How to Set Up Mesh Networks for Superior Home Connectivity
In today’s digital age, having a reliable and fast internet connection is no longer a luxury but a necessity. Whether you’re working from home, streaming your favorite shows, or simply browsing the web, a stable connection is crucial. Enter mesh networks, a revolutionary approach to home connectivity that promises to change the way we think about our online experiences.
What is a Mesh Network?
A mesh network is a type of local area network (LAN) topology where infrastructure nodes (like bridges, switches, and other devices) connect directly, dynamically, and non-hierarchically to as many other nodes as possible. This direct connection between nodes ensures that data can be efficiently routed to and from clients without relying on a central node or router.
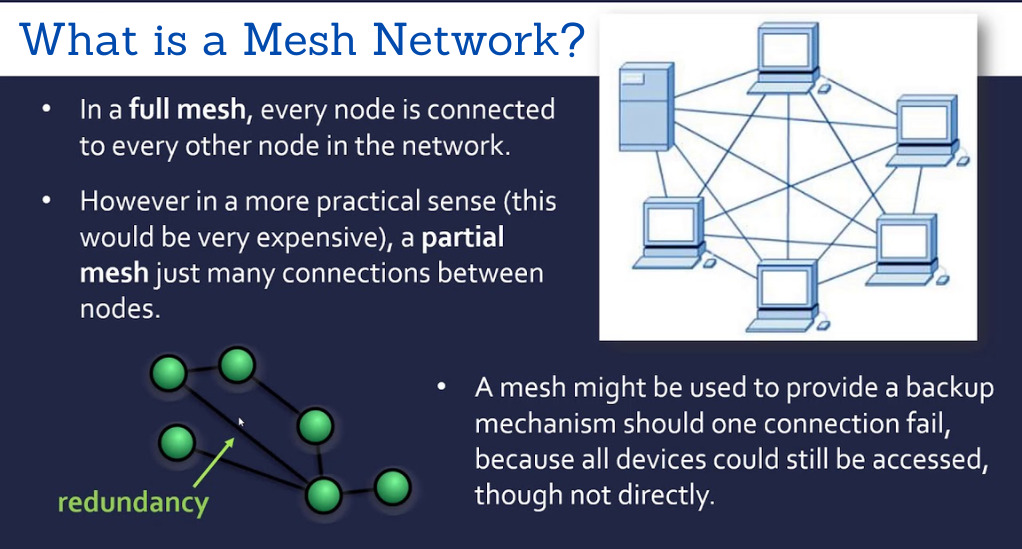
Imagine a fishing net, where each knot represents a node, and the strings connecting them represent the connections. In a mesh network, data can travel through multiple paths to reach its destination, ensuring that even if one path is blocked or fails, there are other routes available.
| Traditional Network | Mesh Network |
|---|---|
| Centralized, relying on a main router | Decentralized, with multiple nodes |
| Limited paths for data transfer | Multiple paths for data routing |
| If the main router fails, the network goes down | If one node fails, data finds another path |
How Does it Differ from Traditional Networks?
Traditional networks, especially in home settings, often rely on a single router to distribute the internet connection to various devices. This setup can lead to ‘dead zones’ or areas in your home where the signal is weak or non-existent. Moreover, if the central router fails, the entire network goes down.
On the other hand, mesh networks eliminate these issues. Since they don’t rely on a single point of access, they can cover larger areas more effectively, reducing or eliminating dead zones. Additionally, the decentralized nature of mesh networks means that they are inherently more resilient. If one node fails, the network dynamically re-routes data through other nodes, ensuring continuous connectivity.
Advantages of Mesh Networks
The rise in popularity of mesh networks isn’t just due to their innovative design; it’s also because of the myriad of benefits they offer over traditional networking systems. Let’s delve deeper into the advantages of adopting a mesh network for your home.
Dynamic Self-organization and Configuration
One of the standout features of mesh networks is their ability to dynamically self-organize and self-configure. What does this mean for the average user? In simple terms, setting up a mesh network is relatively hassle-free. As you add new nodes (or devices) to the network, they automatically find the best way to connect with existing nodes. This dynamic configuration reduces the need for manual setup and adjustments, making the process user-friendly even for those who aren’t tech-savvy.
Fault-tolerance and Reduced Maintenance Costs
Mesh networks are designed with resilience in mind. Due to their decentralized structure, the failure of a single node doesn’t bring down the entire network. Instead, the data finds alternative paths, ensuring continuous connectivity. This fault-tolerance not only provides peace of mind for users but also translates to reduced maintenance costs. With fewer network downtimes and disruptions, there’s less need for frequent technician visits or system overhauls.
Efficient Data Routing
In traditional networks, data often has to pass through multiple routers or switches before reaching its destination, leading to potential bottlenecks and slower speeds. Mesh networks, with their direct node-to-node connections, ensure that data takes the most efficient route possible. This results in faster data transfer speeds and a smoother online experience, whether you’re streaming high-definition videos, gaming, or attending a video conference.
Understanding Mesh Topology
To truly appreciate the benefits of mesh networks, it’s essential to understand the underlying structure or topology that makes them so unique and efficient. Mesh topology stands in contrast to other common network structures, and its design principles are what give it an edge.
Comparison with Star/Tree Network Topologies
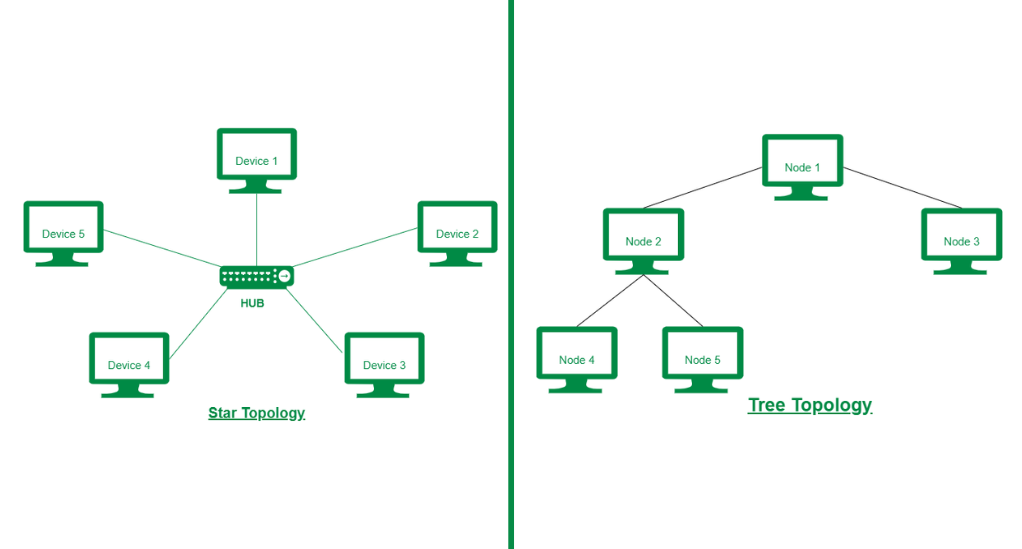
Most traditional home networks follow a star or tree topology. In these setups:
- Star Topology: Every device (or node) connects directly to a central hub or router. If the central hub fails, the entire network becomes inoperative. While this setup is straightforward and easy to manage, it’s not the most resilient.
- Tree Topology: This is a hybrid topology that combines characteristics of star and bus topologies. It consists of groups of star-configured networks connected to a linear bus backbone. While it offers more connection points than a pure star topology, it still has single points of failure.
Mesh Topology, on the other hand, is a game-changer. Here’s how:
- Every node is connected, either directly or indirectly, to every other node in the network.
- Data can take multiple paths to reach its destination, ensuring continuous connectivity even if certain paths or nodes fail.
- There’s no single point of failure. If one node goes offline, the network reroutes data through other nodes.
| Topology Type | Single Point of Failure? | Scalability | Resilience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Star | Yes (Central Hub) | Moderate | Low |
| Tree | Yes | High | Moderate |
| Mesh | No | Very High | Very High |
The Concept of Fully Connected Networks
Within the realm of mesh topology, there’s a subset known as a “fully connected network.” In this setup, every node is directly connected to every other node. While this ensures maximum redundancy and reliability, it can be costly and complex due to the sheer number of connections required.
For instance, in a network of 5 nodes, there would be 10 direct connections. As the number of nodes increases, the number of required connections grows exponentially. While fully connected networks offer unparalleled reliability, they might be overkill for smaller setups and are more commonly found in critical infrastructure where network failure is not an option.
Basic Principles of Mesh Networks
Diving deeper into the world of mesh networks, it’s essential to grasp the foundational principles that drive their operation. These principles not only dictate how data is transmitted but also ensure the network’s adaptability and resilience.
Routed vs. Flooding Techniques
Mesh networks employ two primary techniques for data transmission: routing and flooding.
- Routed Technique: In this method, data is propagated along a specific path, hopping from one node to the next until it reaches its intended destination. The network determines the most efficient route based on various factors, such as node availability and traffic load. This targeted approach minimizes unnecessary data broadcasts and optimizes network performance.
- Flooding Technique: Here, data is broadcasted to all nodes in the network. While this ensures that the information reaches its destination, it can lead to redundant data transmissions and potential network congestion. Flooding is typically used in scenarios where the network topology is unknown or constantly changing.
Self-healing Algorithms: The Backbone of Mesh Networks
One of the standout features of mesh networks is their ability to “self-heal.” This means that if a particular path or node becomes unavailable, the network can automatically find an alternative route for data transmission. Two primary algorithms drive this capability:
- Shortest Path Bridging (SPB): As the name suggests, this algorithm determines the shortest and most efficient path for data transmission. If a node or connection fails, SPB recalculates and identifies a new optimal route.
- TRILL (TRansparent Interconnection of Lots of Links): TRILL is designed to overcome issues in traditional Ethernet networks by introducing a new way to handle data frames. It allows for multiple active paths without the risk of loops, ensuring efficient data routing.
Network Reliability: More Than One Way to Connect
The beauty of mesh networks lies in their inherent redundancy. Since there’s often more than one path between a source and its destination, the network can maintain its performance even when certain nodes or connections fail. This multipath approach not only ensures continuous connectivity but also optimizes data transfer speeds by balancing the load across various routes.
Wired vs. Wireless: Mesh Networks Span Both Realms
While mesh networks are commonly associated with wireless setups, the principles can also apply to wired networks. In wired mesh networks, the direct connections between nodes (often via Ethernet cables) ensure a stable and high-speed connection. However, the cost and complexity can increase with the number of nodes due to the physical cabling required.
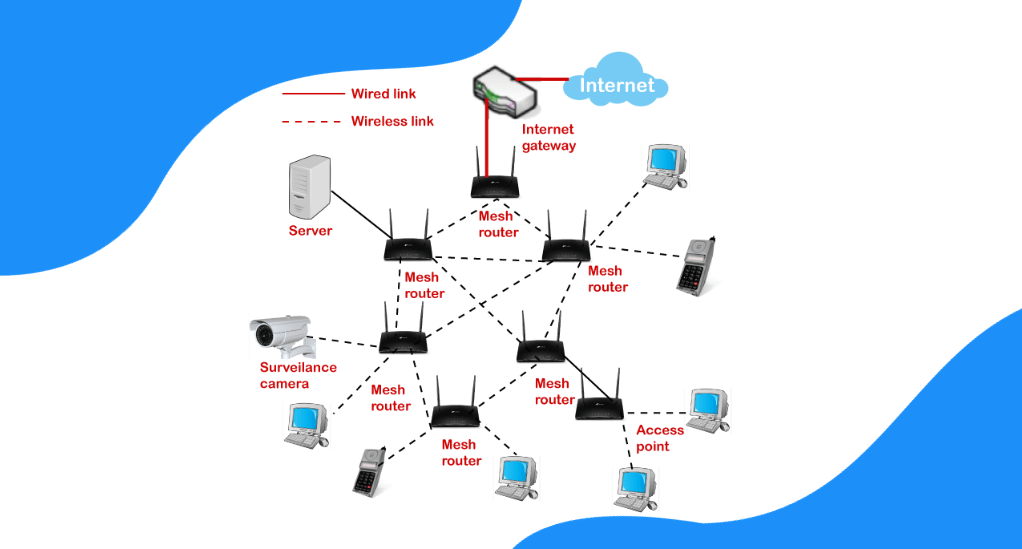
Setting Up Your Mesh Network at Home
With a clear understanding of the principles and advantages of mesh networks, the next logical step is to implement one in your home. Setting up a mesh network might seem daunting, but with the right guidance, it can be a straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you establish a robust mesh network for superior home connectivity.
Equipment Needed
Before diving into the setup, ensure you have the necessary equipment:
- Mesh Network Kits: These are readily available from various manufacturers and typically include multiple nodes or points to cover your entire home.
- Ethernet Cables: While many mesh systems operate wirelessly, having Ethernet cables can be beneficial for initial setup or for wired backhaul connections.
- A Broadband Modem: This connects to your service provider and acts as the gateway to the internet.
- A Smartphone or Computer: Most mesh systems come with a dedicated app or web interface for setup and management.
Step-by-Step Setup Guide
- Position Your Primary Node: Connect the primary node (often the main router) to your modem using an Ethernet cable. This node will act as the gateway to the internet. Place it in a central location, preferably elevated, to ensure optimal signal distribution.
- Power Up & Connect: Turn on the primary node and wait for it to boot up. Using your smartphone or computer, connect to the node’s default Wi-Fi network. Details are usually provided in the user manual or on a sticker on the device.
- Install the Mesh App: Download and install the manufacturer’s app on your smartphone. This app will guide you through the setup process, from naming your network to setting a secure password.
- Add Additional Nodes: Depending on the size of your home and the coverage needed, position additional nodes throughout your house. The app will often provide guidance on optimal placement and will test the connection strength between nodes.
- Test the Network: Once all nodes are connected, perform a speed test to ensure you’re getting the desired bandwidth. Walk around your home and check for any dead zones. Adjust the position of nodes if necessary.
- Configure Advanced Settings: Dive into the app settings to explore advanced features. You can set up guest networks, parental controls, prioritize devices, and more.
- Regularly Update Firmware: Manufacturers frequently release firmware updates to improve performance, add features, or patch security vulnerabilities. Ensure your mesh system is set to automatically update or regularly check for updates manually.
Maintaining and Troubleshooting Your Mesh Network
Once your mesh network is up and running, it’s essential to ensure its continued performance and address any issues that may arise. Like any technology, mesh networks require regular maintenance and occasional troubleshooting. Here’s a guide to keeping your network in top shape and resolving common problems.
Regular Maintenance Tips
- Monitor Network Health: Use the manufacturer’s app or a third-party network monitoring tool to keep an eye on the health of your network. This can provide insights into bandwidth usage, node performance, and potential weak spots.
- Reposition Nodes as Needed: As you add more devices or make changes to your home’s layout, you might need to adjust the position of some nodes to ensure optimal coverage.
- Change Passwords Periodically: For security reasons, it’s a good practice to change your network’s password from time to time. This can prevent unauthorized access and potential bandwidth leeching.
- Backup Network Settings: Most mesh system apps allow you to backup your network settings. Doing so ensures that you can quickly restore your network in case of a reset or when replacing a node.
- Stay Informed: Manufacturers often release newsletters or blogs detailing new features, best practices, and potential issues. Subscribing to these can keep you informed and help you get the most out of your mesh network.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Node Offline: If a node goes offline, first check its power source and cables. If everything seems fine, try restarting the node. If it still doesn’t connect, consider resetting it and adding it back to the network via the app.
- Slow Internet Speeds: If you notice a drop in internet speeds, first check if the issue is with your service provider. If the internet connection is fine, consider the following:
- Device Limit: Too many devices connected to a single node can reduce speeds. Distribute devices evenly among nodes.
- Interference: Ensure nodes are away from devices that can cause interference, like microwaves or cordless phones.
- Backhaul Issues: If you’re using a wired backhaul, check the Ethernet cables and connections.
- Inconsistent Coverage: If certain areas of your home have weak signals, try repositioning the nodes or adding an additional node to cover that area.
- Device Connection Issues: If a specific device struggles to connect, forget the network on that device and reconnect. Ensure the device’s software or firmware is up-to-date.
- Network Resets: If you’re facing multiple issues or the network becomes unresponsive, consider performing a full network reset. Remember to backup your settings before doing so.
Conclusion
In the digital age, where our homes, devices, and lives are intricately intertwined with the internet, having a reliable and robust network is paramount. Mesh networks emerge as a beacon of hope in this landscape, offering unparalleled connectivity, flexibility, and resilience. From understanding its foundational principles to setting it up and ensuring its optimal performance, we’ve journeyed through the intricacies of mesh networking. While technology will continue to evolve, the essence remains the same: to provide seamless, uninterrupted connectivity. As we embrace the future, mesh networks stand as a testament to our relentless pursuit of better, faster, and more reliable digital experiences. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or someone simply seeking a buffer-free streaming session, the promise of mesh networks is clear: a connected world, without boundaries.


Leave a Reply