
How to Improve Your Laptop’s Wi-Fi Connectivity
In today’s digital age, a robust Wi-Fi connection is more than just a luxury—it’s a necessity. Whether you’re attending a virtual meeting, streaming your favorite show, or working on a critical project, a stable and fast Wi-Fi connection can make all the difference. Laptops, being one of the most commonly used devices for both work and leisure, heavily rely on Wi-Fi for most of their tasks.
However, many users often find themselves grappling with inconsistent signals, slow speeds, or intermittent disconnections. This article aims to shed light on the importance of a strong Wi-Fi connection for laptops and the common challenges faced by users. By understanding these challenges, you’ll be better equipped to address them and enjoy a seamless online experience.
The Importance of a Strong Wi-Fi Connection for Laptops
Laptops are designed for mobility, allowing users to work, study, or entertain themselves from virtually anywhere. This mobility, however, is only as good as the Wi-Fi connection supporting it. Here’s why a strong Wi-Fi connection is crucial for laptop users:
- Productivity: For professionals and students alike, a stable Wi-Fi connection ensures that online tasks, whether it’s a video conference, research, or cloud-based work, are completed without interruptions.
- Entertainment: Streaming platforms like Netflix, YouTube, and Spotify rely on a consistent Wi-Fi connection to deliver high-quality content without buffering.
- Software Updates: Regular updates for your operating system and applications are vital for security and performance. A strong Wi-Fi connection ensures these updates are downloaded and installed promptly.
Common Challenges Faced by Users
While the need for a robust Wi-Fi connection is clear, achieving it isn’t always straightforward. Here are some common challenges faced by laptop users:
- Physical Barriers: Walls, floors, and other obstacles can weaken the Wi-Fi signal, especially if the router is placed in a corner or a closed cabinet.
- Distance from the Router: The further your laptop is from the router, the weaker the signal becomes. This is particularly true for larger homes or offices.
- Interference: Other electronic devices, such as microwaves, cordless phones, and even neighboring Wi-Fi networks, can interfere with your Wi-Fi signal.
- Outdated Hardware: Using an old router or a laptop with an outdated Wi-Fi card can significantly hamper your connection quality.
Understanding Wi-Fi Signal Strength
Before diving into solutions, it’s essential to grasp the concept of Wi-Fi signal strength and how it impacts your laptop’s connectivity. Wi-Fi signal strength is a measure of how powerful the connection between your device and the router is. A stronger signal typically translates to faster speeds, more reliable connections, and better overall performance.
What is Wi-Fi Signal Strength?
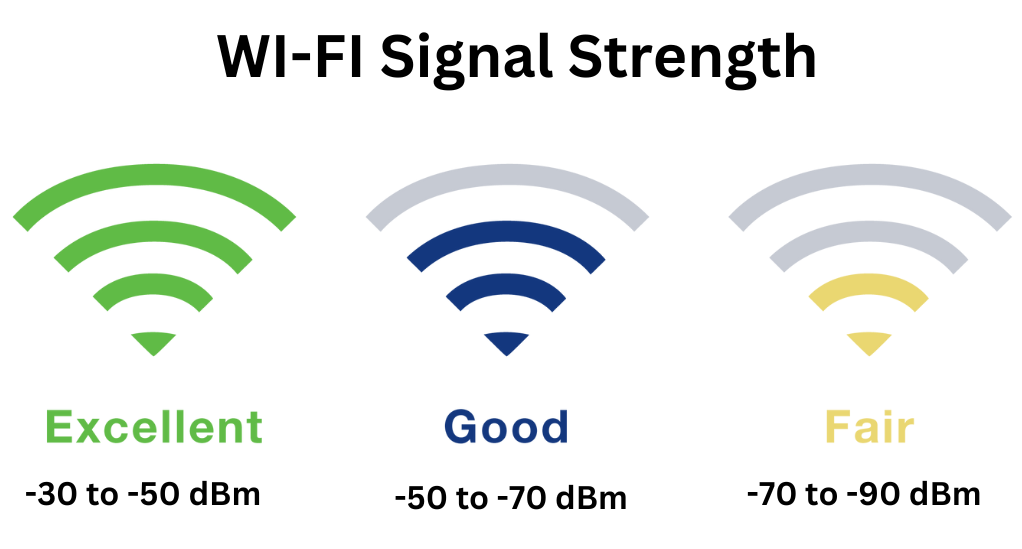
Wi-Fi signal strength is often measured in decibels relative to a milliwatt, or dBm for short. The scale usually ranges from -30 dBm (extremely strong signal) to -90 dBm (barely detectable). Here’s a general breakdown:
- -30 to -50 dBm: Excellent signal strength. Ideal for any online activity, including HD streaming and online gaming.
- -50 to -70 dBm: Good signal strength. Suitable for most online activities, though you might experience minor issues in high-demand tasks.
- -70 to -90 dBm: Poor to very weak signal strength. You’re likely to face connectivity issues, slow speeds, and frequent disconnections.
Tools to Measure Wi-Fi Signal Strength on Your Laptop
To get a clear picture of your current Wi-Fi signal strength, several tools and software can help:
- Built-in Operating System Tools: Both Windows and macOS have built-in utilities that display your current Wi-Fi signal strength. On Windows, hover over the Wi-Fi icon in the system tray. On macOS, hold the Option key and click the Wi-Fi icon in the menu bar.
- Wi-Fi Analyzer Apps: These are specialized apps available for both desktop and mobile platforms. Examples include “Wi-Fi Analyzer” for Windows and “NetSpot” for macOS. They provide a visual representation of your Wi-Fi environment, helping you identify weak spots and interference sources.
- Online Speed Tests: Websites like Speedtest.net and Fast.com can give you an idea of your current internet speeds, which can indirectly indicate your Wi-Fi signal strength.
By regularly monitoring your Wi-Fi signal strength, you can proactively address issues before they escalate, ensuring a consistently strong and reliable connection.
Positioning Your Router Optimally
One of the most straightforward yet often overlooked methods to improve Wi-Fi connectivity is the strategic placement of the router. The router’s position can significantly influence the strength and stability of the Wi-Fi signal it emits. By understanding and addressing the factors that affect signal distribution, you can optimize your Wi-Fi coverage.
The Role of Physical Barriers in Signal Degradation
Physical barriers, such as walls, doors, and furniture, can obstruct and weaken the Wi-Fi signal. Different materials have varying effects on signal strength:
- Brick and Concrete: These materials are among the most challenging for Wi-Fi signals to penetrate, leading to significant signal loss.
- Wood and Glass: While these materials do cause some signal degradation, they are generally more Wi-Fi friendly than brick or concrete.
- Metal: Objects like metal shelves or filing cabinets can reflect Wi-Fi signals, causing interference and “dead zones.”
Understanding the materials in your home or office can help you make informed decisions about where to place your router.
Best Places to Position Your Router
To ensure optimal Wi-Fi coverage, consider the following guidelines when positioning your router:
- Central Location: Placing the router in a central location in your home or office ensures even distribution of the Wi-Fi signal. This reduces the distance the signal has to travel, providing a stronger connection to devices throughout the space.
- Elevated Position: Wi-Fi signals spread out and down from their source. Positioning the router on a high shelf or mounting it on a wall can help the signal cover a larger area.
- Away from Other Electronics: Devices like cordless phones, microwaves, and baby monitors operate on frequencies similar to Wi-Fi and can cause interference. Keep the router away from such devices to minimize disruptions.
- Open Spaces: Avoid placing the router inside cabinets or closets. An open space allows the signal to spread without obstructions.
- Antenna Adjustments: If your router has external antennas, adjust them for better coverage. A vertical orientation is generally best for spreading the signal horizontally across a single floor, while a horizontal orientation can help with multi-floor coverage.
Upgrading Your Router’s Firmware
Just like any other piece of technology, your router runs on software, commonly referred to as firmware. This software is responsible for all the functionalities of the router, from managing your network settings to ensuring security protocols are up-to-date. Periodically updating your router’s firmware can lead to improved performance, added features, and enhanced security.
Why Keeping Your Router Updated Matters

- Performance Enhancements: Manufacturers often release updates that optimize the router’s performance, ensuring faster and more stable connections.
- Security Patches: With the increasing threats of cyber-attacks, it’s crucial to have the latest security patches. Outdated firmware can leave your network vulnerable to intrusions and malware.
- Bug Fixes: Like any software, router firmware can have bugs. Updates often include fixes for known issues, ensuring smoother operation.
- New Features: Firmware updates can introduce new features or improvements to existing ones, enhancing the overall user experience.
Steps to Check and Update Router Firmware
- Access the Router’s Web Interface: This is typically done by entering the router’s IP address into a web browser. Common addresses include
192.168.1.1or192.168.0.1. You’ll need to log in, so have your credentials ready (often “admin” for both username and password by default, but it’s recommended to change these for security reasons). - Navigate to the Firmware or Update Section: The exact name and location vary by manufacturer, but it’s usually found under “System,” “Maintenance,” or “Advanced” tabs.
- Check for Updates: There should be an option to check for or download the latest firmware. If an update is available, there will typically be instructions guiding you through the process.
- Download and Install: If an update is available, download it and follow the on-screen instructions to install. Ensure that the router remains powered on during the entire process to avoid any potential issues.
- Reboot if Necessary: Some updates may require a reboot to take effect. If prompted, restart your router.
Note: Always back up your router’s settings before updating the firmware. This ensures you can restore them in case of any issues.
Using Wi-Fi Extenders and Mesh Networks
Even with optimal router positioning and updated firmware, there might still be areas in your home or office where the Wi-Fi signal is weak or non-existent. These areas, often referred to as “dead zones,” can be a significant hindrance, especially in larger spaces or multi-story buildings. This is where Wi-Fi extenders and mesh networks come into play.
What are Wi-Fi Extenders and How Do They Work?
Wi-Fi extenders, also known as Wi-Fi boosters or repeaters, are devices that capture the Wi-Fi signal from your router and rebroadcast it. The primary purpose is to extend the coverage area of your Wi-Fi network, bridging the gap between the router and areas with weak or no signal.
Key Features of Wi-Fi Extenders:
- Extended Coverage: They effectively reduce or eliminate dead zones in your home or office.
- Easy Setup: Most extenders come with a simple plug-and-play setup.
- Compatibility: They generally work with any standard router or gateway.
However, it’s essential to position the extender halfway between the router and the dead zone to capture a strong signal and extend it further.
The Benefits of Mesh Networks for Larger Spaces
Mesh networks offer a more advanced solution to Wi-Fi coverage issues. Unlike traditional routers that broadcast Wi-Fi from a single point, mesh systems use multiple nodes or satellites placed around the space to create a seamless and robust Wi-Fi network.
Advantages of Mesh Networks:
- Seamless Connectivity: Devices automatically connect to the nearest node, ensuring a consistent signal even when moving around.
- Scalability: You can easily add more nodes to expand coverage, making it ideal for large homes or offices.
- Unified Network: Unlike extenders that might create separate network names (SSIDs), mesh systems provide a single network throughout.
- Smart Features: Many mesh systems come with advanced features like parental controls, guest networks, and integrated security.
While mesh networks are generally more expensive than traditional routers and extenders, they offer a superior solution for those looking for the best possible Wi-Fi coverage and performance.
Adjusting Your Laptop’s Wi-Fi Settings
While external factors like router positioning and network extensions play a significant role in Wi-Fi connectivity, the settings on your laptop itself can also influence the quality of your connection. Tweaking certain settings can lead to noticeable improvements in both speed and stability.
Exploring Advanced Settings for Better Connectivity
- Wi-Fi Channel: Just like a radio, Wi-Fi signals operate on different channels. If multiple devices in your vicinity are on the same channel, it can lead to congestion and reduced performance. Access your router’s settings to switch to a less crowded channel.
- Power Management: Some laptops reduce power to the Wi-Fi adapter when running on battery to save energy. Ensure that your Wi-Fi adapter is set to maximum performance, especially when you’re experiencing connectivity issues.
- Update Network Drivers: Outdated or corrupted drivers can hinder your Wi-Fi performance. Regularly check the manufacturer’s website or use your laptop’s update utility to ensure you have the latest drivers installed.
- Disable VPNs and Proxies: While VPNs and proxies offer privacy and security, they can sometimes slow down your connection. If you’re facing speed issues, consider temporarily disabling them to check if they’re the cause.
- Forget and Reconnect: If you’re facing frequent disconnections, forgetting the network and reconnecting can often reset any minor glitches causing the issue.
Tips for Windows 10 and Windows 11 Users
For those using Windows 10 or Windows 11, here are some specific steps to optimize Wi-Fi settings:
- Network Troubleshooter: Use the built-in troubleshooter to diagnose and automatically fix any Wi-Fi issues. Navigate to Settings > Network & Internet > Status and click on Network troubleshooter.
- Reset Network Settings: If you’re facing persistent issues, resetting all network settings can help. Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Status and click on Network reset. Remember, this will erase all saved networks and passwords.
- Wi-Fi Properties: Access the properties of your Wi-Fi connection and ensure that the protocol version is set to “Automatic” or the latest available version (e.g., Wi-Fi 6).
Considering a Wi-Fi Adapter Upgrade
While software tweaks and optimal router placements can significantly improve your Wi-Fi experience, sometimes the hardware itself can be a limiting factor. If you’re using an older laptop or one with a basic Wi-Fi card, you might not be getting the best possible speeds and range. Upgrading your laptop’s Wi-Fi adapter can be a transformative solution.
When and Why You Should Consider an Adapter Upgrade
- Outdated Hardware: If your laptop is several years old, it’s likely equipped with an older Wi-Fi standard, such as 802.11n. Upgrading to a newer standard like 802.11ac or Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) can offer faster speeds and better range.
- Consistent Connectivity Issues: If you’ve tried all other solutions and still face connectivity problems, the Wi-Fi card could be the culprit. A new adapter might resolve these persistent issues.
- Enhanced Features: Modern Wi-Fi adapters come with features like beamforming, which focuses the Wi-Fi signal towards connected devices, and MU-MIMO, which allows the router to communicate with multiple devices simultaneously. These features can significantly enhance your online experience.
- Dual-Band Support: If your current adapter only supports the 2.4GHz band, upgrading to a dual-band adapter can give you access to the less crowded 5GHz band, often resulting in faster speeds.
Top Wi-Fi Adapters in the Market
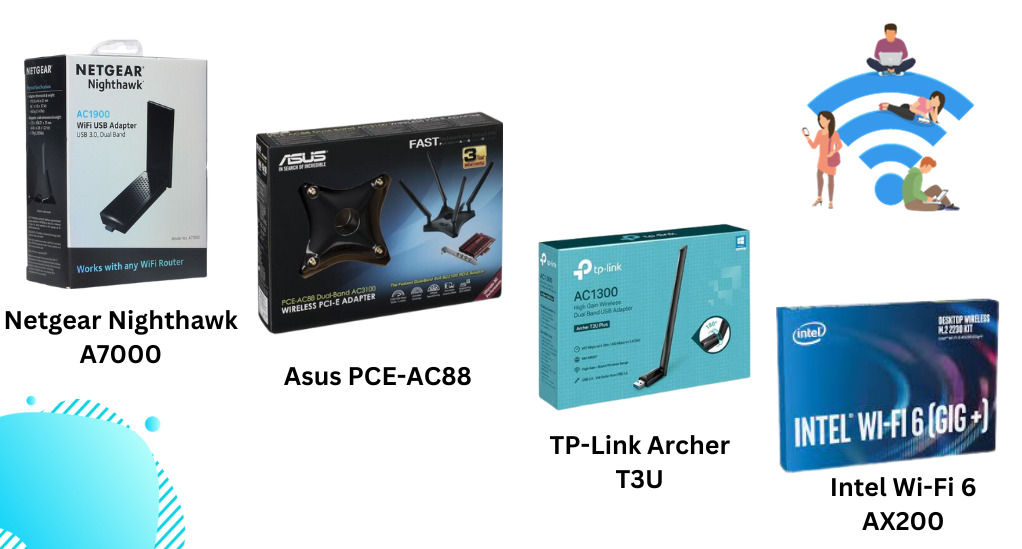

While the best adapter depends on your specific needs and budget, here are some popular options known for their performance and reliability:
- TP-Link Archer T3U: This is a USB Wi-Fi adapter that supports the 802.11ac standard, offering speeds up to 1300Mbps on the 5GHz band.
- Netgear Nighthawk A7000: A high-performance USB adapter with a foldable antenna, it supports both 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands and offers speeds up to 1900Mbps.
- Asus PCE-AC88: For those who prefer internal PCIe cards, this adapter from Asus offers blazing fast speeds up to 2100Mbps on the 5GHz band and comes with external antennas for optimal signal reception.
- Intel Wi-Fi 6 AX200: This internal M.2 card supports the latest Wi-Fi 6 standard, offering faster speeds, increased range, and better performance in crowded areas.
When choosing an adapter, consider factors like compatibility with your laptop, desired speed, range, and any additional features you might need.
Conclusion
In our digital-centric world, a robust Wi-Fi connection is essential for both work and leisure. Throughout this article, we’ve delved into various strategies to optimize your laptop’s Wi-Fi connectivity, from the importance of router positioning and firmware updates to the potential benefits of hardware upgrades. By implementing these tips, users can ensure a seamless online experience, minimizing frustrations like slow speeds and intermittent connections.
As we increasingly rely on digital platforms for our daily tasks, ensuring optimal Wi-Fi connectivity becomes paramount. Whether you’re streaming, gaming, working, or studying, the strategies discussed here set the foundation for a stable and efficient online journey. Here’s to uninterrupted digital adventures and the joys of seamless connectivity!


Leave a Reply