
How to Implement a Successful Cloud Migration
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, organizations of all sizes are recognizing the transformative potential of cloud computing. The digital era demands swift adaptability, and cloud migration has emerged as a critical strategy to address this need. It offers a pathway for businesses to harness the power of remote servers and internet connectivity to reimagine their IT infrastructure. This introductory section sets the stage for comprehending the essence of cloud migration—an endeavor that transcends mere technological adoption. It is a strategic move toward optimization, resilience, and growth in an era defined by innovation and efficiency.
Cloud migration isn’t just a choice; it’s a necessity for organizations seeking to remain competitive in a dynamic marketplace. It embodies the promise of enhanced agility, cost optimization, and scalability. As we delve deeper into this guide, you’ll discover that cloud migration is more than a technological shift; it’s a fundamental shift in how businesses operate and innovate. It’s the journey that unlocks the potential for businesses to embrace digital transformation, seize opportunities, and secure their position in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
What is Cloud Migration?
At its core, cloud migration refers to the process of moving an organization’s data, applications, and IT resources from on-premises or legacy systems to cloud-based infrastructure. The cloud, in this context, represents a network of remote servers hosted on the internet, where data and services are stored and managed.
The Driving Forces Behind Cloud Migration
Several compelling factors drive organizations to embark on a cloud migration journey:
- Cost Efficiency: Cloud computing eliminates the need for large upfront capital expenditures on hardware and data centers. Instead, organizations can adopt a pay-as-you-go model, where they pay only for the resources they use. This cost-effective approach allows for budget flexibility and cost optimization.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud platforms provide scalability that traditional on-premises infrastructure cannot match. Organizations can easily scale up or down to accommodate changing workloads and demand spikes. This flexibility enables businesses to adapt to market fluctuations efficiently.
- Global Accessibility: Cloud services are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. This global accessibility promotes collaboration among geographically dispersed teams, fostering innovation and productivity.
- Security and Compliance: Leading cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, making it possible for organizations to enhance their data security and compliance. Many cloud platforms offer robust encryption, identity and access management, and compliance certifications.
- Innovation and Speed to Market: Cloud services often come with a wide array of tools and services, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and analytics. This empowers organizations to innovate rapidly and bring new products and services to market faster.
The Digital Transformation Imperative
In an era where digital transformation is a survival imperative, cloud migration plays a pivotal role. It enables organizations to modernize their IT infrastructure, accelerate innovation, and deliver enhanced customer experiences. A successful cloud migration can position a business to:
- Embrace Agile Practices: Cloud computing supports agile methodologies, allowing for quicker development cycles and more frequent releases.
- Leverage Big Data and Analytics: Cloud platforms provide the computational power needed to process and derive insights from vast amounts of data.
- Enhance Disaster Recovery: Cloud-based backups and disaster recovery solutions ensure business continuity and data resilience.
- Reduce Environmental Impact: Cloud providers often operate more energy-efficient data centers, reducing an organization’s carbon footprint.
Cloud migration is not merely a technological shift; it represents a strategic move toward business optimization and growth. The subsequent sections of this article will delve deeper into the critical steps, best practices, and strategies for a successful cloud migration. By the end of this guide, you will be well-equipped to embark on your organization’s cloud migration journey with confidence.
Assessing and Planning
Successful cloud migration commences with a meticulous process of assessment and planning. This initial phase serves as the cornerstone upon which a seamless transition to the cloud is built. Within this critical stage, we delve into the essential steps and key considerations that underpin the entire migration journey.
Understanding Your Current Infrastructure
Before you can embark on a cloud migration journey, it’s imperative to have a comprehensive understanding of your existing IT infrastructure. This involves:
- Inventory: Create an inventory of all hardware, software, and applications currently in use. This will serve as a baseline for migration planning.
- Performance Analysis: Evaluate the performance of your existing systems to identify bottlenecks and areas that require improvement.
- Dependency Mapping: Map out the interdependencies between various components within your infrastructure. Understand how different systems and applications rely on each other.
- Data Assessment: Examine the volume, type, and sensitivity of data you are handling. Determine which data needs to be migrated and which can be archived or deleted.
Identifying Goals and Objectives
Clearly defined goals and objectives are essential for a successful cloud migration. Consider the following questions:
- Why Are You Migrating? Define the specific reasons for migrating to the cloud. Is it to reduce costs, improve scalability, enhance security, or enable remote work?
- Business Impact: What impact do you expect this migration to have on your business? Will it lead to revenue growth, operational efficiency, or competitive advantages?
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Establish measurable KPIs that will help you assess the success of your migration efforts. These could include reduced infrastructure costs, increased application performance, or enhanced user satisfaction.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategies
Migrating to the cloud involves inherent risks. It’s essential to identify potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate them:
- Security Risks: Assess the security implications of moving data and applications to the cloud. Develop a robust security strategy that includes encryption, access controls, and threat detection.
- Compliance Concerns: Ensure that your migration complies with industry-specific regulations and standards. This is especially critical in highly regulated sectors like healthcare and finance.
- Downtime and Disruptions: Plan for potential downtime during the migration process. Implement strategies to minimize disruptions to business operations.
- Cost Overruns: Keep a close eye on costs and budget constraints. Consider using cost estimation tools provided by cloud providers to avoid unexpected expenses.
The assessment and planning phase is the cornerstone of a successful cloud migration. It provides the necessary insights and strategies to ensure a smooth transition. Once you have a clear understanding of your current infrastructure, defined objectives, and risk mitigation plans, you can proceed to the next stages of selecting the right cloud service model and choosing the ideal cloud provider.
Selecting the Right Cloud Service Model
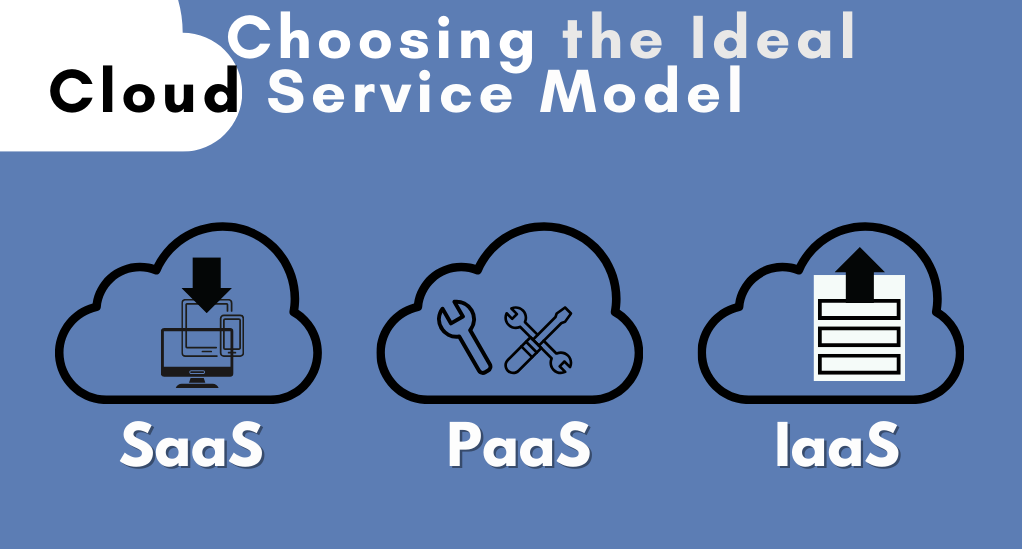
Choosing the appropriate cloud service model is a critical decision in your cloud migration journey. Cloud computing offers three primary service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Let’s explore these models and how to make the right choice.
Comparing IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. It offers a scalable infrastructure foundation that allows you to deploy and manage virtual machines, storage, and networking components. IaaS is ideal if you require more control over the underlying infrastructure, making it suitable for applications that demand customization and scalability.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offers a higher-level development environment. It provides tools and services that streamline application development, deployment, and management. PaaS is an excellent choice for organizations looking to accelerate application development cycles and reduce the operational overhead of managing infrastructure.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS delivers fully functional software applications over the internet. Users can access these applications through web browsers without the need for installation or maintenance. SaaS is ideal for businesses seeking ready-to-use solutions, such as email, customer relationship management (CRM), or collaboration tools.
Choosing Public, Private, or Hybrid Cloud
Once you’ve determined the appropriate service model, the next decision is the cloud deployment model. There are three primary deployment options:
- Public Cloud: Public clouds are hosted and managed by third-party cloud providers, making them cost-effective and scalable. They are ideal for organizations that need on-demand resources and don’t want to invest in physical infrastructure.
- Private Cloud: Private clouds are dedicated to a single organization, providing greater control, customization, and security. They are suitable for businesses with stringent security and compliance requirements.
- Hybrid Cloud: Hybrid clouds combine elements of both public and private clouds. This approach allows organizations to leverage the benefits of public cloud scalability while maintaining sensitive data and critical applications in a private environment. It provides flexibility and data redundancy.
Factors to Consider in Provider Selection
Choosing the right cloud provider is a crucial decision. Factors to consider include:
- Service Offerings: Evaluate the range of services and tools offered by the provider. Consider whether they align with your business needs.
- Reliability and Uptime: Check the provider’s uptime track record and service-level agreements (SLAs). Downtime can have significant impacts on your business.
- Security and Compliance: Assess the provider’s security practices, certifications, and compliance with industry standards.
- Cost Structure: Understand the provider’s pricing model. Compare costs with your budget and long-term growth projections.
- Geographical Reach: Consider the provider’s global data center presence if your organization operates internationally.
Selecting the right cloud service model and provider is a critical step in your cloud migration journey. It lays the foundation for how your applications and data will be hosted and managed in the cloud. Once you’ve made these decisions, you can move on to the next stages of data migration strategies and application migration, which we will explore in the following sections.
Data Migration Strategies

Migrating data to the cloud is undeniably pivotal in the context of a successful migration journey. This fundamental step hinges on the efficient and secure transfer of critical information from legacy systems to the new cloud environment. The accuracy, integrity, and accessibility of data are central to the continuity and effectiveness of organizational operations, making data migration a linchpin of the overall process.
Efficiency in data migration translates into minimal disruptions, reduced downtime, and optimized resource utilization, all of which contribute to a smoother transition. Moreover, it ensures that the valuable data upon which decision-making and business processes rely is readily available in the cloud environment. As we delve further into this guide, you’ll discover the meticulous strategies and practices that underpin successful data migration, safeguarding the lifeblood of your organization’s digital operations.
Data Classification and Categorization
Before migrating data to the cloud, it’s essential to classify and categorize your data. This involves:
- Identifying Critical Data: Determine which data is mission-critical and should be prioritized for migration. This may include customer data, financial records, and core business information.
- Sensitive Data Identification: Identify and tag sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information (PII) and financial records. Implement encryption and access controls for added security.
- Data Ownership: Assign ownership and responsibility for different data sets. Clarify who within your organization is responsible for specific data categories.
Data Transfer Methods and Tools
Selecting the right data transfer methods and tools is crucial for a smooth migration process. Consider the following options:
- Bulk Transfer: For large volumes of data, consider using offline transfer methods, such as shipping physical drives to the cloud provider’s data center. This can be faster and more cost-effective than transferring data over the internet.
- Online Transfer: Smaller datasets can be migrated online using secure data transfer protocols like HTTPS or FTP. Cloud providers often offer data transfer services to facilitate this process.
- Data Transfer Appliances: Some cloud providers offer physical data transfer appliances that can be connected to your on-premises infrastructure for high-speed data transfer.
- Data Migration Tools: Explore third-party data migration tools and services that can help automate and streamline the data migration process. These tools often include data validation and error-checking features.
Ensuring Data Security and Compliance
Data security and compliance are paramount when migrating data to the cloud. Implement the following security measures:
- Encryption: Encrypt data both in transit and at rest. Most cloud providers offer encryption services and key management options.
- Access Controls: Implement robust access controls and permissions to restrict data access to authorized personnel only.
- Data Auditing: Enable data auditing and logging to monitor access and changes to your data. This is essential for compliance and security.
- Compliance Certification: Ensure that your cloud provider complies with industry-specific regulations and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2.
A well-executed data migration strategy is vital for preserving data integrity and security during the cloud migration process. Once your data is successfully migrated, the next phase involves addressing the migration of applications, which we will explore in the following section.
Application Migration
Application migration stands as a pivotal phase within the overarching cloud migration journey. The successful transition of your applications to the cloud demands a deliberate and strategic approach, marked by meticulous planning, comprehensive compatibility assessments, and exhaustive testing protocols. It is in this phase that the heart of your organization’s digital operations, embodied by its software and applications, undergoes a transformative migration.
Careful planning and precise execution during application migration are essential to ensure the seamless functioning of your business processes. Compatibility assessments reveal the intricacies of your software and its interdependencies with the cloud environment, while thorough testing guarantees that the applications function optimally in their new digital home. As you journey further into this guide, you will gain insights into the strategies and best practices that facilitate the successful migration of your organization’s applications, setting the stage for enhanced productivity and innovation in the cloud.
Assessing Application Compatibility
Before migrating applications to the cloud, it’s essential to assess their compatibility with the chosen cloud environment. Consider the following factors:
- Operating System Compatibility: Ensure that your application’s operating system is supported by the cloud provider. Compatibility issues can arise if your application relies on specific OS features.
- Dependencies and Libraries: Identify and document all dependencies and libraries that your application relies on. Ensure that these dependencies are available and compatible in the cloud environment.
- Licensing and Compliance: Review software licenses to ensure compliance in the cloud. Some licenses may require modifications or may not be transferrable to the cloud.
Refactoring and Rehosting Applications
Depending on your application’s architecture, you may need to choose between refactoring and rehosting:
- Rehosting (Lift and Shift): In rehosting, you migrate your application to the cloud with minimal modifications. This approach is suitable for applications that can run in the cloud environment with little to no changes. It’s a quick and cost-effective way to migrate.
- Refactoring (Cloud-Native Transformation): Refactoring involves optimizing your application for the cloud-native environment. This may include redesigning components, using cloud-native services, and adopting microservices architecture. While more complex, this approach can lead to greater scalability and cost savings.
Testing and Quality Assurance
Thorough testing is crucial to ensure that migrated applications function correctly and meet performance expectations:
- Functional Testing: Verify that your application’s core functions work as expected in the cloud environment.
- Performance Testing: Assess the performance of your application under different workloads and conditions. Identify bottlenecks and optimize as needed.
- Security Testing: Conduct security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and ensure that security measures are in place.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Involve end-users in testing to validate that the application meets their needs and expectations.
- Rollback Plan: Prepare a rollback plan in case issues arise during migration. This plan should outline steps to revert to the previous environment without data loss.
Incremental Migration
Consider adopting an incremental migration approach, where you migrate applications in phases rather than all at once. This allows you to identify and resolve issues incrementally, reducing the impact of potential disruptions.
Application migration is a complex but necessary step in your cloud migration journey. Careful assessment, compatibility testing, and the choice between rehosting and refactoring are key factors in a successful migration. Once your applications are successfully migrated, the next phase involves post-migration optimization, which we will explore in the following section.
Post-Migration Optimization
After successfully migrating your data and applications to the cloud, the journey doesn’t end; it transforms. The post-migration phase focuses on optimizing your cloud environment to ensure that it operates efficiently, securely, and cost-effectively. Let’s explore the critical aspects of post-migration optimization.
Performance Monitoring and Tuning
Effective performance monitoring and tuning are essential to ensure that your cloud resources are used efficiently:
- Resource Utilization: Continuously monitor resource utilization to identify over-provisioned or underutilized resources. Adjust resource allocation accordingly to optimize costs.
- Application Performance: Utilize monitoring tools to track application performance metrics such as response times, latency, and error rates. Address performance issues promptly to maintain a positive user experience.
- Scaling: Implement auto-scaling policies that automatically adjust resource allocation based on demand. This ensures that your applications can handle traffic spikes without incurring unnecessary costs during low-demand periods.
Cost Management and Optimization
Cost management is a continuous effort to control and optimize cloud expenses:
- Cost Visibility: Use cloud provider cost management tools to gain visibility into your cloud spending. Categorize and analyze costs to identify areas where savings can be realized.
- Cost Allocation: Allocate costs to specific departments or projects within your organization to promote accountability and budget transparency.
- Reserved Instances: Take advantage of reserved instances or savings plans offered by cloud providers to secure lower pricing for predictable workloads.
- Resource Tagging: Implement resource tagging to track and categorize cloud resources. This enables more granular cost analysis and allocation.
Scaling for Future Growth
Cloud migration is not just about immediate benefits; it’s also about future-proofing your IT infrastructure:
- Capacity Planning: Continually assess your organization’s growth and future resource needs. Plan for scaling resources and applications accordingly.
- Cloud Native Services: Explore and leverage cloud-native services and technologies to stay at the forefront of innovation and scalability.
- Security and Compliance: Regularly review and update security and compliance measures to adapt to evolving threats and regulatory requirements.
- Disaster Recovery: Ensure that your cloud environment includes robust disaster recovery and backup solutions to safeguard against data loss and disruptions.
Continuous Improvement
Post-migration optimization is an ongoing process. Establish a culture of continuous improvement, where teams are encouraged to identify and implement enhancements to the cloud environment. Regularly review performance metrics, costs, and security measures to refine your cloud strategy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, implementing a successful cloud migration is a multifaceted journey that can transform your organization’s IT infrastructure, operations, and competitiveness. This comprehensive guide has provided you with a structured approach to navigate this process effectively.
From understanding the fundamentals of cloud migration to assessing your existing infrastructure, selecting the right cloud service model and provider, and meticulously planning the migration, you have learned the critical steps involved in the early phases.
You’ve also explored the intricacies of data migration, including data classification, transfer methods, and security measures. Application migration was discussed, emphasizing compatibility assessment, refactoring, and thorough testing to ensure a smooth transition.
The post-migration phase was examined in detail, highlighting the importance of performance monitoring, cost management, scalability, and a commitment to continuous improvement.
By following the insights and best practices outlined in this guide, you are well-equipped to embark on your cloud migration journey with confidence. Successful cloud migration can unlock new opportunities for innovation, agility, and growth within your organization, ultimately positioning you for success in today’s dynamic digital landscape.
As you move forward, remember that cloud migration is not a one-time event but an ongoing strategy that adapts to the evolving needs of your business. Embrace the transformative power of the cloud, and may your journey be marked by efficiency, security, and prosperity.
Should you have any further questions or require additional assistance on specific aspects of cloud migration, do not hesitate to seek expert guidance and resources tailored to your organization’s unique requirements.
Safe travels on your path to cloud success!


Leave a Reply