Understanding the OSI Model in Network Communication
The OSI Model, or Open Systems Interconnection Model, is a fundamental concept in the world of computer networking. At its core, this model is a guideline that dictates how data is transferred over a network. It’s like a blueprint for understanding and designing networks that allows different computer systems to communicate efficiently and effectively. Think of it as the universal language for computers to talk to each other.
Brief overview of the OSI Model
In this article, we’re diving into the OSI Model, exploring its significance and how it has become an essential part of modern networking. Although it was developed decades ago, the OSI Model remains relevant today, laying the groundwork for network design and troubleshooting. It’s an indispensable tool for IT professionals, playing a key role in making sure our internet and networks run smoothly.
Importance of OSI in modern networking
Understanding the OSI Model isn’t just for tech experts. It’s useful for anyone interested in how network communication works. Whether you’re a student, an IT professional, or just curious about networking, this article will guide you through the basics of the OSI Model, its seven layers, and why it’s such an integral part of our connected world.
Understanding the OSI Model
The OSI Model is like a map that guides data on its journey through a network. To make it easy to understand, this map is divided into seven distinct layers. Each layer has a specific role in handling, processing, and transmitting data. Let’s break down these layers one by one.
The Conceptual Framework
- Historical Background: Its goal was to make it easier for different types of computer systems to talk to each other.
- The Universal Language for Networking: It ensures that no matter what type of computer or software you are using, they can all communicate effectively.
The Seven Layers Explained
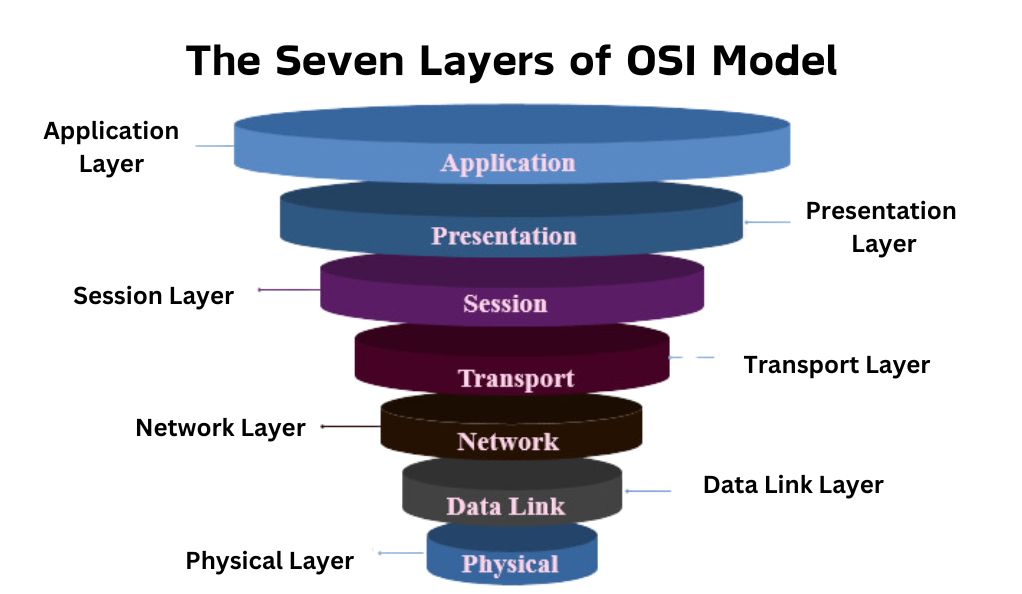
- Layer 1: Physical Layer
- This is all about the physical parts of the network, like cables and switches. It’s like the roads and highways that data travels on.
- Layer 2: Data Link Layer
- Think of this as the layer that makes sure data packets are properly addressed so they reach the right destination.
- Layer 3: Network Layer
- It’s like the traffic controller, ensuring data takes the best route.
- Layer 4: Transport Layer
- This layer is responsible for keeping data transfer stable and reliable. It’s like making sure your data’s journey is smooth, without any bumps.
- Layer 5: Session Layer
- It’s all about communication sessions. Imagine it as setting up and ending phone calls between computers.
- Layer 6: Presentation Layer
- This layer translates data into a format that the application layer can understand. It’s like a translator for data.
- Layer 7: Application Layer
- The top layer where applications access network services. It’s the interface that users and applications interact with.
The OSI Model in Action
When we talk about the OSI Model in action, we are referring to how it is used in real-life scenarios for transmitting data across networks. This process might seem complex, but understanding it can help us appreciate how efficiently our network communications are carried out.
Communication Process
Data Flow through the OSI Layers:

Data Flow through the OSI Layers:
- The journey of data from the sender to the receiver is fascinating. It starts at the top layer (Application Layer) of the sender’s side, moves down through the layers, travels across the network, and then moves up through the layers on the receiver’s side.
- Imagine sending an email. Your email starts at the top layer, where it’s put into a format suitable for transmission.
Real-World Example: Email Transmission Process:
In the process of sending an email, the Application Layer involves composing the message. The Presentation Layer translates it for the network. The Session Layer establishes a connection. The Transport Layer divides the email into manageable parts. The Network Layer finds the best route. The Data Link Layer prepares each part, and the Physical Layer sends data over cables or wireless networks to the recipient.
Troubleshooting and Network Management
- OSI Model’s Role in Identifying and Resolving Network Issues:
- The OSI Model is like a detective’s toolkit for network problems. When there’s an issue, like a website not loading, network professionals use the OSI Model to find out which layer the problem is occurring at. This method helps in quickly identifying and fixing issues.
- Layer-Specific Troubleshooting Techniques:
- For example, if the issue is at the Physical Layer, it could be a problem with cables or hardware. If it’s at the Application Layer, the issue might be with the software or application settings.
OSI Model vs. Internet Protocol Suite
When it comes to networking models, the OSI Model is often compared to the Internet Protocol Suite, commonly known as TCP/IP. While both are critical in the world of networking, they have distinct differences and purposes. Let’s explore how these two models compare and why each is important.
Comparing OSI and TCP/IP models
- OSI Model:
- The OSI Model has seven layers, each with a specific function.
- It’s a conceptual framework used to understand and design network systems.
- TCP/IP Model:
- The TCP/IP Model has four layers: the Network Interface, Internet, Transport, and Application layers.
- It’s more focused on how data is transmitted over the internet.
- Key Differences:
- Number of Layers: OSI has seven layers, while TCP/IP has four.
- Approach: OSI is more theoretical, a guideline for understanding networks. TCP/IP is practical, used for actually transmitting data over the internet.
- Flexibility: OSI is more flexible and comprehensive. TCP/IP is straightforward and widely used for internet communication.
Why OSI is still relevant despite the dominance of TCP/IP
- Even though TCP/IP is the standard for internet communication, the OSI Model is still relevant and useful.
- OSI provides a detailed understanding of how networks should work. It’s like the theory behind networking.
- TCP/IP is the implementation, putting the theory into practice.
- The OSI Model helps in troubleshooting and network design, offering a more granular approach to understanding network interactions.
The Future of Networking with OSI
As we move into the future, the role of the OSI Model in networking continues to evolve. It’s not just a historical concept; it’s a framework that adapts and grows with new technologies. Let’s look at how the OSI Model is shaping the future of networking.
OSI Model in Modern Technologies
- Role in Emerging Network Technologies:
- The OSI Model is crucial in the development of new networking technologies, like 5G and IoT (Internet of Things). It provides a structured approach to developing these technologies, ensuring they are compatible with existing systems.
- In cloud computing, the OSI Model helps in creating and managing cloud-based networks, making sure they are secure and efficient.
- Security Implications and the OSI Model:
- With the rise in cyber threats, understanding the OSI Model is more important than ever.
- For instance, security measures at the Physical Layer include securing cables and hardware, while at the Application Layer, it involves protecting data from malware and unauthorized access.
Challenges and Evolution
- Limitations and Criticisms of the OSI Model:
- One criticism of the OSI Model is that it’s more theoretical than practical. Some argue that it doesn’t perfectly match real-world networking scenarios.
- However, these limitations don’t diminish its value. They highlight the need for continuous evolution and adaptation of the model.
- Potential Developments and Future of OSI in Networking:
- The future of the OSI Model includes integrating it with emerging technologies like AI (Artificial Intelligence) and machine learning to make networks smarter and more efficient.
- There’s also a push towards making the OSI layers more flexible and adaptable to different networking environments and requirements.
Conclusion
The OSI Model, with its seven layers, serves as a fundamental guide for comprehending network communication, simplifying its complexities since the 1980s. It aids in troubleshooting, network design, and adaptation to evolving technologies. Even in today’s digital era, the OSI Model remains an integral part of networking, with enduring relevance for networking professionals, students, and anyone curious about internet workings. Understanding this model is essential for grasping the basics of network communication, making it an invaluable asset.


Leave a Reply