How to Protect Your Personal Data Online
In today’s digital age, the vast majority of our personal and professional lives are intertwined with the online world. From social media interactions to online banking, and from e-commerce shopping to work-related tasks, the internet is a treasure trove of personal data. This makes it a prime target for cybercriminals. Understanding the risks associated with online data breaches and the significance of protecting your data has never been more crucial.

Why is Online Data Protection Essential?
- Personal Privacy: At the most basic level, everyone has a right to privacy. This includes the right to keep personal details, preferences, communications, and browsing habits away from prying eyes.
- Financial Security: Many online data breaches aim to access financial information. Stolen credit card details, bank account numbers, or even just your full name and address can be used fraudulently, leading to financial loss.
- Professional Reputation: For professionals and businesses, a data breach can mean a loss of customer trust, damage to reputation, and even legal repercussions.
- Identity Theft: One of the most severe outcomes of a data breach is identity theft. Cybercriminals can use personal data to impersonate individuals, leading to a range of crimes from fraudulent financial transactions to misrepresentation.
Installing Antivirus Software
In the vast landscape of the internet, various malicious entities, often referred to as malware, lurk in the shadows. These can range from viruses and trojans to ransomware and spyware. One of the primary defenses against such threats is antivirus software.
What is Antivirus Software?
Antivirus software is a program designed to detect, prevent, and remove malicious software from your computer or network. It acts as a security guard, constantly monitoring for suspicious activity and threats, and taking action when needed.
Why is Antivirus Essential?
- Real-time Protection: Modern antivirus solutions offer real-time scanning, which means they continuously monitor your computer for signs of malicious activity. This ensures that threats are detected and dealt with as soon as they appear.
- Comprehensive Scanning: Apart from real-time protection, antivirus software can perform deep scans of your entire system, identifying hidden threats or dormant malware.
- Protection Against Phishing: Many antivirus solutions now come with anti-phishing tools. Phishing attacks are attempts by scammers to trick you into giving out personal information by pretending to be a trustworthy entity.
- Regular Updates: Cyber threats are continually evolving. Antivirus software is regularly updated to recognize and combat the latest malware strains.
Choosing the Right Antivirus:
When selecting an antivirus solution, consider the following factors:
- Reliability: Ensure the software is from a reputable provider.
- Performance Impact: Some antivirus programs can slow down your system. Opt for one that provides robust protection without significantly affecting performance.
- Features: Look for additional features like firewalls, VPNs, and password managers.
- Cost: While many excellent free antivirus solutions exist, sometimes it’s worth investing in a premium version for advanced features.
| Antivirus Software | Key Features | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Norton | Real-time protection, VPN, Password Manager | Premium |
| McAfee | Home Network Security, Identity Theft Protection | Premium |
| Avast | Free version available, Wi-Fi security scans | Free/Premium |
| Bitdefender | Multi-layer ransomware protection, VPN | Premium |
| Kaspersky | Privacy protection, Safe Money feature | Premium |
Crafting Strong Passwords
Passwords are the keys to our digital lives. They guard our personal, financial, and professional information. However, the strength and uniqueness of these passwords determine the robustness of this protection. A weak password is akin to a flimsy lock on a treasure chest—it won’t hold up against a determined intruder.
The Pitfalls of Weak Passwords
- Predictability: Common passwords like “password123” or “qwerty” are the first ones hackers try. Using easily guessable passwords leaves your accounts vulnerable.
- Personal Information: Passwords based on personal information, such as birthdays or names, can be easily cracked, especially if this information is publicly available.
- Reusing Passwords: Using the same password across multiple sites is risky. If one site is compromised, all your accounts become vulnerable.
Tips for Creating Robust Passwords
- Length Matters: A longer password is generally more secure than a shorter one. Aim for at least 12 characters.
- Mix It Up: Use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special symbols.
- Avoid Dictionary Words: Password cracking tools often use dictionary attacks. Avoid using complete words found in the dictionary.
- Use Phrases: Consider using a random combination of words or a memorable phrase, making it both long and complex.
- Regularly Update: Change your passwords periodically. If a service you use has been breached, change your password for that service immediately.
Password Managers: Your Digital Vault
Remembering a unique, strong password for every account can be challenging. This is where password managers come in:
- What are they? Software that stores and manages your passwords in an encrypted format.
- How do they work? You only need to remember one strong master password. The manager does the rest, auto-filling login fields when needed.
- Additional Features: Many offer password generation tools, ensuring you always have a strong, random password.
| Password Manager | Key Features | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| LastPass | Cloud-based, browser extension, mobile app | Free/Premium |
| Dashlane | VPN service, dark web monitoring | Premium |
| 1Password | Travel mode (hide certain vaults), breach reports | Premium |
| Keeper | Biometric login, secure file storage | Premium |
| Bitwarden | Open-source, self-hosting option | Free/Premium |
Risks of Public Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi networks, often found in cafes, airports, and libraries, offer the convenience of internet access on the go. However, this convenience often comes at the cost of security. These open networks are playgrounds for cybercriminals, making it essential to understand the risks and navigate them with caution.
Why Public Wi-Fi Can Be Dangerous
- Unencrypted Networks: Most public Wi-Fi networks are unencrypted, meaning the data you send and receive is visible to others on the same network. This can include login credentials, personal messages, and financial information.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Cybercriminals can intercept the data being transferred between your device and the network, capturing sensitive information.
- Rogue Hotspots: Malicious actors can set up fake Wi-Fi hotspots with names similar to legitimate networks. Unsuspecting users might connect to these, giving attackers direct access to their devices.
- Malware Distribution: Public networks can be used to distribute malware. Once your device is infected, it can be used to steal data, monitor your activities, or even launch attacks on other devices.
Tips for Safe Public Wi-Fi Use
- Avoid Accessing Sensitive Information: Refrain from accessing bank accounts, entering credit card details, or logging into sensitive accounts when on public Wi-Fi.
- Use a VPN: Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) encrypt your internet traffic, making it unreadable to anyone trying to intercept it. Always turn on your VPN when using public networks.
- Forget the Network After Use: Ensure your device forgets the network after use, preventing it from automatically reconnecting in the future.
- Turn Off Sharing: Disable file and printer sharing in your device settings to prevent unauthorized access.
- Use HTTPS: Ensure the websites you visit use HTTPS, encrypting the data between the website and your browser.
- Enable Firewall: Turn on your device’s firewall to block incoming malicious traffic.
Use a VPN: Your Digital Shield
The internet, while a vast reservoir of information and connectivity, is also rife with prying eyes. Whether it’s hackers, advertisers, or even governments, your online activities can be monitored, logged, and exploited. Enter Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) – the unsung heroes of digital privacy.
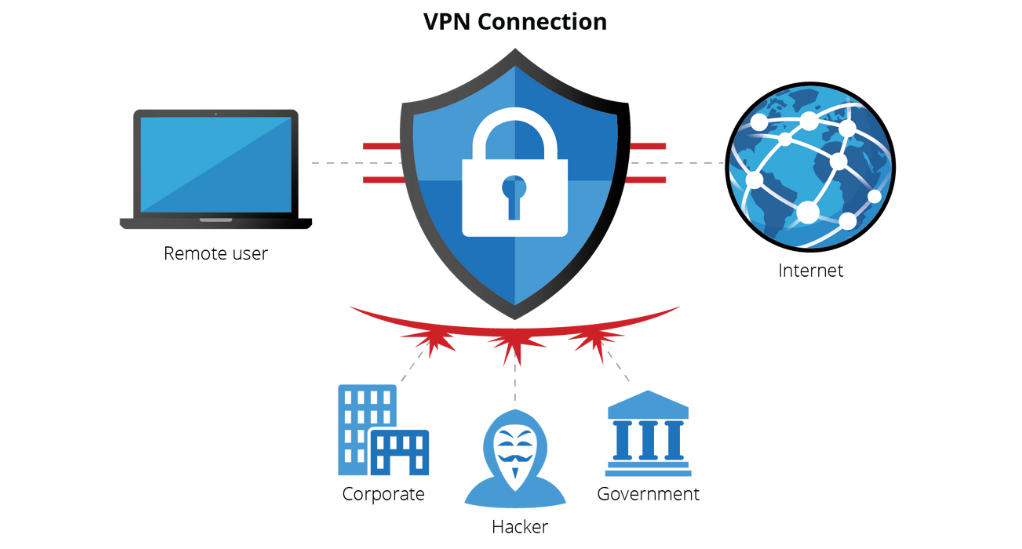
What is a VPN?
A VPN is a service that encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a server in a location of your choice. This not only masks your IP address but also ensures that your online actions are virtually untraceable.
Benefits of Using a VPN:
- Enhanced Privacy: With a VPN, your internet service provider (ISP), hackers, or any eavesdroppers can’t see your internet activities. Your real IP address is also hidden, making your online presence anonymous.
- Secure Data Transmission: If you’re transmitting sensitive data, a VPN ensures it’s encrypted and safe from interception.
- Bypass Geo-restrictions: Access content that’s restricted in your region. Whether it’s a streaming service, news outlet, or a social media platform, a VPN can make it appear as if you’re accessing the internet from a different location.
- Safe Online Transactions: For those who often conduct transactions or manage their bank accounts online, VPNs offer an added layer of security.
- Avoid Bandwidth Throttling: ISPs sometimes throttle your bandwidth if they detect data-intensive activities like streaming or gaming. A VPN can prevent your ISP from seeing the type of content you’re accessing, ensuring consistent speeds.
Choosing the Right VPN
When selecting a VPN service, consider the following:
- No-logs Policy: Ensure the VPN provider doesn’t log your activities. This ensures that even if they’re compelled to share data, there’s nothing to hand over.
- Strong Encryption: Look for services that offer 256-bit encryption, ensuring your data is securely scrambled.
- Server Locations: More server locations mean more options for bypassing geo-restrictions.
- Speed: While a VPN can slow down your connection slightly due to the encryption process, some VPNs offer faster speeds than others.
- Price: While there are free VPNs available, they might come with data limits or display ads. Paid VPNs offer unlimited data and additional features.
Data Encryption and SSL Protocols
In the vast expanse of the digital universe, data is constantly in motion. Whether it’s a simple email, an online purchase, or a file transfer, ensuring this data’s security during transit is paramount. This is where encryption, particularly the Secure Socket Layer (SSL) protocol, comes into play.
Understanding Data Encryption
Data encryption translates data into another form, or code, so that only people with access to a decryption key or password can read it. It’s like sending a sealed letter instead of a postcard; only the recipient with the key can open and read it.
Why is Encryption Important?
- Confidentiality: Only the intended recipients can interpret the encrypted data.
- Integrity: Encryption ensures that the data isn’t tampered with during transit.
- Authentication: It verifies the sender’s identity, ensuring the data’s source is genuine.
Delving into SSL
SSL (Secure Socket Layer) is a protocol that establishes encrypted links between a web server and a browser, ensuring all data passed between them remains private.
Features of SSL
- End-to-End Encryption: Data is encrypted on the sender’s side and only decrypted on the recipient’s side.
- Authentication: SSL certificates verify the identity of the server and sometimes the client, ensuring data is sent to the right server.
- Data Integrity: It ensures data isn’t altered during transit.
How to Identify SSL-Protected Websites:
- HTTPS: Instead of the standard ‘HTTP’ in the URL, SSL-protected sites start with ‘HTTPS’, where the ‘S’ stands for ‘secure’.
- Padlock Icon: A padlock symbol in the address bar indicates an active SSL.
- Certificate Information: Clicking on the padlock will provide details about the website’s SSL certificate and its issuer.
The Importance of SSL for Businesses
- Customer Trust: An SSL certificate assures customers that their data, especially sensitive information like credit card details, is secure.
- SEO Boost: Search engines, especially Google, give preference to SSL-protected websites, improving their search ranking.
- Data Protection: SSL protects user data, reducing the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches.
Regularly Updating Your Operating System
The digital realm is in a constant state of evolution. New features are introduced, user experiences are enhanced, and, most importantly, security loopholes are identified and patched. At the heart of this dynamic environment is your operating system (OS), the software that powers your devices. Regularly updating your OS is akin to fortifying the walls of a fortress, ensuring that vulnerabilities are addressed and potential threats are kept at bay.

Why OS Updates are Crucial?
- Security Patches: One of the primary reasons for OS updates is to fix security vulnerabilities. Hackers are always on the lookout for weaknesses, and an outdated OS can be a goldmine for them.
- New Features: Updates often come with new features or enhancements that improve the overall user experience.
- Performance Improvements: Over time, developers optimize the OS to run more efficiently, ensuring your device operates faster and more smoothly.
- Bug Fixes: No software is perfect. Updates address known bugs or issues that might cause the system to crash or malfunction.
- Compatibility: New applications or software might require the latest OS version to function correctly.
Risks of Not Updating
- Vulnerability to Attacks: An outdated OS can have known security flaws that hackers can exploit.
- Software Incompatibility: You might miss out on using the latest apps or tools that require a more recent OS version.
- Degraded Performance: Over time, without updates, your device might become sluggish or encounter frequent crashes.
Best Practices for OS Updates
- Automatic Updates: Enable automatic updates so that your device installs them as soon as they’re available. This ensures you don’t miss out on crucial patches.
- Backup Before Updating: Before installing a significant update, back up your data. This ensures that, in the rare event something goes wrong, you won’t lose important files.
- Stay Informed: Subscribe to tech news or your OS provider’s newsletter. Being aware of major updates or known issues can help you prepare.
- Verify Source: Only download updates from official sources. Cybercriminals often disguise malware as “system updates” on third-party sites.
The Necessity of Data Backups
In the digital age, our data is our most valuable asset. From cherished family photos and important work documents to digital libraries and software configurations, our devices hold vast amounts of information that shape our personal and professional lives. But what happens when disaster strikes? A system crash, malware attack, or even a simple human error can result in data loss. This is where the importance of regular data backups comes into play.
Understanding Data Backups
A data backup is essentially a copy of your data stored in a separate location, ensuring that if something happens to the original data, you have a fallback.
Why Backups are Essential?
- Protection Against Data Loss: Whether it’s due to hardware failures, software corruption, or accidental deletions, data loss can be devastating. Regular backups ensure you can recover your data in such events.
- Defense Against Ransomware: Ransomware attacks involve malware encrypting your data and demanding a ransom for its release. With a recent backup, you can restore your system without paying the ransom.
- Archival Integrity: Over time, files can get corrupted. Backups allow you to access previous versions of your data, ensuring its integrity.
- Ease of Migration: If you’re upgrading to a new device or switching platforms, backups make the migration process smoother.
Best Practices for Data Backups
- 3-2-1 Rule: Always have at least three copies of your data. Store two backup copies on different devices or platforms, and keep one copy offsite, like on a cloud service.
- Regular Scheduling: Automate your backups to occur regularly, whether daily, weekly, or monthly, depending on your data’s nature and frequency of change.
- Test Your Backups: Periodically check your backups to ensure they’re working correctly. A backup is only good if you can restore data from it.
- Encrypt Backups: Especially for sensitive data, ensure your backups are encrypted, adding an extra layer of security.
- Stay Updated: As with all software, ensure your backup tools are up-to-date to benefit from the latest features and security patches.
Mindful Sharing on Social Media
Social media platforms have revolutionized the way we communicate, connect, and share our lives. From daily updates and vacation photos to professional achievements and life events, these platforms offer a window into our world. However, with this openness comes a responsibility to share mindfully. Every post, tweet, or story can have implications, both intended and unintended.
The Risks of Oversharing
- Personal Privacy: Sharing too much personal information, such as your home address, workplace, or daily routines, can make you vulnerable to stalking, theft, or other malicious activities.
- Identity Theft: Cybercriminals can piece together information from various posts to impersonate you, leading to fraud or unauthorized transactions.
- Professional Repercussions: A controversial post or an image from a wild party can come back to haunt you during job interviews or professional evaluations.
- Emotional Impact: Sharing personal struggles or emotions can sometimes lead to unwanted attention, judgment, or cyberbullying.
- Digital Footprint: Everything you share online leaves a trace. Even if you delete a post, it might have been screenshot, shared, or archived elsewhere.
Tips for Mindful Sharing
- Think Before You Post: Before hitting the ‘share’ or ‘post’ button, take a moment to consider the content’s implications. Ask yourself if it’s something you’d be comfortable with the entire world seeing.
- Review Privacy Settings: Regularly check and update your privacy settings on social media platforms. Ensure that you’re only sharing with the intended audience.
- Limit Personal Information: Avoid posting sensitive information like your home address, phone number, or financial details.
- Be Cautious with Location Sharing: While it’s tempting to check-in at every location or share vacation photos in real-time, it can alert people that your home is empty or give away your current location.
- Educate Young Users: If you have children or younger family members using social media, educate them about the risks and guide them on safe sharing practices.
Smartphone-Based Payments
The rise of smartphones has not only transformed communication but also the way we handle our finances. Gone are the days when we solely relied on cash or physical cards for transactions. Today, smartphone-based payments, often referred to as mobile wallets or digital wallets, offer a convenient, fast, and increasingly secure way to pay.
Understanding Smartphone-Based Payments
Smartphone-based payments allow users to store payment information, like credit or debit card details, on their mobile devices. Through technologies like NFC (Near Field Communication) or QR codes, users can make contactless payments at physical stores or online checkouts.
Advantages of Mobile Wallets
- Convenience: No need to carry physical cards or cash. A tap or scan with your smartphone, and the transaction is complete.
- Speed: Transactions are often faster than traditional methods, especially with features like one-tap pay.
- Enhanced Security: Mobile wallets use encryption and tokenization to secure transaction data. Even if intercepted, this data is useless without the unique key.
- Reduced Contact: In times where hygiene is paramount, contactless payments minimize physical interaction.
- Loyalty and Rewards: Many mobile wallets offer integrated loyalty programs, providing users with rewards, discounts, or cashback.
Conclusion
In our rapidly evolving digital age, the internet has become an integral part of our daily lives, offering unparalleled convenience, access, and opportunities. However, with these benefits come inherent risks. From safeguarding our personal data and financial transactions to mindful sharing on social platforms, the responsibility of digital security rests on each individual’s shoulders.
Throughout this article, we’ve explored various facets of online safety, from the foundational importance of strong passwords and regular OS updates to the advanced protection offered by VPNs and multi-factor authentication. The tools and practices highlighted are not just recommendations but essential components in building a robust digital defense.
As technology continues to advance, so will the tactics employed by cybercriminals. Staying informed, being proactive, and adopting a security-first mindset are crucial. Remember, in the digital realm, your safety is as much about the tools you use as it is about the habits you cultivate.


Leave a Reply