Understanding End-to-End Encryption and Its Benefits
In the rapidly advancing realm of encryption technology, understanding forthcoming trends and the potential influence of quantum computing is pivotal. This necessitates an in-depth exploration of the emerging trends that are shaping the industry and a closer look at how the formidable force of quantum computing will define the future of encryption.
In this guide, we embark on a journey to elucidate the significant advancements on the horizon in the encryption landscape, and we delve into the complex yet exciting world of quantum computing, a force potent enough to reshape the contours of encryption technology. Join us as we navigate through the futuristic pathways of encryption, unveiling developments that are set to redefine security and privacy in the digital age.
How Does End-to-End Encryption Work
In this digital age where data breaches are a constant threat, understanding the mechanisms that safeguard sensitive information is paramount. This section explores the fundamentals of end-to-end encryption, a technology at the heart of secure communications.
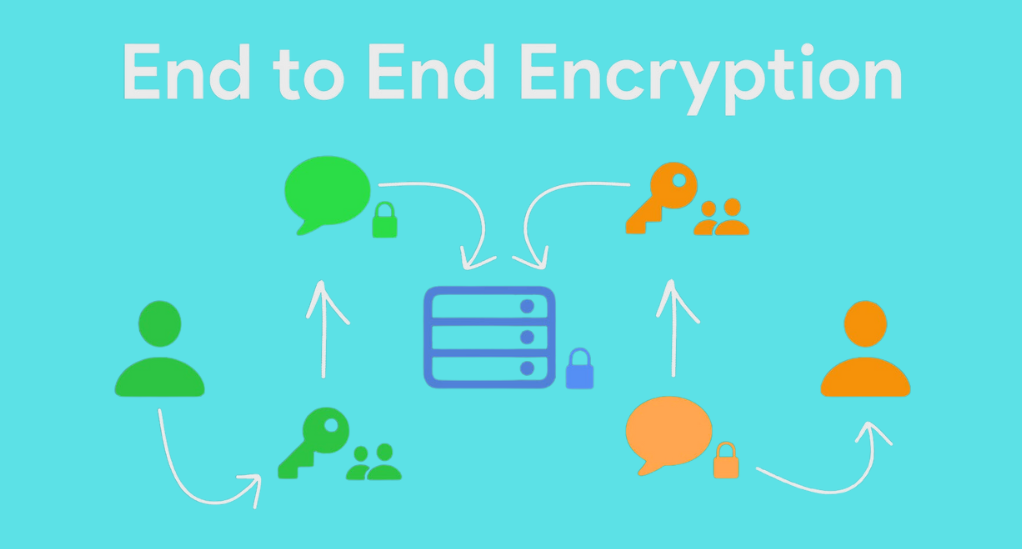
Overview of Encryption
Encryption is the core process of coding information to protect it from unauthorized access, rooted in the field of cryptography. It includes two main types: symmetric, using one key for both encryption and decryption, and asymmetric, using two keys – a public one and a private one.
The Process of Encrypting and Decrypting Messages
With a firm grasp on the types of encryption, we venture into the meticulous process of encrypting and decrypting messages, which ensures secure transmission of data.
Encryption involves the generation of unique keys to transform data into an unreadable format using specialized algorithms, ensuring its security during transmission. Upon receipt, the recipient utilizes the appropriate key to decrypt the data, reversing the encryption process and gaining access to the original information, ensuring secure data retrieval.
Real-world Examples and Applications
To bring the concept closer to home, let’s examine real-world applications where end-to-end encryption is a cornerstone in ensuring data security.
- Messaging Apps: Applications like WhatsApp and Signal use end-to-end encryption to secure messages, making them accessible only to the communicating parties.
- Email: Services such as ProtonMail offer end-to-end encryption, keeping email contents confidential and secure.
- Cloud Storage: Platforms like Tresorit use end-to-end encryption to protect files stored in the cloud, allowing only the owner with the decryption key to access the data.
End-to-End Encryption Benefits
Understanding the benefits of end-to-end encryption not only heightens our appreciation for this advanced technology but also encourages the wider adaptation of its applications in our daily lives. Below, we unfold the paramount benefits such as bolstering privacy and security, preventing third-party access, and securing communications in both business and personal spheres.
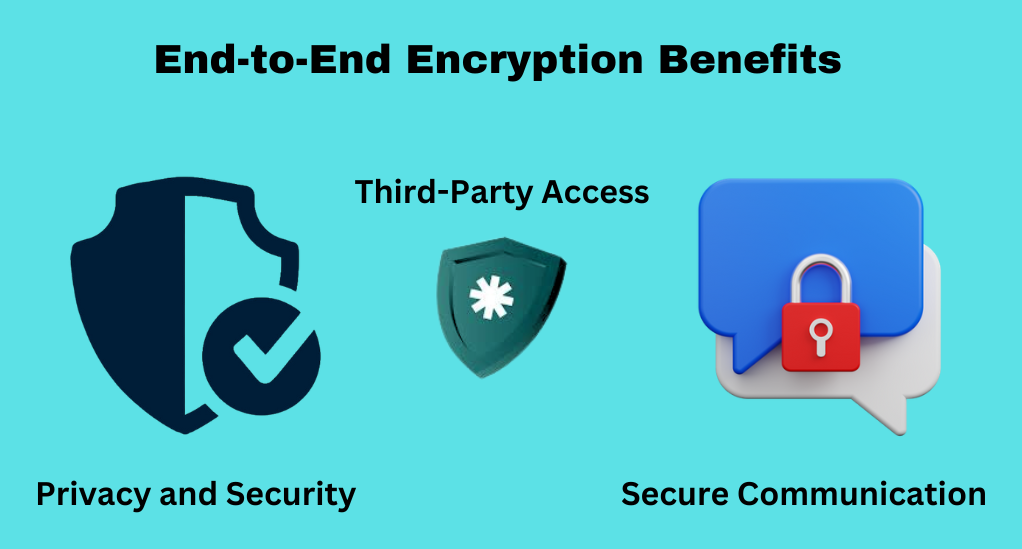
Privacy and Security
In our interconnected world, end-to-end encryption is a guardian of privacy and security. It protects personal data and keeps it out of reach for unauthorized users. It also maintains the confidentiality of sensitive communications, ensuring they stay between sender and recipient, whether it’s government secrets or corporate strategies, ensuring strong privacy and security.
Protection from Third-Party Access
End-to-end encryption serves as a formidable safeguard against third-party access. It shields data from service providers, rendering even communication facilitators unable to decipher encrypted messages, guaranteeing unprecedented levels of privacy. Additionally, it provides a robust defense against hackers by creating a near-impenetrable barrier that makes it exceedingly challenging for them to access and decipher encrypted data, bolstering cybersecurity efforts significantly.
Secure Communication in Business and Personal Use
End-to-end encryption secures communication in business and personal realms, ensuring information exchange safety. It safeguards corporate secrets and client confidentiality, fostering trust. In personal use, it enables private conversations and secure transactions, preserving privacy and security in the digital landscape.
| Aspect | Business Use | Personal Use |
|---|---|---|
| Data Sensitivity | High (Corporate secrets, client data) | Varied (Can range from low to high) |
| Communication Tools | Secure corporate messaging platforms | Encrypted messaging apps |
| Security Measures | Multi-factor authentication, secure networks | Secure passwords, private networks |
Symmetric vs Asymmetric Encryption: The Pillars of Security
In this section, we unpack the complex yet fascinating world of encryption technologies, delving into the details of symmetric and asymmetric encryption techniques. Understanding the core principles behind these encryption methods is vital in appreciating the security and robustness of end-to-end encryption systems. Let’s venture step by step into this in-depth exploration.
Definition and Overview of Symmetric Encryption
Symmetric encryption employs a single shared key for both data encryption and decryption. The sender uses this key to encrypt the data, and the recipient uses the same key for decryption, with key sharing occurring securely before transmission. This approach is commonly applied in secure file transfers, online banking, and VPNs, particularly in scenarios where speed and efficiency are essential.
Definition and Overview of Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetric encryption uses a public key for encryption (known to all) and a private key for decryption (secret), enhancing security by keeping the private key confidential. It’s vital in digital signatures, SSL/TLS for secure browsing, and secure multi-party communications, widely ensuring secure data transmission and authentication in digital contexts.
Comparisons and Use Cases for Both Types
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of both symmetric and asymmetric encryption can guide you in choosing the appropriate method for different scenarios. Here we present a comparison and dive into specific use cases for each:
| Attributes | Symmetric Encryption | Asymmetric Encryption |
|---|---|---|
| Key usage | Single key | Key pair (public and private) |
| Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Security Level | High | Higher, due to the two-key system |
| Use Cases | VPNs, File Encryption | SSL/TLS, Digital Signatures |
Use Cases Detailed
- Symmetric Encryption
- VPNs: Creating secure channels for communication over unsecured networks.
- File Encryption: Protecting sensitive files stored locally or in the cloud.
- Asymmetric Encryption
- SSL/TLS: Establishing secure communications over computer networks.
- Digital Signatures: Authenticating the identity of the sender and ensuring the integrity of the message.
Algorithms Powering End-to-End Encryption
In the vast landscape of digital security, algorithms act as the unsung heroes. They are the backbone of end-to-end encryption, ensuring our digital communications are protected and secure. In this comprehensive guide, we will uncover the pivotal algorithms in end-to-end encryption, their role in fortifying security, and the captivating journey of their evolution over time.
Common Algorithms Used in End-to-End Encryption
When it comes to end-to-end encryption, certain algorithms have been recognized as industry standards due to their efficiency, robustness, and reliability.
Symmetric algorithms like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) provide robust encryption solutions with key lengths of 128, 192, or 256 bits, offering secure data protection on a global scale. In contrast, the older DES (Data Encryption Standard) has been phased out due to its vulnerabilities, relying on a fixed 56-bit key length.
Asymmetric algorithms such as RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman), serve as pioneers in public-key cryptography, enabling secure data transmission and digital signatures. ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) offers enhanced security with shorter key lengths compared to RSA by utilizing elliptic curves over finite fields, making it an efficient choice for modern encryption needs.
How Algorithms Play a Role in Security
The strength of encryption doesn’t just depend on keeping keys secret but also on the complexity and design of the encryption algorithms.
Confusion and Diffusion
At the heart of encryption algorithms lies the principle of introducing confusion and diffusion. Confusion ensures that the relationship between the plaintext (original message) and ciphertext (encrypted message) is complex, while diffusion dissipates the properties of plaintext over the ciphertext.
Key Length and Complexity
The length and complexity of the encryption key play a crucial role. Longer keys generally offer more security but can slow down the encryption process.
Resistance to Attacks
A well-designed algorithm is resistant to various attacks, such as brute force, where attackers try every possible key, or cryptanalysis, where attackers find weaknesses in the algorithm itself.
The Evolution of Encryption Algorithms
Like all technological realms, the world of encryption algorithms has witnessed profound evolution. This transformation ensures that encryption keeps pace with the growing capabilities of potential attackers.
From DES to AES
While DES was groundbreaking in its time, it fell vulnerable to brute-force attacks due to its limited key size. The introduction of AES, with longer key lengths and a more complex encryption process, marked a significant advancement in encryption technology.
Rise of Asymmetric Cryptography
RSA introduced a revolutionary approach by using two distinct keys, changing the dynamics of encryption. This spurred the development of ECC, providing equivalent security to RSA but with shorter key lengths.
Quantum Computing and Beyond
The looming potential of quantum computers has driven the cryptography community to develop post-quantum encryption methods, which are believed to be resistant to quantum attacks. The journey of encryption algorithms is, thus, a continuous quest for stronger security in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
Navigating the Best End-to-End Encryption Software
In the modern digital landscape, securing communications and data is more critical than ever. One effective way to achieve this is by utilizing end-to-end encryption software. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into a review of popular software options, factors you should consider when making a choice, and expert recommendations to guide your decision. Step by step, we will equip you with the knowledge to choose the best encryption tool tailored for your needs.
Review of Popular End-to-End Encryption Software
In this section, we dissect and evaluate some of the renowned end-to-end encryption software solutions that have proven to be leaders in the industry.
- Encryption Algorithm: Signal Protocol
- User Friendly: Yes, with a simple and intuitive interface
- Features: Messaging, voice and video calls, file sharing
- Security: Renowned for robust security with end-to-end encryption enabled by default
Signal
- Encryption Algorithm: Signal Protocol
- User Friendly: Yes, with a focus on privacy and security
- Features: Messaging, voice and video calls, disappearing messages
- Security: Open-source and peer-reviewed, setting the gold standard for secure communications
| Attribute | Signal | |
|---|---|---|
| Algorithm | Signal Protocol | Signal Protocol |
| Usability | User-friendly with intuitive design | Privacy-focused user interface |
| Features | Extensive, including file sharing | Comprehensive, with added security features |
| Security Level | High, with end-to-end encryption default | Very high, with open-source and peer-reviewed credentials |
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Encryption Software
Before settling on an encryption software, it’s pivotal to assess certain criteria to ensure it caters to your specific needs and preferences. Here, we delineate some of the critical factors to keep in mind:
- Ease of Use
Consider the software’s user interface and how easy it is to navigate. It should offer a seamless experience even for individuals with limited technical knowledge.
- Features
Identify the features that are crucial for your communication needs — be it messaging, file sharing, or video calling.
- Security
Dive deep into the security protocols the software employs. It should ideally offer robust encryption to safeguard your data effectively.
- Cost
While many encryption tools are free, some offer premium features at a cost. Assess whether the premium features warrant the extra expense.
Expert Recommendations
In this crucial section, we bring to you the viewpoints of experts in the cybersecurity realm to help you make an informed decision.
For Individuals: For personal use, experts often recommend Signal due to its focus on privacy and a robust encryption protocol.
For Businesses: Business entities might find WhatsApp Business to be a viable option given its widespread use and features that facilitate professional communication.
Emerging Softwares: Keep an eye out for emerging software solutions like Wire and Threema which are steadily gaining reputation for both individual and business uses, bringing innovative features and robust security to the table.
Implementing End-to-End Encryption: A Detailed Guide for All
In the contemporary digital era, securing sensitive information is paramount. End-to-end encryption stands as a bastion of security in this context, shielding data from unauthorized access. Whether you are an individual looking to protect personal data or a business safeguarding critical information, understanding and implementing end-to-end encryption can be a lifesaver. In this guide, we traverse a step-by-step pathway to implement end-to-end encryption and delve into special considerations for different users.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Implement End-to-End Encryption
Embarking on the journey to secure your communications and data through end-to-end encryption? Here is a detailed roadmap to help you implement it meticulously:
Step 1: Research and Education
To grasp the essentials of encryption, particularly the mechanics of end-to-end encryption, and delve into the world of encryption algorithms and their vital roles in maintaining security, is paramount.
Step 2: Choosing the Right Platform
In the process of software evaluation, it’s crucial to assess various platforms that provide end-to-end encryption, considering their features and capabilities. Additionally, consulting with experts for recommendations can greatly aid in making an informed choice.
Step 3: Setup and Configuration
Once you’ve selected the encryption software or application that suits your needs, the next steps involve installing it and configuring the settings to activate end-to-end encryption, following the platform’s provided guidelines meticulously.
Step 4: Utilizing Encryption Tools
Mastering the responsible management of encryption keys is essential. Once proficient, you can initiate secure communication across various channels, including messaging, calls, and file transfers, ensuring your data remains safeguarded through encryption.
Step 5: Continuous Learning and Updates
Continual software updates are imperative to benefit from the most up-to-date security enhancements and patches. Simultaneously, ongoing learning about the ever-evolving encryption landscape is crucial for utilizing the tool effectively and maintaining a high level of security awareness.
Considerations for Businesses and Individual Users
As we delve deeper, it is imperative to spotlight the different considerations that businesses and individual users should entertain while venturing into end-to-end encryption.
For Businesses
- Compliance: Businesses must ensure they are compliant with regulatory requirements concerning data protection.
- Employee Training: Employees should be trained to use encryption tools efficiently and responsibly, emphasizing the importance of safeguarding sensitive data.
- Data Management: Companies should adopt secure data management practices, including regular backups and access controls.
For Individual Users
- Personal Data Protection: Individual users should prioritize protecting personal data, including photographs, financial details, and communication.
- Awareness: Being aware of phishing scams and other cyber threats is crucial. It’s vital to avoid sharing sensitive information through unencrypted or dubious platforms.
- Password Security: Implementing strong password policies is a foundational step in securing one’s digital footprint.
Understanding the Future of Encryption
In the ever-evolving landscape of encryption technology, staying ahead of the curve necessitates an understanding of the emerging trends and the influence of quantum computing on the future of encryption. As we navigate through this labyrinth of innovation, let us explore the upcoming trends shaping the encryption landscape and how quantum computing stands as a double-edged sword in the progression of encryption technology.
Upcoming Trends in Encryption Technology
As we stand on the cusp of technological advancements that are set to redefine the encryption sphere, it is pertinent to be aware of the trends that are expected to take center stage in the near future.
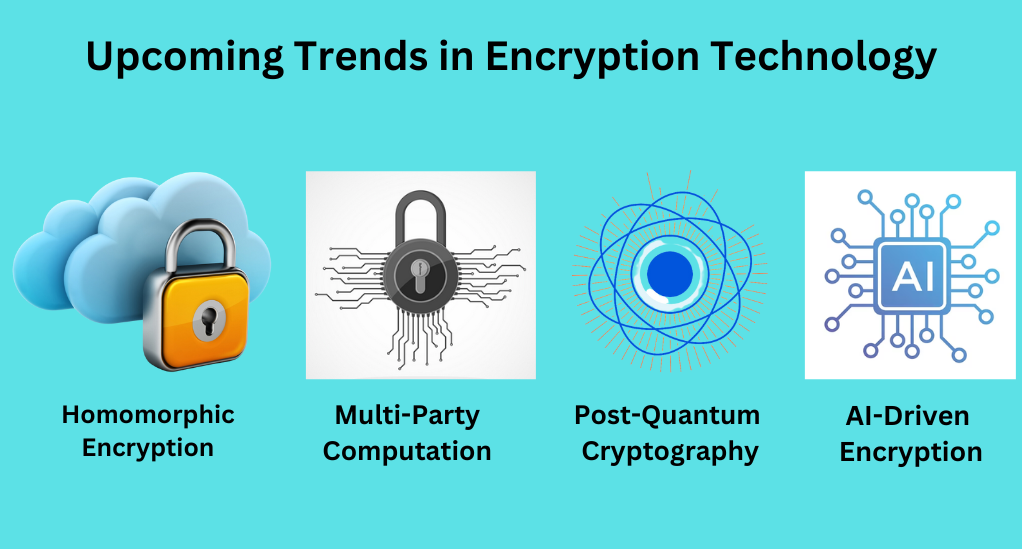
Homomorphic Encryption
Homomorphic encryption enables computations on encrypted data without decryption, crucial in secure cloud computing for data privacy and efficient resource use. It safeguards sensitive information during cloud computations, addressing today’s data-driven privacy and security concerns.
Multi-Party Computation
Multi-Party Computation in cryptography allows collaborative computation while keeping inputs confidential. It’s vital for privacy in analytics and secure voting systems, ensuring data stays private during collective computations.
Post-Quantum Cryptography
Post-Quantum Cryptography is a cryptographic approach specifically engineered to fortify data against potential quantum attacks. Its critical application lies in the protection of sensitive information from the looming threats posed by quantum computers, particularly in governmental and financial institutions, where the security of data is of utmost importance.
AI-Driven Encryption
AI-Driven Encryption enhances encryption and threat detection in business cybersecurity. It uses AI to adapt to evolving threats, offering proactive data protection in a complex digital landscape.
The Role of Quantum Computing in the Future of Encryption
Quantum computing, with its enormous computational power, is set to revolutionize encryption, bringing both opportunities and challenges to the forefront.
Opportunities and Challenges
Quantum computing presents both opportunities and challenges in the realm of cybersecurity. On the one hand, it offers the potential for enhanced security through the creation of nearly uncrackable encryption keys and faster cryptographic algorithms, bolstering the efficiency of secure communications. However, it also poses significant challenges by threatening current encryption standards like RSA and ECC, compelling the need for a transition to post-quantum cryptography, a process demanding substantial time and resources to ensure the continued protection of sensitive data in an evolving digital landscape.
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration into the futuristic landscape of encryption technology, it becomes increasingly clear that we are on the brink of unprecedented advancements. The emerging trends like homomorphic encryption and multi-party computation are charting a course towards a more secure digital future. Meanwhile, quantum computing stands as a groundbreaking force, bringing forth both formidable opportunities and challenges that necessitate a reevaluation and reinforcement of existing encryption frameworks. As we stand on this juncture, it is imperative to stay informed and prepared, ready to adeptly navigate the dynamic path that lies ahead in the encryption domain, thereby ensuring security and privacy in the continually evolving digital epoch.


Leave a Reply