Supply Chain Transparency: Revolutionizing Industries through Blockchain Technology
In the early stages of industrialization, supply chain management was a straightforward process, primarily focused on the transportation of goods from manufacturers to consumers. However, as industries expanded and globalized, the complexity of the supply chain exponentially increased, evolving into a network involving multiple stakeholders, each responsible for a specific segment of the value chain. Consequently, from the procurement of raw materials to production, distribution, and retail, the supply chain has transformed into a multifaceted ecosystem that demands meticulous management and coordination.
The Emergence of Blockchain Technology
In recent years, blockchain technology has emerged as a groundbreaking innovation with the potential to revolutionize various industries, including supply chain management. Initially conceived to support cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain has swiftly transcended its original purpose, offering a secure and transparent platform for transactions and data management.
Operating on a decentralized network, blockchain ensures that data is stored in blocks and linked in a chronological chain. Remarkably, this structure guarantees data immutability and transparency, as each transaction is recorded publicly and verified by network participants. Consequently, these characteristics position blockchain as an ideal solution for modernizing supply chain management, fostering transparency, and enhancing security.
Blockchain: A Brief Overview
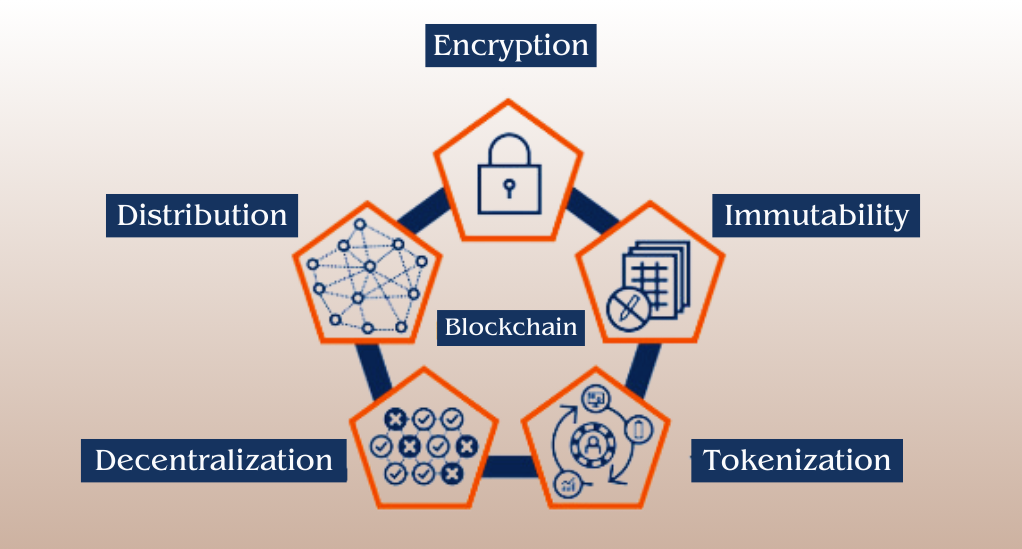
In the realm of digital advancements, blockchain stands as a pivotal digital ledger technology that meticulously records transactions across numerous computers, thereby ensuring the security and immutability of the data. Each block in the chain encapsulates a series of transactions, and remarkably, every time a new transaction unfolds on the network, a record of that transaction is seamlessly added to every participant’s ledger. This decentralized approach astutely prevents any single entity from exerting control over the entire blockchain, and consequently, all transactions are transparent and verifiable by all users.
Key Features and Benefits
- Decentralization: Unlike centralized systems, where a single entity has control over the data, blockchain operates on a decentralized network, enhancing security and reducing the risk of fraud.
- Transparency: All transactions on the blockchain are public, promoting transparency and allowing for easy verification of transactions.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered, ensuring the integrity of the data and preventing tampering.
- Security: Blockchain employs cryptographic techniques for securing data, making it extremely difficult to hack or manipulate.
| Aspect | Blockchain | Traditional Databases |
|---|---|---|
| Data Structure | Blocks linked in a chain | Tables and rows |
| Control | Decentralized (No single entity has control) | Centralized (Controlled by a single entity) |
| Transparency | High (All transactions are public) | Low (Restricted access to data) |
| Security | High (Cryptographic techniques, immutable records) | Variable (Dependent on security measures implemented) |
| Scalability | Moderate (Limited by block size and network consensus) | High (Can handle large volumes of data efficiently) |
The Intersection of Blockchain and Supply Chain
In the contemporary business environment, supply chains have become more global and complex than ever before. Consequently, this complexity brings forth several challenges, including a lack of transparency, inefficiencies, and vulnerabilities to fraud. Fortunately, the integration of blockchain technology into supply chain management can potentially address these issues, offering a new paradigm of operation that is secure, transparent, and efficient.
Current Challenges in Supply Chain Management
- Lack of Transparency
In traditional supply chains, the journey of a product from manufacturer to consumer involves multiple intermediaries, making it difficult to track and verify the authenticity of products. This lack of transparency can lead to counterfeit products entering the market and eroding consumer trust. - Inefficiencies
Supply chains often suffer from inefficiencies due to manual processes and disparate systems that do not communicate well with each other. These inefficiencies can result in delays, increased costs, and wasted resources. - Vulnerabilities to Fraud
Traditional supply chains are susceptible to fraud due to centralized control and lack of transparency. Fraudsters can manipulate data, leading to financial losses and damage to brand reputation.
How Blockchain Can Address These Challenges
Blockchain technology can revolutionize supply chain management by addressing the aforementioned challenges in the following ways:
1. Enhancing Transparency
Blockchain’s decentralized ledger allows for real-time tracking of products at every stage of the supply chain. This transparency ensures that all stakeholders have access to the same information, reducing the chances of fraud and counterfeit products.
2. Streamlining Operations
Blockchain can automate various processes in the supply chain through smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. This automation can streamline operations, reduce delays, and lower costs.
3. Improving Security
Blockchain’s immutable and secure nature makes it extremely difficult for fraudsters to manipulate data. This security feature can protect the supply chain from various forms of fraud, including data tampering and counterfeit products.
Smart Contracts and Supply Chain
In the blockchain ecosystem, smart contracts represent a significant innovation that has the potential to automate and streamline various processes in supply chain management. Let’s delve deeper into understanding the concept of smart contracts and their applications in the supply chain sector.
The Concept of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts where the terms and conditions are directly written into lines of code. These contracts are stored on the blockchain, making them transparent, immutable, and secure. The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that smart contracts are executed automatically when the specified conditions are met, without the need for intermediaries.
Applications in Supply Chain Management
Smart contracts can revolutionize supply chain management in several ways, including:
- Automated Payments
Smart contracts can automate payment processes, ensuring that payments are released automatically once the goods are delivered or services are rendered, reducing delays and disputes. - Quality Assurance
Smart contracts can be used to enforce quality standards. For instance, a smart contract can be programmed to reject goods if they do not meet the specified quality criteria, ensuring compliance with quality standards. - Real-Time Tracking and Reporting
Smart contracts can facilitate real-time tracking of goods by recording every transaction on the blockchain. This feature allows for transparent and efficient reporting, helping stakeholders to monitor the progress of shipments and manage inventory effectively. - Regulatory Compliance
Smart contracts can assist in ensuring regulatory compliance by automatically enforcing legal and contractual obligations, reducing the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties.
The Future of Supply Chain Management
As we stand on the cusp of a new era in supply chain management, it is imperative to explore the potential advancements that lie ahead. The integration of blockchain technology with predictive analytics, big data, and the Internet of Things (IoT) promises to revolutionize the supply chain landscape, fostering innovation and efficiency. Let’s explore these prospects in detail.
Predictive Analytics and Big Data
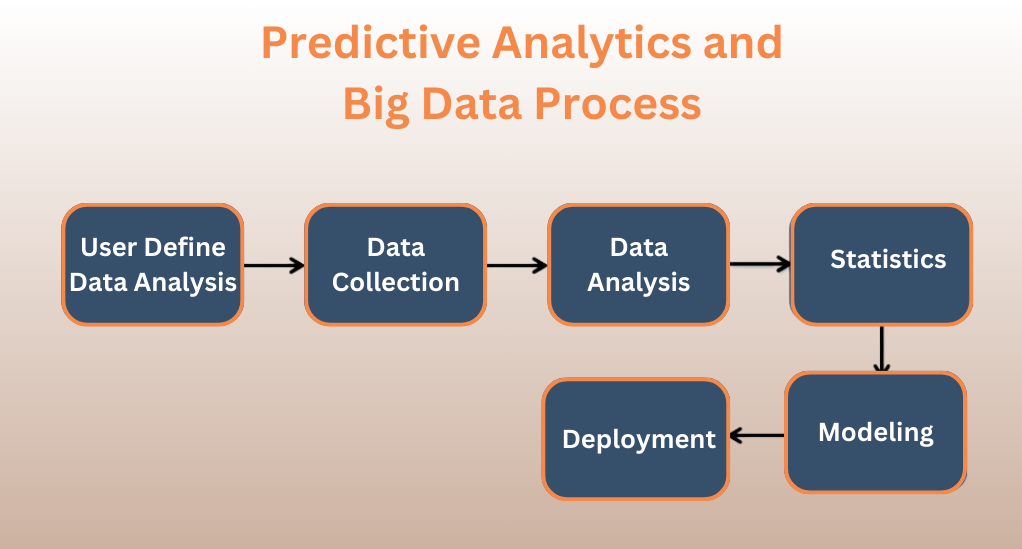
Predictive analytics and big data are set to play a pivotal role in the future of supply chain management. These technologies can work in tandem with blockchain to offer insights that can help in making informed decisions. Here’s how:
- Demand Forecasting
Predictive analytics can analyze historical data to forecast future demand accurately, helping businesses to optimize inventory levels and avoid stockouts or overstocking. - Risk Management
By analyzing vast datasets, businesses can identify potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate them, ensuring a smooth and resilient supply chain. - Consumer Behavior Analysis
Big data analytics can help in understanding consumer behavior patterns, enabling businesses to tailor their strategies to meet consumer preferences and enhance customer satisfaction.
Integration with Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) epitomizes a network of interconnected devices that seamlessly communicate with each other and share data. Significantly, the integration of IoT with blockchain can usher in a plethora of benefits to the supply chain sector:
Firstly, Real-Time Monitoring: IoT devices are capable of monitoring the condition of goods in transit in real-time, thereby providing valuable data that can be meticulously recorded on the blockchain. This ensures an unprecedented level of transparency and traceability.
Secondly, Automated Processes: IoT stands as a facilitator of automation in various supply chain processes, ranging from inventory management to logistics. This not only enhances efficiency but also significantly reduces manual interventions, paving the way for a streamlined workflow.
Lastly, Enhanced Security: The synergistic combination of IoT and blockchain fortifies security measures, establishing a secure and tamper-proof platform for data exchange. This robust integration acts as a shield, protecting the supply chain from potential fraud and cyber-attacks, thereby fostering a safer and more reliable supply chain ecosystem.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
As blockchain technology continues to permeate various sectors, including supply chain management, it brings along a set of legal and ethical considerations that need to be addressed. In this section, we will explore these aspects in detail, shedding light on the regulatory landscape and the ethical implications of adopting blockchain technology.
Data Security and Privacy
In the era of data-driven operations, ensuring data security and privacy becomes paramount. Blockchain, with its immutable and transparent nature, offers a secure platform for data management. However, it also raises concerns regarding data privacy, especially when sensitive information is involved. Organizations need to adhere to data protection regulations and implement measures to safeguard user privacy while maintaining transparency.
- GDPR Compliance
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a regulation that governs data protection and privacy in the European Union. Organizations utilizing blockchain technology need to ensure compliance with GDPR, particularly in terms of data erasure and user consent. - Intellectual Property Rights
Blockchain can be used to record and verify intellectual property rights, helping in preventing counterfeiting and piracy. However, it also necessitates the development of legal frameworks to govern the registration and enforcement of these rights on the blockchain.
Regulatory Compliance
Adopting blockchain technology in supply chain management requires adherence to existing regulations and standards. Organizations need to work closely with regulatory bodies to ensure compliance and foster a conducive environment for the integration of blockchain technology.
- Standardization
Standardization of blockchain protocols and technologies is essential to facilitate interoperability and widespread adoption. Industry stakeholders need to collaborate to develop standardized frameworks that govern the use of blockchain in supply chain management. - Legal Recognition
For blockchain-based transactions and smart contracts to be legally binding, there needs to be legal recognition of these technologies. Governments and regulatory bodies should work towards providing a legal framework that recognizes and governs blockchain transactions.
Ethical Considerations
The adoption of blockchain technology brings forth ethical considerations, particularly in terms of transparency and accountability. Organizations need to balance the benefits of transparency with the potential risks associated with data exposure.
- Responsible Data Management
Organizations should adopt responsible data management practices, ensuring that data recorded on the blockchain is accurate, reliable, and used ethically. - Inclusive Participation
Blockchain platforms should promote inclusive participation, ensuring that all stakeholders, including small-scale producers and marginalized communities, have equal access and representation on the platform.
Conclusion
In the rapidly evolving landscape of supply chain management, blockchain technology stands as a beacon of innovation, heralding a future of enhanced transparency and efficiency. Initially conceived to support cryptocurrencies, it has expanded its horizons to revolutionize the complex networks of modern supply chains. Through decentralization and the introduction of smart contracts, blockchain promises to mitigate fraud, streamline operations, and foster unprecedented levels of transparency and security.
However, this transformative journey is not without its challenges, particularly in the realms of data security and regulatory compliance. As we venture forward, the focus must be on fostering responsible data management and ensuring inclusive participation. Embracing blockchain technology paves the way for a resilient and efficient supply chain ecosystem, steering industries towards a future marked by collaboration, innovation, and sustainable growth.


Leave a Reply