Understanding the Different Types of Malware: A Comprehensive Guide
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, the threat of malware is a constant presence. As technology advances, so does the sophistication of malware attacks, making it imperative for individuals and organizations to stay informed and vigilant. This section serves as an introduction to the complex world of malware, tracing its evolution and emphasizing the importance of being well-informed about potential threats. Let’s delve step by step into this critical subject.
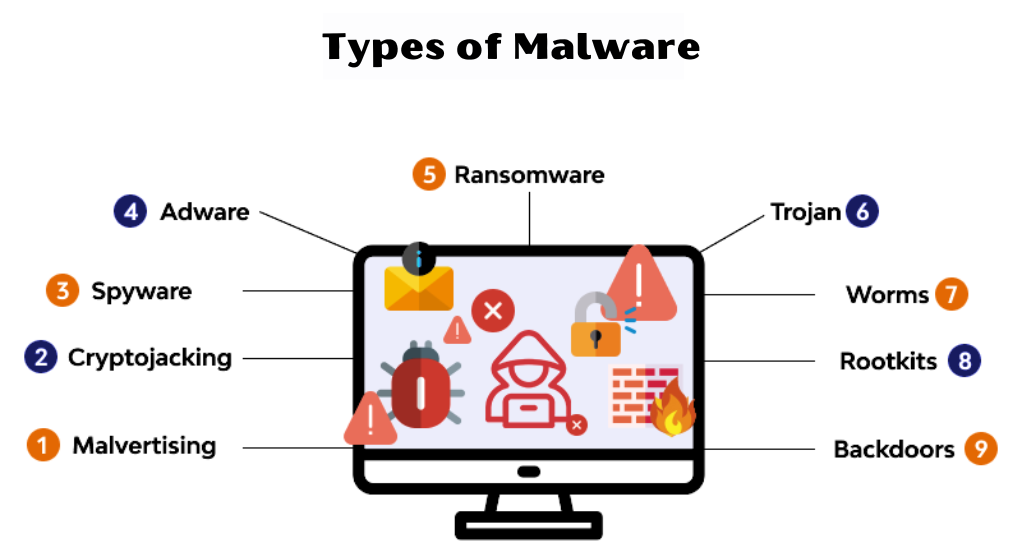
The Importance of Being Informed about Malware
In today’s digital age, our reliance on technology is greater than ever before. From personal data storage to financial transactions, a significant portion of our daily activities is conducted online. This digital dependency, however, comes with its own set of vulnerabilities, primarily in the form of malware attacks. Being well-informed about the different types of malware is not just a necessity but a responsibility for every internet user. Knowledge about malware helps in:
- Identifying Potential Threats: Understanding the characteristics of various malware types enables users to identify potential threats before they can cause harm.
- Implementing Protective Measures: Being informed allows users to implement protective measures such as ransomware protection and malware detection techniques, safeguarding their digital assets.
- Mitigating Damage: In the event of a malware attack, informed individuals can take swift actions to mitigate damage and prevent further loss.
The Evolution of Malware Over the Years
To fully grasp the gravity of the malware threat, it’s essential to understand its evolution. Let’s take a chronological journey through the development of malware:
- 1980s – The Dawn of Malware: In the early days, malware was primarily in the form of computer viruses, which required user action to spread. These were relatively simple and were more of an annoyance than a serious threat.
- 1990s – The Rise of Worms and Trojans: This decade saw the emergence of worms and trojans. Worms could replicate themselves and spread without user intervention, while trojans disguised themselves as legitimate software to trick users into installing them.
- 2000s – The Spyware Era: The new millennium brought the rise of spyware, which could collect user data without their knowledge. This era also saw the advent of ransomware, which encrypts user data and demands a ransom for its release.
- 2010s – Sophisticated Attacks: In this decade, malware attacks became more sophisticated, targeting specific organizations or individuals with advanced techniques like spear phishing.
- 2020s – AI and Machine Learning: The current era is witnessing the integration of AI and machine learning in malware, making them more intelligent and capable of bypassing traditional security measures.
Understanding Malware: A Brief Overview
In this section, we will delve deeper into the world of malware, providing you with a foundational understanding that will help you navigate the subsequent, more detailed sections of this article. Let’s begin by defining malware and understanding its various dissemination methods.
Malware, a portmanteau of “malicious software,” refers to any software intentionally designed to cause damage, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems, networks, or devices. It encompasses a broad range of software types, including viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, and spyware, each having unique characteristics and modes of operation. Understanding these different forms is crucial in developing a robust defense strategy.
How Malware Spreads
Malware can infiltrate systems through various channels. Here, we will explore the most common methods of malware dissemination:
- Email Attachments and Phishing: Malware often spreads through malicious email attachments or links. Phishing emails impersonate legitimate organizations to trick users into providing personal information or downloading malware.
- Compromised Websites: Visiting websites that have been compromised can result in malware being downloaded onto your system without your knowledge.
- Removable Media: Malware can spread through removable media like USB drives. Once the infected media is connected to a system, the malware can replicate itself onto that system.
- Software Vulnerabilities: Malware often exploits vulnerabilities in software to infiltrate systems. Keeping software up-to-date is a crucial step in preventing malware infections.
- Social Engineering: This involves manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information or performing actions that compromise security.
- Network Propagation: Some malware types can propagate through networks, exploiting vulnerabilities to infect multiple systems connected to the same network.
Types of Computer Viruses
In this section, we will explore the intricate world of computer viruses, one of the most well-known forms of malware. Understanding the different types of computer viruses and their characteristics can equip you with the knowledge to safeguard your digital assets effectively.
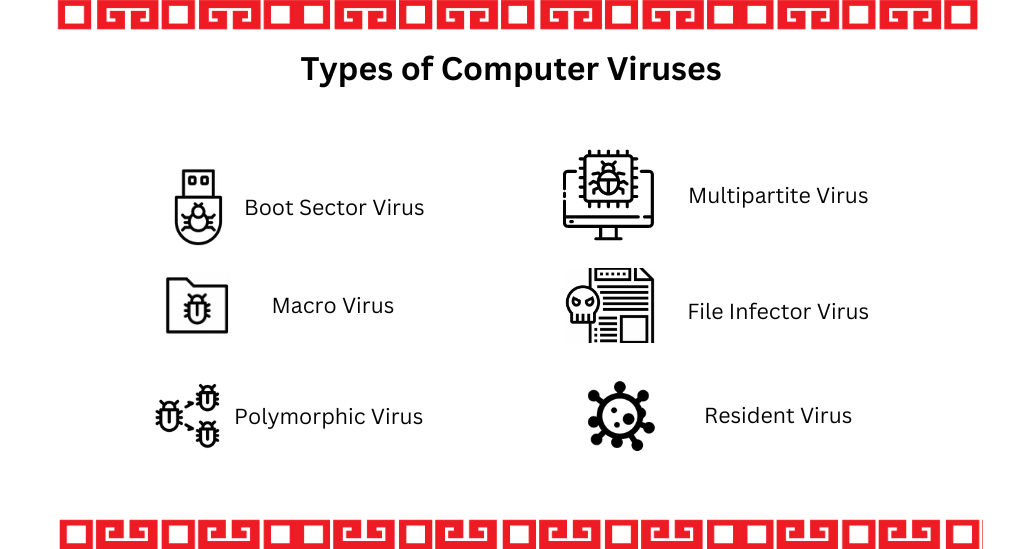
Definition and Characteristics
A computer virus is a type of malware that, once executed, replicates itself by modifying other computer programs and inserting its own code. These viruses can have various effects, ranging from harmless pranks to causing significant damage to systems and data. Here, we will delve into the different types of computer viruses and their distinctive traits.
| Type of Virus | Characteristics | Common Transmission Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Boot Sector Virus | Infects the boot sector of a hard drive | Removable media, infected websites |
| Macro Virus | Targets the macro language in applications like Microsoft Word | Email attachments, document sharing |
| Polymorphic Virus | Alters its code to avoid detection | Downloading infected files, email attachments |
| Resident Virus | Resides in a computer’s memory and activates when the system is booted | Infected software installations, downloads |
| Multipartite Virus | Can infect both program files and the boot sector | Infected websites, removable media |
| File Infector Virus | Infects executable files | Downloading infected files, email attachments |
Protection and Prevention Strategies
Protecting your digital environment from computer viruses requires a multi-faceted approach. Here are some strategies that can be employed:
- Use Reliable Antivirus Software: Install a reliable antivirus software that offers real-time protection against various types of malware, including viruses.
- Keep Software and Systems Updated: Regular updates can patch vulnerabilities that viruses might exploit.
- Safe Browsing Habits: Avoid visiting suspicious websites and downloading files from untrusted sources.
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up your data to recover it in case of a virus attack.
- Educate and Train Users: Educate users on safe online practices to prevent virus infections.
Spyware Characteristics
As we continue our journey into the world of malware, we now turn our attention to spyware, a type of malware designed to spy on users, collect their personal information, and send this data to third parties without the users’ consent. Understanding the characteristics of spyware is vital in safeguarding your privacy and securing your digital assets. Let’s delve into the intricate details of spyware.
What is Spyware?
Spyware is a type of malicious software that infiltrates your computer to monitor and collect your personal data and browsing habits. This information can be used for various nefarious purposes, including identity theft, fraud, or targeted advertising. Spyware operates stealthily, often without the user’s knowledge, making it particularly dangerous. Here, we will explore the different types of spyware and their characteristics.
| Type of Spyware | Characteristics | Common Transmission Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Adware | Displays unwanted advertisements and collects data on your browsing habits | Bundled with free software, infected websites |
| Trojan Spyware | Disguised as legitimate software to collect sensitive data | Email attachments, malicious downloads |
| Tracking Cookies | Collects data on your browsing habits and personal information | Visiting infected websites, online ads |
| System Monitors | Records keystrokes and captures screen information | Infected email attachments, malicious downloads |
| Banking Spyware | Targets online banking information and credentials | Phishing emails, malicious websites |
Tips for Identifying and Protecting Against Spyware
Protecting yourself against spyware requires vigilance and the adoption of safe online practices. Here are some tips to help you identify and protect against spyware:
- Be Wary of Unsolicited Communications: Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown or unsolicited emails.
- Use Reliable Security Software: Install security software that offers comprehensive protection against various forms of spyware.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep your software and operating systems updated to patch any security vulnerabilities.
- Safe Browsing Habits: Adopt safe browsing habits, including using secure connections and avoiding suspicious websites.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Stay informed about the latest developments in spyware and educate others on how to protect themselves.
Ransomware Protection
In this segment, we venture into the realm of ransomware, a type of malware that encrypts files on a victim’s device, holding them hostage until a ransom is paid to the attacker. In recent years, ransomware attacks have surged, targeting individuals, corporations, and even government agencies. Understanding ransomware and implementing robust protection strategies are vital in safeguarding your digital assets. Let’s dissect this malicious software and learn how to shield ourselves effectively.
Understanding Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that restricts access to a computer system or files until a ransom is paid to the cybercriminal. These attacks can cause significant data loss and financial damage. Ransomware usually infiltrates systems through phishing emails or malicious websites. Here, we will explore the different types of ransomware and their modus operandi.
| Type of Ransomware | Characteristics | Common Transmission Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Crypto Ransomware | Encrypts valuable files on the victim’s system, demanding a ransom for decryption | Phishing emails, malicious downloads |
| Locker Ransomware | Locks the victim out of their operating system, demanding a ransom to unlock it | Infected websites, malicious attachments |
| Scareware | Frightens victims with fake malware alerts, urging them to pay a fee for “cleaning” the system | Pop-up ads, fraudulent websites |
| RaaS (Ransomware as a Service) | Allows individuals to launch ransomware attacks without coding skills, often in exchange for a share of the ransom | Dark web platforms, email campaigns |
The Importance of Ransomware Protection
The surge in ransomware attacks in recent years underscores the critical importance of ransomware protection. These attacks can lead to data loss, financial repercussions, and a tarnished reputation. Implementing robust ransomware protection strategies can help prevent these attacks and safeguard sensitive data. Here are some reasons why ransomware protection is essential:
- Data Security: Protecting your data from being encrypted and held hostage.
- Financial Safety: Avoiding the financial losses associated with ransom payments and data recovery.
- Maintaining Reputation: Preventing the reputational damage that comes with being a victim of a ransomware attack.
- Legal Compliance: Adhering to legal requirements for protecting sensitive data.
Best Practices for Ransomware Protection
To shield your digital environment from ransomware attacks, adopting the following best practices is crucial:
- Regular Backups: Maintain regular backups of your important files in a secure location, separate from your main system.
- Use Antivirus Software: Employ comprehensive antivirus software that offers real-time protection against malware, including ransomware.
- Email Safety: Be cautious with email attachments and links, especially from unknown or suspicious sources.
- Software Updates: Regularly update your software and operating systems to patch vulnerabilities that could be exploited by ransomware.
- Employee Training: Educate employees or family members on the signs of phishing emails and the importance of safe online practices.
- Network Security: Implement network security measures, including firewalls and secure Wi-Fi, to prevent unauthorized access.
Malware Detection Techniques
As we progress further into our comprehensive guide, we now focus on malware detection techniques. These techniques are essential tools in the fight against malware, helping to identify and remove malicious software before it can cause significant damage. In this section, we will explore both traditional and advanced malware detection techniques, providing you with a robust understanding to safeguard your digital assets effectively.
Traditional Detection Techniques
Traditional malware detection techniques have been the cornerstone of cybersecurity for many years. Let’s delve into these techniques and understand how they operate:
- Signature-Based Detection: This technique relies on a database of known malware signatures to identify and block malware. It is highly effective against known threats but struggles to detect new, unknown malware variants.
- Heuristic-Based Detection: This method uses algorithms to analyze the behavior and characteristics of files, identifying potential malware based on a set of rules. It can detect new variants of malware but may sometimes flag legitimate files as malicious (false positives).
- Sandboxing: In this approach, suspicious files are executed in a controlled, isolated environment (sandbox) to observe their behavior without risking the main system. It helps in identifying malware based on its actions in the sandbox.
Advanced Detection Techniques
As malware continues to evolve, so do the techniques to detect them. Here, we explore some of the advanced malware detection techniques that are being employed to counter sophisticated malware threats:
| Technique | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Machine Learning and AI | Utilizes algorithms to analyze patterns and behaviors | High accuracy and speed | Requires substantial computational resources |
| Behavioral Analysis | Monitors application and process behavior in real-time | Identifies anomalies indicating malware | May produce false positives |
| EDR | Provides continuous monitoring and response to advanced threats | Comprehensive approach to detection | Can be complex to implement |
| Threat Hunting | Proactively searches for indicators of compromise within a network | Identifies and mitigates threats early | Requires skilled personnel |
Malware Attack Simulation Tools
As we approach the final sections of our comprehensive guide, we now turn our focus towards malware attack simulation tools. These tools play a pivotal role in strengthening an organization’s defense mechanisms by simulating realistic malware attacks to identify vulnerabilities and assess the effectiveness of existing security measures. In this section, we will explore the importance of these tools and highlight some popular options in the market.
Importance of Simulation Tools
Malware attack simulation tools are an invaluable asset in the modern cybersecurity landscape for several reasons:
- Identifying Vulnerabilities: These tools help in uncovering weaknesses in your security infrastructure, allowing for timely rectification before an actual attack occurs.
- Testing Security Measures: Simulation tools enable organizations to test the effectiveness of their security measures, ensuring that they can withstand real-world attack scenarios.
- Compliance and Reporting: Many industries require regular security assessments for compliance. Simulation tools can assist in meeting these requirements by providing detailed reports on the security posture of an organization.
- Employee Training: Using simulation tools, organizations can create realistic training scenarios to educate employees about the nature of malware attacks and how to respond effectively.
Popular Malware Attack Simulation Tools
There are several reputable malware attack simulation tools available in the market, each offering unique features and capabilities. Here, we highlight a few popular options:
- Metasploit: A powerful tool that allows for the simulation of real-world attacks on your network to identify vulnerabilities and weak points.
- Atomic Red Team: This tool enables organizations to test their defenses by executing simple “atomic tests” that mimic malware attack behaviors.
- Mimikatz: A well-known tool that can simulate credential harvesting attacks, helping organizations to identify and rectify vulnerabilities related to authentication and authorization.
- Burp Suite: A graphical tool for testing web application security, including the simulation of various types of malware attacks.
- Nessus: A widely-used vulnerability scanner that can simulate attacks to identify vulnerabilities in networks, operating systems, and applications.
Using Simulation Tools for Enhanced Security
Utilizing malware attack simulation tools effectively involves integrating them into your regular security assessment routines. Here are some steps to consider:
- Regular Simulations: Conduct regular simulations to identify new vulnerabilities that may arise due to changes in the network or application infrastructure.
- Integrated Approach: Use a combination of different simulation tools to cover various aspects of your security infrastructure.
- Response Protocols: Develop and test response protocols based on the insights gained from the simulation exercises.
- Continuous Improvement: Use the results of the simulations to continuously improve your security measures, adapting to the evolving threat landscape.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we have embarked on an enlightening journey through the intricate world of malware, unraveling its various forms and the potent strategies to counteract them. From understanding the foundational aspects of malware to delving deep into specific types like ransomware and spyware, we have equipped ourselves with the knowledge to navigate the digital realm with heightened vigilance and security.
As we stand at the crossroads of an era dominated by digital interactions, the threat landscape continues to evolve, bringing forth new challenges. However, armed with the insights garnered through this guide, we are better prepared to face these challenges head-on. The road ahead calls for continuous learning and adaptation, fostering a culture that prioritizes security and promotes safe online practices.
As we forge ahead, let us commit to being the vanguards of our digital sanctuaries, implementing robust security measures and fostering collaborations that amplify our defenses. Let us also be the harbinger of knowledge, sharing insights and information with our communities to create a united front against malware threats.
In conclusion, the fight against malware is a continuous journey, one that demands vigilance, resilience, and a proactive approach. As we step into a future where the boundaries between the virtual and real worlds blur, let us carry the beacon of safety and security, illuminating the path for others to follow.


Leave a Reply