How to Ensure Data Security in the Cloud: A Comprehensive Guide
In the digital era where data is the cornerstone of business operations and personal communications, securing it has become more critical than ever. As we increasingly rely on cloud platforms to store and manage data, understanding and implementing robust cloud data security measures is paramount. This comprehensive guide is designed to walk you through the intricacies of cloud data security, offering insights into the potential threats, legal frameworks, best practices, and the tools and technologies that can help in building a secure cloud environment. Join us as we delve deep into each aspect, providing you with a roadmap to safeguard your valuable data in the cloud.
Understanding Cloud Data Security

In today’s digital age, the cloud has become a fundamental element in the storage and management of data for both individuals and organizations. As we entrust a significant portion of our sensitive information to cloud service providers, understanding the nuances of cloud data security becomes not just beneficial, but necessary. In this section, we will dissect what cloud data security entails, its importance, and the different types of cloud deployments available.
Definition of Cloud Data Security
Cloud data security refers to the policies, procedures, and technology used to protect data, applications, and associated infrastructure through cloud services. It encompasses a broad range of controls and mechanisms that work in unison to maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data hosted in the cloud.
Why is it Essential?
In the interconnected world we live in, data is more vulnerable than ever to unauthorized access and cyber-attacks. Cloud data security ensures that your data remains safe from such threats, providing peace of mind and fostering trust between businesses and their customers. Moreover, a robust cloud data security strategy can help in:
- Protecting Intellectual Property: Safeguarding the proprietary information of a business.
- Compliance with Legal Requirements: Meeting the regulatory requirements for data protection.
- Preventing Financial Loss: Avoiding potential financial repercussions that come with data breaches.
The Different Types of Cloud Deployments
Understanding the various cloud deployment models is pivotal in crafting a security strategy that is tailored to your needs. Let’s delve into the three primary types of cloud deployments:
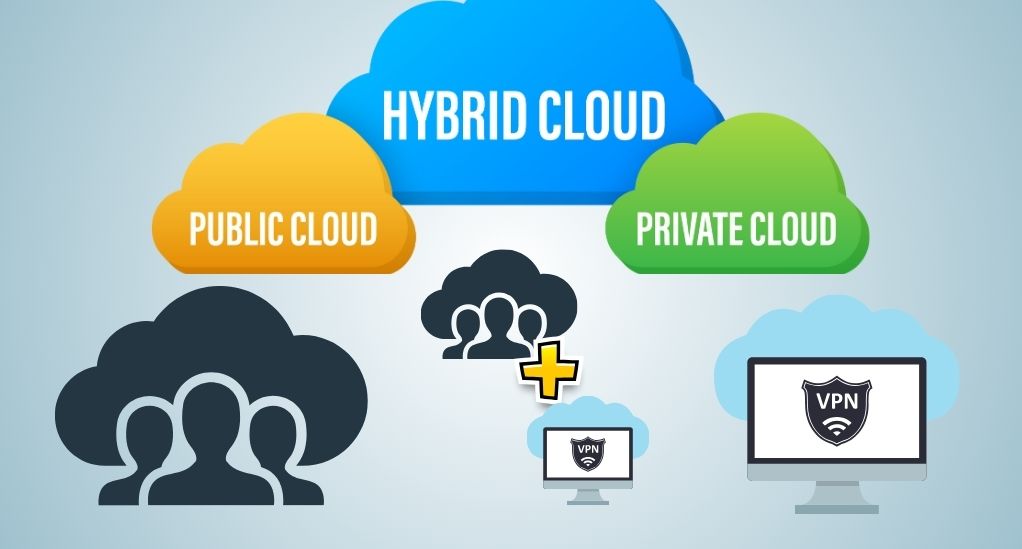
Public cloud
Public cloud platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure offer cost-effective and scalable solutions with the added benefit of requiring no maintenance. However, this comes with a downside of lesser control over security and potential vulnerabilities due to the shared resources environment. While being ideal for small enterprises and start-ups due to lower upfront costs, the use of public clouds entails a risk of increased exposure to cyber-attacks and data breaches.
Private clouds
Private clouds, available through providers like IBM Cloud and Oracle Cloud, offer enhanced security and dedicated resources for businesses, allowing for greater control over data. However, they are more expensive and require ongoing maintenance, posing potential challenges for smaller enterprises. Despite the higher costs, they remain a popular choice for large organizations prioritizing secure and dedicated cloud infrastructure.
Hybrid clouds
Hybrid clouds, offered by providers like Google Cloud and AWS, merge the benefits of public and private clouds, providing flexible and adaptable infrastructure solutions. While they allow for customization and scalability, they can introduce complexity in management and potential compatibility issues. Nonetheless, they remain a versatile choice for businesses seeking a balanced cloud solution.
Potential Threats to Cloud Data Security
In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, being cognizant of the potential threats is the first line of defense in securing your data. In this section, we will delineate the various threats that lurk in the cyber space, aiming to compromise the sanctity of your data stored in the cloud.
Data Breaches
A data breach is an incident where confidential information is accessed, stolen, or leaked without authorization. It is one of the most prevalent threats to cloud data security. Data breaches can occur due to various reasons including weak passwords, lack of encryption, and insider threats. Understanding the common causes can help in devising strategies to prevent such breaches.
Common Causes of Data Breaches
- Phishing Attacks: Cyber criminals tricking individuals into providing sensitive information.
- Weak Passwords: Utilizing passwords that are easy to guess or crack.
- Unpatched Software: Failing to update software with security patches can leave vulnerabilities.
Data Loss
Data loss through accidental deletion, hardware failure, or catastrophic events can severely impact business continuity and incur financial losses. Preventive strategies include regular data backups and establishing a disaster recovery plan to safeguard against severe disruptions and protect the organization’s assets.
Account Hijacking
Account hijacking involves an attacker gaining unauthorized access to a user’s account to carry out malicious activities. It can lead to data theft, financial loss, and damage to reputation.
How to Protect Your Account
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implementing MFA to add an extra layer of security.
Regular Monitoring: Keeping an eye on account activities to detect any unusual patterns.
Insider Threats
Insider threats to data security come from individuals like employees or business partners misusing their access within an organization. To mitigate these threats, it is essential to implement strict access control measures and foster education and awareness about safe data practices among staff, creating a more secure operational environment.
DDoS Attacks
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks involve overwhelming a system with traffic, rendering it unavailable. It is a method often used to distract from other malicious activities happening simultaneously.
Legal and Compliance Requirements
In the complex landscape of cloud computing, adhering to legal and compliance requirements is not just a necessity but a cornerstone in building a secure and trustworthy environment. This section will guide you through the pivotal regulations and industry-specific mandates that govern the sphere of cloud data security.
GDPR and Other Data Protection Laws
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a regulation enacted by the European Union to protect the privacy and personal data of its citizens. Apart from GDPR, there are other significant data protection laws globally, such as:
- CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act): A state statute intended to enhance privacy rights and consumer protection for residents of California, USA.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): A US law designed to provide privacy standards to protect patients’ medical records and other health information.
- PDPA (Personal Data Protection Act): Singapore’s primary law that governs the collection, use, and disclosure of individuals’ personal data by organizations.
Industry-Specific Regulations
Different industries have their own set of regulations to ensure data security. For instance:
Healthcare: Adherence to HIPAA is crucial to protect sensitive patient data.
Finance: Regulations like the Sarbanes-Oxley Act in the US govern the financial reporting and auditing of public companies to prevent fraud.
Education: Laws such as the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) in the US protect the privacy of student education records.
The Role of Compliance in Ensuring Data Security
Compliance with legal mandates is crucial not only for avoiding legal issues but also for enhancing data security. It aids in setting firm security benchmarks and managing risks effectively, while also building trust with customers through adherence to recognized standards, thus fostering a reliable and positive business environment.
Best Practices for Cloud Data Security
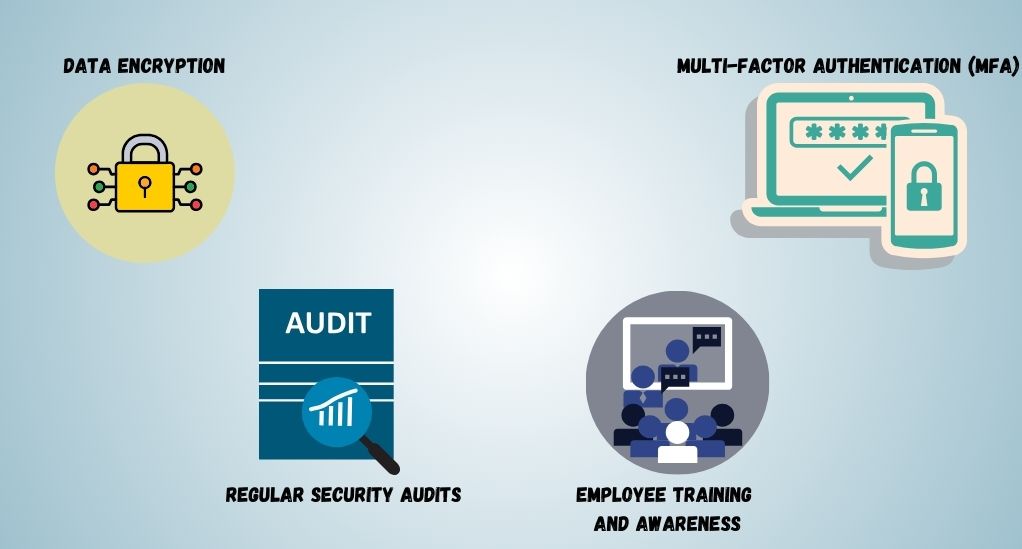
In a world where data is the new currency, safeguarding it should be a priority for every organization. Implementing best practices in cloud data security can be your fortress against the myriad of cyber threats that exist today. In this section, we will walk you through the strategies and measures that can be adopted to fortify your cloud data security.
Data Encryption
Data encryption is a method where data is converted into a code to prevent unauthorized access. Here are the key aspects to consider:
- At Rest: Encrypting data when it is stored.
- In Transit: Encrypting data when it is being transferred over a network.
- End-to-End: Ensuring data is encrypted from the point of origin to the destination.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring more than one method of authentication from independent categories of credentials to verify the user’s identity. Implementing MFA can significantly reduce the risk of cyber attacks.
Regular Security Audits
Conducting security audits at regular intervals can help in identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring that the security measures in place are effective. It involves:
- Risk Assessment: Identifying potential risks and assessing their impact.
- Penetration Testing: Simulating a cyber attack to identify vulnerabilities.
- Compliance Checks: Ensuring adherence to legal and regulatory requirements.
Employee Training and Awareness
Building a culture of security awareness among employees is crucial. It involves:
Training Programs: Conducting regular training sessions on security best practices.
Phishing Simulations: Carrying out simulated phishing attacks to educate employees on how to identify and respond to such threats.
Updates on Latest Threats: Keeping the team updated on the latest cyber threats and how to avoid them.
Tools and Technologies for Cloud Data Security
In the dynamic landscape of cloud computing, leveraging the right tools and technologies is pivotal in crafting a robust security posture. This section aims to guide you through the array of tools and technologies available in the market, helping you make informed decisions in securing your cloud environment.
Firewalls
Firewalls act as barriers between your secure internal network and untrusted external networks such as the internet. A set of defined rules govern what kind of traffic is allowed and prohibited, enhancing security. Here, we delve into the types of firewalls available:
- Network Firewalls: Monitor traffic between your network and the external world, blocking unauthorized access.
- Web Application Firewalls (WAF): Protect web applications by monitoring and filtering traffic between a web application and the internet.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
IDS are designed to detect unauthorized access or anomalies in your network. They come in various forms:
Network-based IDS (NIDS): Monitors the traffic on your network.
Host-based IDS (HIDS): Monitors the inbound and outbound packets from the device it is installed on and will alert the user or administrator of suspicious activity.
Anti-Virus Software
Anti-virus software is a program designed to prevent, search for, detect, and remove software viruses, and other malicious software like worms, trojans, adware, and more. It is essential to keep the anti-virus software updated to fend off the latest threats.
Encryption Tools
Encryption tools help in protecting sensitive data by encrypting it into an unreadable format. These tools play a crucial role in securing data both at rest and during transmission. Some popular tools include:
- Symmetric Encryption Tools: Where the same key is used for encryption and decryption.
- Asymmetric Encryption Tools: Utilizing a pair of keys, one public and one private, enhancing security.
Lessons from Real-Life Incidents
In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, learning from real-life incidents can be a goldmine of insights, helping organizations to fortify their defenses. In this section, we will analyze some notable incidents, the repercussions they had, and the lessons that can be drawn from them.
Analysis of Past Data Breaches
Over the years, several high-profile data breaches have occurred, shedding light on the vulnerabilities that existed and the magnitude of the damage they caused. Let’s delve into a couple of them:
- Target (2013): In one of the most significant breaches, attackers gained access to Target’s network, compromising the personal information of over 70 million customers.
- Lesson: The necessity of robust network security and regular vulnerability assessments.
- Yahoo (2013-2014): Yahoo experienced a massive breach where 3 billion user accounts were compromised over several incidents.
- Lesson: The importance of timely disclosure and robust password policies.
How Companies Successfully Protected Their Data
While there have been instances of breaches, there are also cases where companies successfully thwarted attacks, showcasing the effectiveness of their security measures. Here, we highlight a few strategies that worked:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Companies that implemented MFA managed to add an extra layer of security, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Regular Security Training: Organizations with regular training programs ensured that their employees could identify and respond to threats effectively.
Lessons Learned and How to Avoid Similar Incidents
Drawing from the incidents and success stories, here are some lessons and strategies to avoid similar pitfalls:
Robust Access Control: Implementing stringent access control measures to ensure that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive data.
Incident Response Plan: Having a well-defined incident response plan to act swiftly in the event of a security breach.
Regular Updates and Patch Management: Ensuring that all systems are updated with the latest security patches to fend off potential threats.
Future Trends in Cloud Data Security

As we navigate the complex landscape of cloud data security, it is pivotal to keep an eye on the emerging trends that are set to shape the future. In this section, we will explore the innovations and developments that are on the horizon, preparing you to stay a step ahead in securing your cloud environment.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) significantly enhance cloud data security by employing predictive analytics to foresee potential threats, and automating responses to security incidents, thus reducing response time and fortifying the security infrastructure.
Quantum Computing and its Implications for Data Security
Quantum computing, with its immense computational power, brings both opportunities and challenges to the realm of data security:
Cryptanalysis: Quantum computers have the potential to break widely-used encryption algorithms, necessitating the development of quantum-resistant encryption methods.
Secure Communications: On the flip side, quantum computing can also facilitate more secure communication channels through quantum encryption techniques.
The Evolving Landscape of Cloud Data Security
As we forge ahead, the landscape of cloud data security is set to evolve, with several trends gaining prominence:
- Zero Trust Architecture: Moving away from the traditional security perimeter to a zero trust model where trust is never assumed and verification is required at every step.
- Secure Access Service Edge (SASE): The convergence of network security and wide area networking capabilities into a single cloud-native service, enhancing security and performance.
- Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs): Technologies that protect user’s privacy by design, including differential privacy and homomorphic encryption, are expected to gain traction.
Conclusion
In wrapping up this detailed guide, it’s clear that adopting a proactive approach to cloud data security is essential. We’ve navigated through the crucial areas of understanding cloud data security, addressing potential threats, and exploring legal requirements. With a landscape that’s continually evolving, staying updated on the latest developments is more than beneficial; it is vital. It provides the essential toolkit to navigate a complex environment, helping to ensure data remains secure in the face of new challenges.
As we conclude, we underline the necessity and responsibility that comes with ensuring data security in this digital age. Going beyond just securing data, it’s about fostering trust and establishing a reliable reputation. It urges the adoption of regular training and the implementation of robust security measures. Equipping oneself with the right knowledge and tools, as outlined in this guide, will serve as a steadfast companion in the journey of securing cloud environments, a step towards a secure and reliable digital future.


Leave a Reply