: Assign a name for your VPN connection.
- Server Name or Address: Enter the server address provided by your VPN service.
- VPN Type: Select the protocol recommended by your VPN service (e.g., L2TP/IPsec, OpenVPN).
- Type of Sign-in Info: Choose the authentication method (usually ‘Username and password’) and enter your VPN credentials.
- Connect: Once configured, go back to the ‘VPN’ section in ‘Network & Internet’ settings, select your VPN connection, and click ‘Connect’.
- Verify Connection: Open your web browser and search for “What is my IP” to ensure your IP address reflects the VPN server’s location.
Using a VPN on iPhone
Apple’s iPhone, with its robust security features, further benefits from the added protection of a VPN. Whether you’re safeguarding your data on public Wi-Fi or accessing geo-restricted content, setting up a VPN on an iPhone is a breeze.
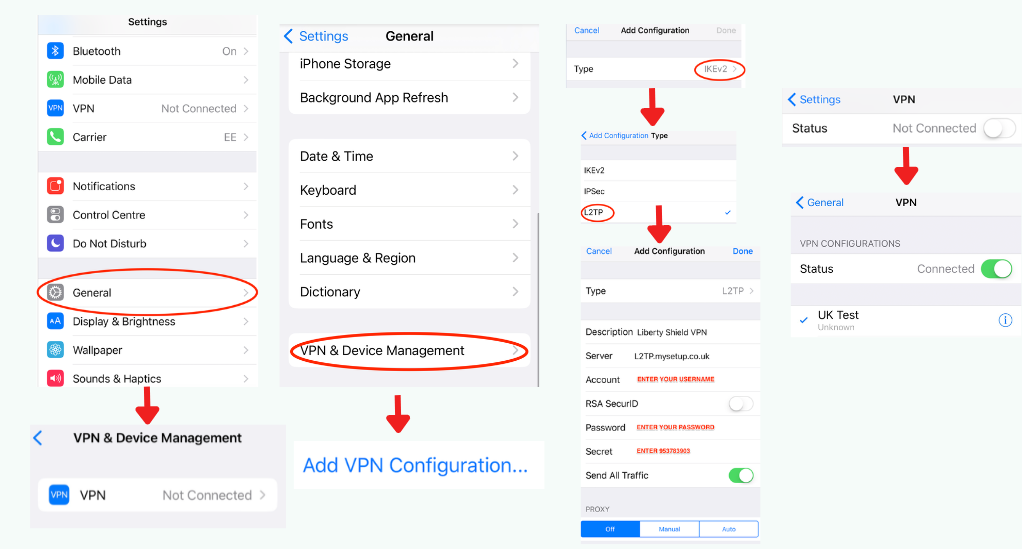
Installing and Configuring through an App
Most leading VPN providers offer dedicated iOS apps available on the App Store, making the setup process straightforward:
- Select a VPN Service: Research and choose a VPN service that aligns with your requirements, considering factors such as server availability, speed, and user reviews.
- Download the App: Open the App Store on your iPhone, search for the chosen VPN service, and download the app.
- Setup and Login: Launch the VPN app and sign in using your credentials. If it’s your first time, some apps might guide you through a brief setup process.
- Choose a Server and Connect: Browse through the list of available servers or let the app select the optimal one for you. Tap ‘Connect’ to initiate the VPN connection.
- Ensure Connectivity: Most apps will display a ‘Connected’ status. Additionally, you can swipe into your iPhone’s Control Center to see a VPN icon, indicating an active connection.
Manual Setup and Activation
For users who prefer manual configurations or if a dedicated app isn’t available, the iPhone supports native VPN settings:
- Open Settings: On your iPhone, tap on the ‘Settings’ icon and scroll down to ‘General’.
- Navigate to VPN: In the ‘General’ menu, find and select the ‘VPN’ option.
- Add VPN Configuration: Tap on ‘Add VPN Configuration…’ and fill in the necessary details:
- Type: Choose the protocol as suggested by your VPN provider (e.g., L2TP, IKEv2).
- Description: Provide a name for this VPN connection.
- Server: Enter the server address given by your VPN service.
- Account: Your VPN username.
- Password & Secret: Enter the password and (if required) the secret key provided by your VPN service.
- Activate VPN: Once configured, head back to the main ‘VPN’ screen, select your VPN configuration, and toggle the switch to ‘On’.
- Verify Your Connection: Launch Safari and search for “What is my IP” to confirm that your IP address matches the VPN server’s location.
Setting Up a VPN on Android
Android, the world’s most popular mobile operating system, offers vast flexibility and customization options. This adaptability extends to VPNs, allowing users to choose between dedicated apps or manual configurations for their devices.
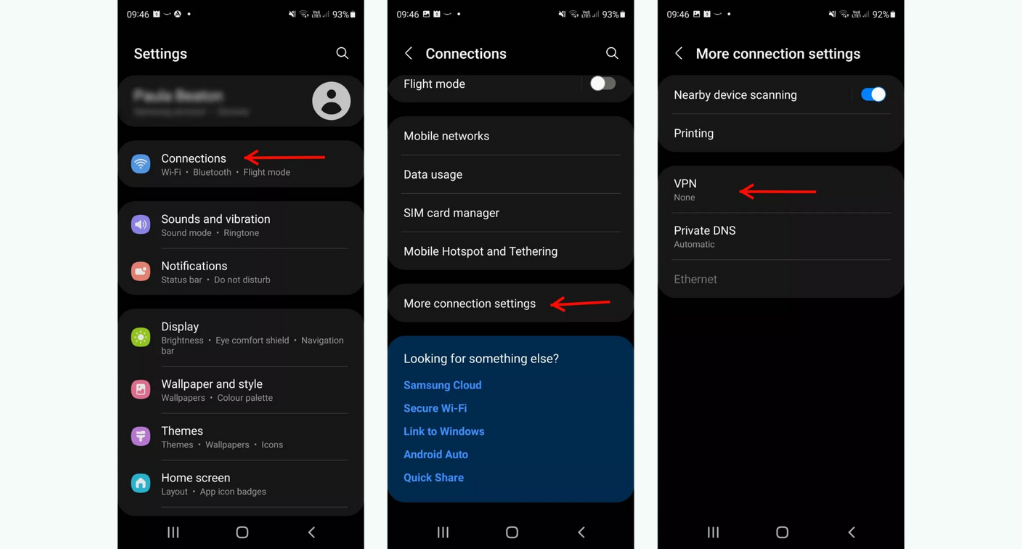
Navigating the Settings for VPN Activation
Most top-tier VPN providers have dedicated apps available on the Google Play Store, streamlining the setup process for Android users:
- Pick a VPN Service: Start by researching and selecting a VPN service that meets your needs, taking into account factors like server diversity, speed, and user feedback.
- Download the App: Open the Google Play Store on your Android device, search for your chosen VPN service, and install the app.
- Setup and Sign In: Once installed, open the VPN app. You’ll typically be prompted to sign in using your account credentials. Some apps might also guide you through a brief setup or tutorial phase.
- Select a Server and Connect: Browse the available servers or use the app’s recommendation for the best connection. Tap ‘Connect’ to initiate the VPN.
- Confirm Your Connection: Most VPN apps will show a ‘Connected’ status once the VPN is active. Additionally, you’ll notice a key or VPN icon in your device’s notification bar, indicating a secure connection.
The Difference Between App-Based and Manual Setup
While using a dedicated app is the most straightforward method, Android also supports manual VPN configurations:
- Access Settings: On your Android device, open the ‘Settings’ app and navigate to ‘Network & Internet’.
- VPN Options: Within ‘Network & Internet’, find and select the ‘VPN’ option.
- Add VPN Profile: Tap on the ‘+’ icon or ‘Add VPN’ (varies by device) and provide the necessary details:
- Name: Assign a name for this VPN profile.
- Type: Select the protocol recommended by your VPN provider (e.g., PPTP, L2TP/IPsec).
- Server Address: Input the server address provided by your VPN service.
- Username & Password: Enter your VPN credentials.
- Connect: After setting up the profile, tap on its name and enter your credentials to connect.
- Check Your Connection: Open a browser and search for “What is my IP” to ensure your IP address corresponds to the VPN server’s location.
Choosing the Right VPN Service
With the myriad of VPN services available in the market, selecting the right one can be a daunting task. However, understanding your specific needs and being aware of certain key factors can guide you towards making an informed decision.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a VPN
- Security Protocols: Ensure the VPN service supports robust encryption protocols like OpenVPN or L2TP/IPsec. These protocols determine how your data is encrypted and transmitted, playing a pivotal role in your online security.
- Server Locations: A vast server network spread across multiple countries allows for better speed, reliability, and the ability to bypass geo-restrictions.
- Speed and Bandwidth: A good VPN shouldn’t significantly slow down your internet connection. Opt for services that offer unlimited bandwidth and high-speed servers.
- Privacy Policies: Scrutinize the VPN provider’s logging policy. Ideally, they shouldn’t keep logs of your online activities, ensuring complete anonymity.
- Platform Compatibility: Ensure the VPN service offers applications or support for all the devices you intend to use, be it Windows, Android, iPhone, or even routers.
- Customer Support: Reliable customer support can be a lifesaver, especially if you encounter any issues or need assistance with setup.
- Price: While free VPNs might be tempting, they often come with limitations and potential security risks. Compare prices, but remember that with VPNs, you often get what you pay for.
Recommendations for Reliable VPN Services
While individual needs may vary, here are some universally acclaimed VPN services known for their reliability, security, and performance:
- ExpressVPN: Renowned for its speed and robust security features, ExpressVPN offers a vast server network spanning 94 countries.
- NordVPN: With a strong emphasis on privacy and a no-logs policy, NordVPN is a favorite among security enthusiasts.
- CyberGhost: User-friendly and with a vast server network, CyberGhost is ideal for those new to VPNs.
- Private Internet Access (PIA): Known for its commitment to privacy, PIA offers advanced configuration options for tech-savvy users.
- Surfshark: A newer entrant in the market, Surfshark has quickly gained a reputation for its speed, security, and budget-friendly pricing.
Conclusion
In an age where our digital footprints are constantly monitored, analyzed, and often exploited, VPNs have emerged as a beacon of hope, offering a sanctuary of privacy and security. They have transitioned from being a tool for tech enthusiasts to an essential utility for the everyday internet user. As we move forward, the evolution of VPN technology will undoubtedly continue to align with the ever-growing demand for online anonymity and freedom. It’s imperative for users to stay informed, make conscious choices, and prioritize their digital well-being, ensuring that their online experiences remain both enriching and secure.


Leave a Reply