Cost-Efficiency in Cloud Computing: Tips and Strategies
In recent years, the business world has witnessed a paradigm shift from traditional IT setups to cloud-based solutions. This transition is not just a trend but a necessity, driven by the desire to achieve greater efficiency and cost-effectiveness in operations. Before we delve deeper into the strategies to achieve cost-efficiency through cloud computing, it is essential to understand the foundational aspects that make cloud computing a lucrative choice for businesses.
The Importance of Cost-Efficiency in Cloud Computing
In the face of growing competition and evolving market dynamics, businesses are constantly seeking innovative solutions that can enhance operational efficiency while maintaining financial prudence. Cloud computing stands at the forefront of this transformation, offering a plethora of benefits that go beyond mere cost savings.
The essence of cost-efficiency in cloud computing lies in its ability to optimize resource utilization, streamline processes, and minimize waste. It offers a scalable environment where businesses can adapt to changing demands without incurring substantial costs. Moreover, it fosters innovation by providing a platform where new applications can be developed and deployed swiftly, without the need for significant capital investment.
To appreciate the full spectrum of cost-efficiency that cloud computing brings to the table, it is vital to dissect the various components that constitute cloud computing and understand how each contributes to achieving financial prudence.
| Aspect | Traditional IT Setup | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Expenditure | High (Infrastructure, maintenance) | Low (Pay-as-you-go model) |
| Scalability | Limited (Requires substantial investment) | High (Easy to scale up or down) |
| Flexibility | Low (Rigid infrastructure) | High (Customizable solutions) |
| Energy Efficiency | Low (High energy consumption) | High (Optimized resource utilization) |
| Innovation | Limited (Time-consuming deployment) | High (Quick deployment of new applications) |
The Shift from Traditional IT Setups to Cloud-Based Solutions
The transition from traditional IT setups to cloud-based solutions is not just a technological shift, but a strategic move towards sustainable business operations. This shift is characterized by a transition from capital-intensive investments in IT infrastructure to operational expenses that are more manageable and aligned with the business’s growth trajectory.
Understanding the Basics of Cloud Computing
In the journey towards achieving cost-efficiency through cloud computing, the first step is to grasp the fundamental concepts that define this technology. Cloud computing is not just a tool, but a transformative approach to managing and delivering computing services. Let’s dissect the core components of cloud computing and understand how each facet contributes to a more cost-efficient business operation.
Definition and Core Components of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of various services over the internet, including storage, databases, servers, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence. These services are designed to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. Typically, you only pay for the cloud services you use, helping to lower operating costs, run your infrastructure more efficiently, and scale as your business needs change.
The Transition from CapEx to OpEx Models
One of the most significant shifts that cloud computing brings to a business is the transition from Capital Expenditure (CapEx) to Operating Expense (OpEx) models.
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx)
In the traditional IT setup, businesses incur substantial costs in acquiring and managing IT hardware and software. These capital expenditures are often high and come with the added burden of maintenance and upgrades.
- Operating Expense (OpEx)
On the other hand, cloud computing operates on an OpEx model, where businesses can leverage high-end IT services without the upfront costs. The pay-as-you-go pricing structure allows for greater flexibility and scalability, enabling businesses to adapt swiftly to changing market dynamics without a significant financial burden.
Benefits of the OpEx Model
- Cost-Efficiency: Businesses only pay for the services they use, avoiding the sunk costs associated with unused or underutilized resources.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Companies can easily scale their operations up or down based on demand, without the need for substantial investment in infrastructure.
- Faster Deployment: Cloud services allow for quick deployment of applications, reducing the time-to-market and enabling businesses to respond swiftly to market opportunities.
Key Cost-Saving Benefits of Cloud Models
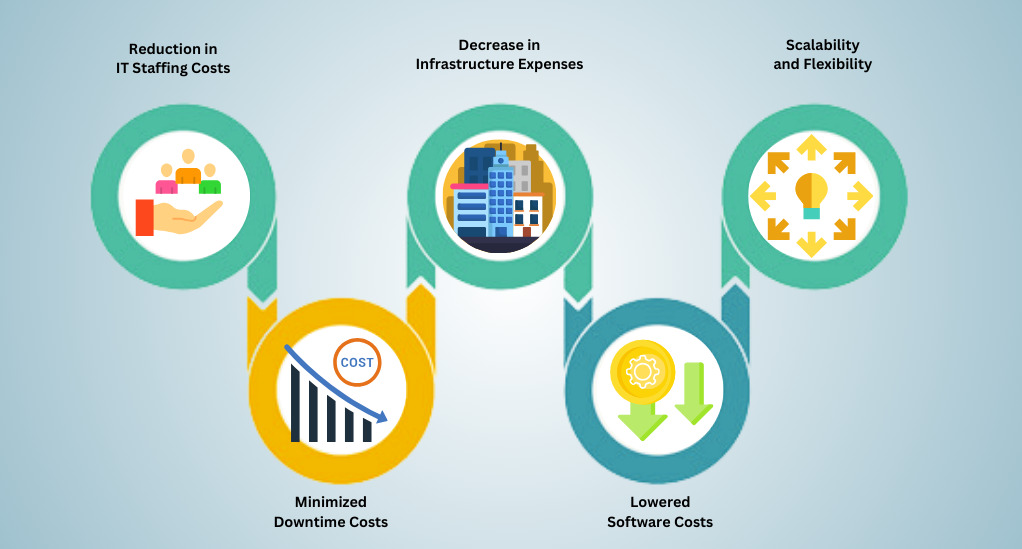
In the pursuit of operational excellence and financial prudence, businesses are increasingly turning to cloud computing. This section elucidates the myriad cost-saving benefits that cloud models bring to the table, offering insights into how you can leverage these advantages to bolster your business’s bottom line.
1. Reduction in IT Staffing Costs
Adopting cloud computing notably reduces IT staffing costs without compromising efficiency. This approach allows for a leaner IT team that can focus on core competencies and strategic initiatives, fostering innovation and growth. Cloud service providers handle the maintenance, updates, and troubleshooting of cloud resources, negating the need for a large in-house IT team and specialized staff, thereby streamlining operations and cutting costs.
2. Decrease in Infrastructure Expenses
Cloud computing alleviates infrastructure expenses for businesses by eliminating hefty initial investments in data centers and servers, thanks to a flexible pay-as-you-go pricing model. It also enhances energy efficiency by optimizing resource utilization, thereby reducing utility bills. Furthermore, it saves physical space that would have been occupied by traditional servers and data centers, potentially decreasing rental costs. This approach fosters a more economically efficient and sustainable operational framework.
3. Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud computing, known for its scalability and flexibility, enables businesses to quickly adapt to market changes. It allows for easy scaling to meet demand, helping to avoid the financial burdens tied to modifying physical infrastructures. Additionally, it promotes optimal resource utilization through real-time monitoring and adjustments, preventing wastage. Importantly, it ensures business continuity by offering reliable data backup and recovery solutions, minimizing downtime and safeguarding against data loss. This makes it a cost-effective and resilient option for contemporary businesses.
4. Minimized Downtime Costs
Downtime, characterized by financial losses and reputational damage, is a significant concern for businesses. Cloud computing addresses this by offering built-in redundancy and disaster recovery solutions, drastically reducing downtime risks and associated costs. Additionally, the automatic updates feature of cloud services ensures system reliability, further mitigating downtime caused by software issues, thereby safeguarding a company’s financial and reputational assets.
5. Lowered Software Costs
The Software as a Service (SaaS) model in cloud computing offers businesses an economical solution to access premium software applications. Through a subscription-based pricing system, companies can avoid the substantial costs associated with buying licenses and managing software installations. Additionally, SaaS providers take care of automatic updates and maintenance, ensuring businesses always have access to the newest features without extra costs, thereby significantly lowering overall software expenses.
Deep Dive into Cloud Models
As we venture further into the realm of cloud computing, it becomes imperative to understand the different cloud models available and how they can be leveraged for maximum cost-efficiency. In this section, we will dissect each cloud model, offering a comprehensive view of their features and benefits.
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS stands as the foundational layer in the cloud computing hierarchy, offering a virtualized computing infrastructure that is provisioned and managed over the internet. Let’s explore the nuances of IaaS:
- Comprehensive Offering: IaaS provides all the infrastructure to support web apps, including storage, servers, and networking resources. This extensive offering negates the need for significant investment in physical infrastructure.
- Benefits for SMBs: Small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) often operate under budget constraints and may lack extensive IT staff. IaaS offers them a level playing field by allowing access to the same technologies that larger corporations use, without the colossal initial investment.
- Case Study – Netflix: In the early 2000s, Netflix transitioned from a DVD rental service to a cloud-based streaming service, significantly reducing its data center costs and scaling its services to meet increasing demand.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS serves as a platform that facilitates the entire web application lifecycle, from building to managing and updating. Here’s a closer look at PaaS:
- Streamlined Application Development: PaaS offers a platform that includes the infrastructure, middleware, development tools, and more, facilitating streamlined application development without the hassle of infrastructure management.
- Cost-Efficiency: By providing a comprehensive platform, businesses can focus on developing and managing their applications without worrying about infrastructure management, thereby reducing costs significantly.
- Case Study – Capital One: Capital One adopted a cloud-first strategy in 2015, aiming to reduce their data centers from eight to three by 2020. This strategy enabled them to streamline operations and improve the speed of their IT services, while also reducing costs.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is a software distribution model where applications are hosted by a service provider and made available to customers over the internet. Let’s delve into the benefits of SaaS:
- Ease of Use: SaaS eliminates the need for businesses to install and run applications on their computers or data centers, reducing the burden of software maintenance, ongoing operation, and support.
- Cost-Effective: The SaaS model operates on a subscription basis, allowing businesses to avoid the high costs associated with purchasing, installing, updating, and maintaining software, thereby reducing overall costs.
- Case Study – Xerox: Xerox Corporation transitioned to a private cloud model, consolidating its data centers and significantly reducing operational costs. This shift also provided increased scalability, adding to cost savings.
Industry-Specific Applications and Cost Savings
As cloud computing continues to revolutionize the business landscape, various industries are harnessing its potential to foster innovation and achieve significant cost savings. In this section, we will delve into the industry-specific applications of cloud computing, illustrating how different sectors can benefit from adopting cloud models.
Healthcare: Shared Information Systems and Seamless Record Sharing
The healthcare sector is significantly benefiting from cloud computing, notably in information sharing and record management. This technology centralizes electronic health records, ensuring easy access and distribution of patient data, enhancing care quality while reducing costs. Moreover, it has spurred the growth of telemedicine, enabling remote consultations and expanding healthcare reach. Additionally, it allows for the analysis of large datasets for research, fostering innovation and further cost savings.
Education: Leveraging SaaS for Administrative Tasks and Digital Storage
The education sector is increasingly utilizing SaaS platforms within cloud computing to enhance administrative efficiency and promote digital learning. Cloud-based Learning Management Systems (LMS) are being adopted to streamline content delivery and manage e-learning initiatives, reducing the costs traditionally associated with classroom education. Moreover, these platforms are facilitating smoother administrative operations and fostering a collaborative learning environment, thereby lowering operational costs and creating a more engaging learning experience.
Retail: Improving Supply Chain Efficiency through Real-Time Tracking
The retail sector is utilizing cloud computing to streamline operations and enhance customer experiences. This technology aids in real-time inventory management, minimizing costs associated with stock discrepancies. Additionally, it facilitates the expansion of e-commerce platforms, reducing the overheads of physical storefronts. Furthermore, cloud-based CRM systems are fostering customer loyalty by personalizing experiences, potentially increasing sales while lowering marketing costs.
Finance: Harnessing Cloud-Based Analytics for Data Processing
The finance sector is harnessing cloud computing to amplify its data processing and analytics capabilities. This technology ensures stringent data security and compliance, helping to avoid significant costs associated with data breaches and non-compliance. Moreover, it facilitates real-time analytics, aiding in better decision-making and potentially increasing profits. Additionally, cloud computing is instrumental in developing high-speed automated trading systems, potentially boosting profits while reducing operational costs.
The Future of Cloud Computing and Potential Cost Savings
As we stand on the cusp of a new era in technological advancements, cloud computing is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of businesses across various industries. In this concluding section, we will explore the emerging trends in cloud computing and how they hold the promise of further cost savings and efficiency improvements for businesses.
Advancements in AI and Machine Learning for Predictive Analytics
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) with cloud computing is set to revolutionize the way businesses operate. Here’s how:
- Predictive Analytics: AI and ML can analyze vast amounts of data to provide predictive analytics, helping businesses to make informed decisions and optimize operations, potentially leading to significant cost savings.
- Automated Processes: AI and ML can automate repetitive tasks, reducing the need for human intervention and thereby lowering operational costs.
- Smart Resource Allocation: AI-powered cloud systems can intelligently allocate resources based on demand, avoiding overutilization and reducing costs.
The Role of Automation in Reducing Manual Tasks and Errors
Automation stands as a cornerstone in the future of cloud computing, promising to streamline operations and reduce costs. Here’s a closer look:
- Error Reduction: Automation can significantly reduce errors in processes, avoiding costly mistakes and improving the overall efficiency of operations.
- Improved Productivity: Automation can enhance productivity by handling repetitive tasks quickly and efficiently, freeing up human resources to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Cost Savings: By automating various processes, businesses can achieve substantial cost savings, as automation can handle tasks more quickly and efficiently compared to manual processes.
Internet of Things (IoT): Managing Vast Data with Cloud Solutions
The Internet of Things (IoT) is set to generate a massive amount of data, and cloud computing will play a crucial role in managing this data effectively. Here’s how:
- Data Management: Cloud computing offers scalable solutions for managing the vast amount of data generated by IoT devices, potentially saving costs associated with data storage and management.
- Real-Time Analytics: Cloud computing can facilitate real-time analytics of IoT data, providing businesses with actionable insights that can help in optimizing operations and reducing costs.
- Security and Compliance: Cloud providers offer robust security features that can help in safeguarding the sensitive data generated by IoT devices, potentially saving costs associated with data breaches and non-compliance.
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of cloud computing, it is evident that this technology holds immense potential for businesses seeking to achieve cost-efficiency and operational excellence. From the foundational concepts to industry-specific applications and future prospects, cloud computing stands as a beacon of innovation and cost savings.
As businesses navigate the complex landscape of the modern market, cloud computing offers a promising pathway to achieving scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. By harnessing the power of cloud computing, businesses can position themselves at the forefront of technological advancements, ready to embrace the opportunities and challenges of the future with agility and foresight.
Thank you for joining us on this insightful journey into the world of cloud computing. We hope that this guide has equipped you with the knowledge and strategies to leverage the cost-saving potential of cloud computing to its fullest.


Leave a Reply