
How to Choose the Right Blockchain Platform for Your Business
In the digital age, where data integrity and transactional transparency have become paramount, blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary force. It promises to reshape industries, redefine trust, and democratize data access. But what exactly is blockchain, and why has it become such a buzzword in the business world? Let’s delve deep into its origins, its potential, and why choosing the right platform is crucial for businesses.
A Brief History of Blockchain
Blockchain’s roots can be traced back to the conceptualization of cryptographic secured chain of blocks by Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta in 1991. However, it wasn’t until 2008 that the term “blockchain” was popularized with the introduction of Bitcoin by the pseudonymous entity, Satoshi Nakamoto. Originally designed as a public ledger for Bitcoin transactions, blockchain’s potential applications soon expanded far beyond cryptocurrency.
What Makes Blockchain Unique?
At its core, blockchain is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that allows data to be stored across a network of computers in a way that is transparent, immutable, and secure. Here’s a breakdown of its defining features:
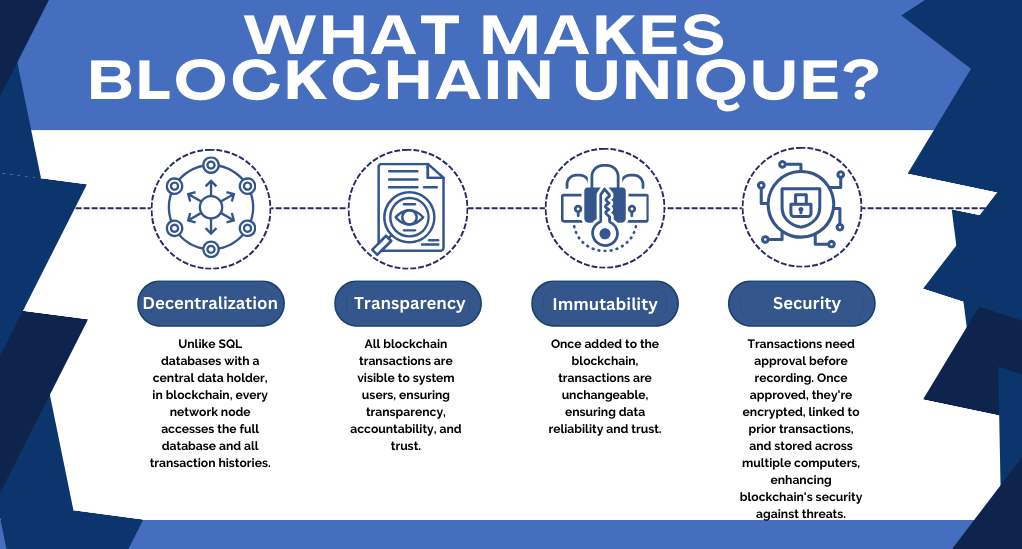
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional databases, such as a SQL database, where there’s a central entity holding the data, in blockchain, every participant (node) on the network has access to the entire database and the complete history of all transactions.
- Transparency: Every transaction on the blockchain is visible to anyone with access to the system. This transparency ensures accountability and trust among participants.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This feature ensures data integrity and trustworthiness.
- Security: Transactions must be agreed upon before they are recorded. After a transaction is approved, it is encrypted and linked to the previous transaction. Along with the fact that information is stored across a network of computers, this makes blockchain highly secure against malicious attacks.
The Business Case for Blockchain
Blockchain’s potential applications in business are vast and varied. From supply chain management to real estate, from healthcare to finance, industries are exploring ways to leverage blockchain for greater efficiency, transparency, and security. Here are a few compelling reasons why businesses are turning to blockchain:
| Industry | Application of Blockchain |
|---|---|
| Finance | Secure and transparent cross-border transactions, fraud reduction. |
| Supply Chain | Real-time tracking of goods, ensuring authenticity. |
| Healthcare | Secure patient data sharing, drug traceability. |
| Real Estate | Transparent property transactions, reducing fraud. |
The Importance of Choosing the Right Platform
With the rise in the popularity of blockchain, numerous platforms offering varied functionalities have emerged. Each platform has its strengths, weaknesses, and unique features. For businesses, choosing the right platform is not just a technical decision but a strategic one. The right platform can align with a company’s goals, ensure scalability, and provide the necessary support and security features.
Understanding Blockchain Technology: Beyond the Hype
Blockchain, often hailed as the ‘next internet,’ has garnered significant attention, both for its groundbreaking potential and the myths surrounding it. To truly grasp its significance, it’s essential to demystify the technology and understand its core principles.
The Essence of Blockchain
Blockchain operates as a chain of blocks, where each block contains a set of transactions. These blocks are linked and secured using cryptographic principles. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
- Transaction Initiation: A user initiates a transaction, which is then broadcast to a network of computers, known as nodes.
- Transaction Verification: These nodes validate the transaction using algorithms. Verified transactions are then grouped together into a block.
- Block Addition: This block is added to the existing chain in a linear, chronological order.
- Consensus Algorithm: A critical aspect of blockchain is the consensus mechanism, where nodes agree on the validity of transactions. Popular methods include Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
- Immutable Record: Once added, the data within a block cannot be altered, ensuring a permanent and tamper-proof record.
Why Blockchain Matters to Businesses
Blockchain’s decentralized nature offers a paradigm shift from traditional centralized systems. Here are its standout benefits:
- Trust: With its transparent and immutable nature, blockchain fosters trust among participants. Every transaction is traceable, ensuring accountability.
- Efficiency: By eliminating intermediaries, blockchain accelerates transactions and reduces costs.
- Security: Cryptographic encryption ensures that data breaches are near-impossible, making blockchain a secure harbor for data.
- Transparency: All participants have access to the same data, ensuring a single version of truth and reducing discrepancies.
Real-World Applications
While cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are the most well-known applications of blockchain, the technology’s potential spans far beyond:
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts with terms directly written into code lines. They automatically enforce and validate the terms of a contract, ensuring efficiency and trustworthiness.
- Supply Chain Management: Ensuring the authenticity of products by tracking them from origin to shelf.
- Voting Systems: Creating tamper-proof and transparent voting systems for elections.
- Identity Verification: Offering a secure and immutable identity verification system, reducing fraud and identity theft.
Key Advantages of Blockchain for Businesses: A Deeper Dive
While the buzz around blockchain is undeniable, it’s its transformative potential that has industries from finance to healthcare sitting up and taking notice. Let’s explore some of these advantages in detail.
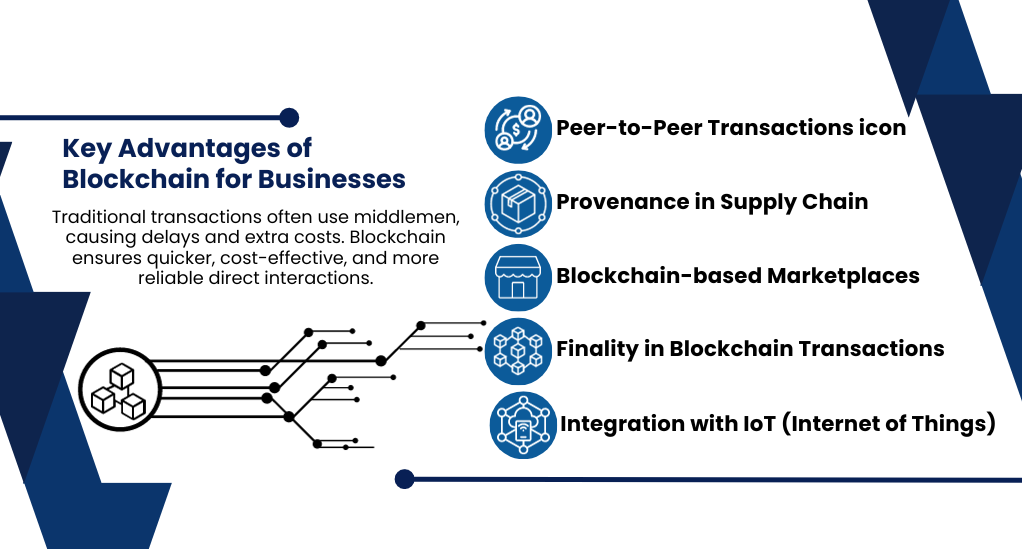
1. Peer-to-Peer Transactions
Traditional transaction methods often involve intermediaries, leading to delays and added costs. Blockchain facilitates direct transactions between parties, ensuring speed, reduced costs, and enhanced trust.
2. Provenance in Supply Chain
Blockchain’s ability to provide a transparent and unchangeable record makes it invaluable in supply chain management. Businesses can trace the origin and journey of products, ensuring authenticity and building consumer trust.
3. Blockchain-based Marketplaces
Decentralized marketplaces, built on blockchain, offer a platform for buyers and sellers to interact directly. This not only reduces costs but also ensures transparency and security in transactions.
4. Finality in Blockchain Transactions
The irreversible nature of blockchain transactions ensures that once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This provides certainty and trust in the system, crucial for high-value transactions.
5. Integration with IoT (Internet of Things)
The convergence of blockchain with IoT promises a future where devices can communicate and transact securely. From smart homes to intelligent supply chains, the possibilities are endless.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Blockchain Platform: Navigating the Choices
The blockchain landscape is vast, with numerous platforms offering a range of functionalities. For businesses, this abundance of choice can be both a boon and a challenge. Making the right decision is not merely about technical compatibility but aligning with business goals and future scalability. Here’s a guide to help businesses navigate their choices:
Level of Privacy Required
Blockchain configurations can vary from public to private, and understanding the distinction is crucial:
- Public Blockchains: Open to anyone, these blockchains are fully decentralized. While they offer high levels of security, they might not be suitable for businesses needing to keep their transaction data confidential.
- Private Blockchains: Restricted to chosen participants, they offer more control over who can access the network and validate transactions. Ideal for businesses that prioritize privacy.
- Hybrid Blockchains: Combining elements of both public and private blockchains, they offer flexibility in terms of transparency and control.
Network Size and Growth Goals
The scalability of a blockchain platform is crucial for businesses anticipating growth:
- Number of Nodes: Consider how many nodes the network will start with and the anticipated growth. More nodes can offer better security but might impact transaction speeds.
- Geographical Distribution: The physical location of nodes can affect transaction speeds, especially in a global business context.
- Transaction Complexity: Platforms that can handle complex transactions might be more resource-intensive but are essential for businesses with multifaceted operations.
The Need for Cryptocurrency Tokens
While blockchain is the underlying technology for cryptocurrencies, not all business applications require a token system:
- Tokenized Networks: Useful for incentivizing certain behaviors within the network, such as rewarding nodes for validating transactions.
- Token-less Networks: Ideal for businesses looking for the benefits of a distributed ledger without the complexities of managing a cryptocurrency.
Consensus Mechanisms and Scalability
The method by which transactions are verified and added to the blockchain is a vital consideration:
- Proof of Work (PoW): While secure, it’s resource-intensive and might not be ideal for businesses looking for eco-friendly options.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): A more energy-efficient alternative to PoW, where validators are chosen based on the number of tokens they hold.
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): A variation of PoS where token holders vote for a few representatives to validate transactions, enhancing scalability.
Public vs. Private Blockchains: A Closer Look
While touched upon earlier, the distinction between public and private blockchains deserves a deeper exploration:
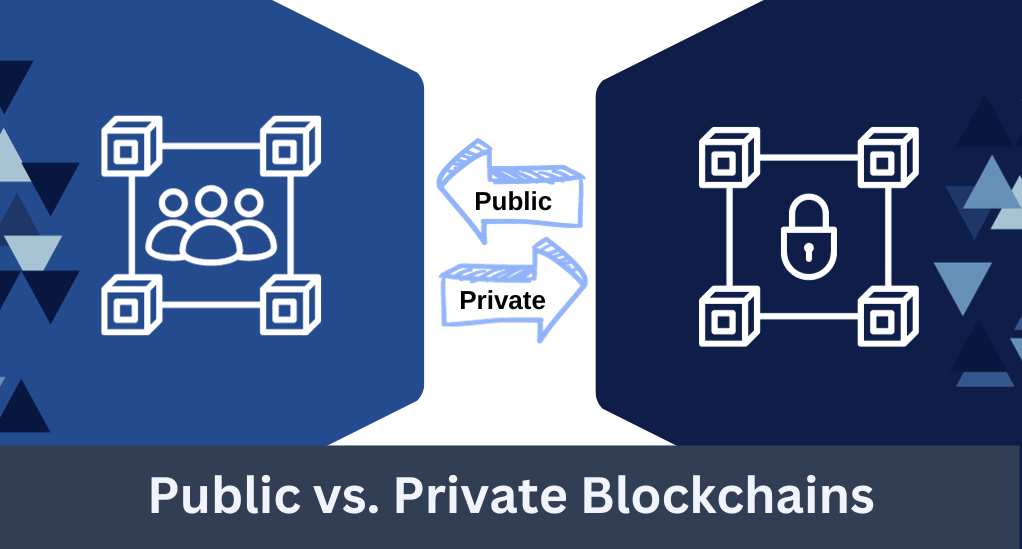
- Transparency vs. Control: Public blockchains offer unparalleled transparency, making every transaction visible to anyone. Private blockchains, on the other hand, offer more control over participants and data visibility.
- Security Considerations: Both public and private blockchains offer robust security features, but the decentralized nature of public blockchains makes them inherently more resistant to malicious attacks.
- Use Cases: Public blockchains are ideal for applications where transparency is paramount, such as public records or charity donations. Private blockchains are better suited for internal business processes where data confidentiality is crucial.
The Potential of Blockchain for Corporations: Beyond Digital Currency
While the initial buzz around blockchain was primarily centered on its application in the world of digital currencies, its potential reaches far beyond. Corporations across industries are realizing the transformative power of blockchain, leveraging it to drive innovation, enhance transparency, and create value.
A New Paradigm for Business Operations
Blockchain introduces a new way of conducting business, emphasizing transparency, decentralization, and trust:
- Decentralized Decision Making: Traditional hierarchical structures can sometimes slow down decision-making processes. With blockchain, corporations can implement decentralized models, allowing for quicker and more efficient decisions based on consensus mechanisms.
- Transparent Business Models: Blockchain’s immutable and transparent nature ensures that all stakeholders, from customers to shareholders, have a clear view of transactions and operations, fostering trust and accountability.
- Enhanced Security Protocols: The cryptographic nature of blockchain ensures that data breaches become exceedingly rare, providing corporations with a robust and secure framework for their operations.
Real-world Corporate Applications of Blockchain
The versatility of blockchain means its applications in the corporate world are vast and varied:
- Supply Chain Optimization: Companies like Walmart and Maersk are using blockchain to track products from origin to consumer, ensuring authenticity and reducing instances of fraud.
- Smart Contracts in Real Estate: Automating and streamlining property transactions, reducing the need for intermediaries, and ensuring both parties meet their obligations.
- Healthcare Data Management: Hospitals and healthcare providers are leveraging blockchain to securely store patient data, ensuring privacy and easy access when required.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Artists and creators can use blockchain to timestamp their creations, ensuring their intellectual property rights are protected and they receive fair compensation for their work.
Challenges and Considerations for Corporations
While blockchain offers numerous advantages, it’s essential for corporations to be aware of the challenges:
- Integration with Existing Systems: Incorporating blockchain into existing IT infrastructures can be complex and requires careful planning.
- Regulatory Landscape: The regulatory environment for blockchain is still evolving, and corporations need to stay updated to ensure compliance.
- Talent Acquisition: As a relatively new field, there’s a shortage of skilled blockchain professionals. Corporations need to invest in training and talent acquisition to harness the full potential of blockchain.
Conclusion: The Future of Blockchain in Business
Blockchain’s potential to revolutionize business operations is undeniable. Its transformative power is evident in its ability to enhance transparency, ensuring that every stakeholder, from consumers to investors, has a clear and unalterable view of transactions. This transparency, combined with the technology’s capacity to streamline operations, positions blockchain as a game-changer in the corporate landscape. As industries continue to evolve, the integration of such a robust and secure system can redefine traditional business models, making them more efficient and trustworthy.
As the technology matures, it’s becoming increasingly integrated into the very fabric of business operations across sectors. This integration underscores the importance for corporations to stay informed about the latest developments in the blockchain arena. Adapting to and innovating with blockchain is no longer a choice but a necessity for businesses aiming for long-term success. In an era marked by rapid digital transformation, those who harness the full potential of blockchain will not only stay ahead of the curve but also drive unparalleled value, trust, and growth for their stakeholders.


Leave a Reply